The modern data stack came bearing many promises. A shift from the on-premise legacy systems, it aimed to provide a faster, scalable, and more cost-effective way of storing and analyzing data.
However, that promise was short-lived.
Instead of easing data management, modern cloud data warehouses created a new set of problems. The stack turned out to be nothing more than a collection of disparate technologies, pieced together.
In this article, we further explore the challenges of a modern data stack, along with solutions to help you make the most of your data.
Try Userpilot Now
See Why 1,000+ Teams Choose Userpilot
Why is managing the modern data stack so challenging?
When you scratch the surface, it becomes apparent that the modern data stack is just the legacy data stack repackaged.
Let’s discuss the challenges that come with a modern data stack in greater detail below to see just how they make handling a modern data stack difficult.
Maintaining several tools is an operational burden
Each tool in the modern data stack is picked to address a specific process, from data collection to data analysis.
Ensuring these tools work together well ultimately comes with significant overhead and high setup time. But the troubles don’t end there.
Plus, each data stack component requires individual monitoring for updates and maintenance, increasing the time spent on your stack’s upkeep. And as you add more tools to your data stack, that means more maintenance efforts – ultimately overloading your data teams.
It’s difficult to ensure data quality and consistency across the system
Ensuring data quality across your modern data stack isn’t easy since different tools save data in different formats. This also introduces the risk of your modern data stack tools not saving data accurately when transferring.
Such inconsistencies can lead to faulty data analytics and potentially misguide data-driven business decisions too.
You can end up creating data siloes
While the modern data stack’s integration capabilities were meant to remove data siloes, the reality is anything from it. Even with MDS, siloes occur when certain tools or departments keep raw data to themselves. So you can’t access or share valuable insights with others across the organization.
This results in lacking or incomplete data lakes or cloud data warehouses since not all data pipelines feed into them as they should. Plus, such siloes also hinder collaboration, leading to fragmented insights and poor decision-making.
You end up facing increased security threats
With data spread over multiple tools and so many data pipelines, it’s difficult to ensure data security. You have to continuously monitor numerous systems to identify where certain data is stored, who accessed it, and why.
Tracking all these moving parts of a modern data stack only increases the likelihood of data theft or unauthorized access.
However, you can avoid such threats by conducting regular security audits and updates. These help ensure your cloud data warehouses remain free of any vulnerabilities. Additionally, consider investing in tools that have certifications such as HIPAA, SOC 2, ISO, etc., ensuring data protection.
How Userpilot is fixing the modern data stack
Userpilot is an all-in-one product growth platform that provides a holistic view of the user experience with product analytics, session replay, user engagement and feedback, and data sync capabilities.
Here’s how our solutions can help you collect and manage data effectively:
Gather quantitative, qualitative, and visual data in a single platform
Userpilot replaces multiple tools by offering different features for collecting different types of data. This includes quantitive, qualitative, and visual data — all collected using the same tool.
You don’t have to switch contexts either, so you can easily analyze all 3 data types together within Userpilot.
For quantitative data, you can use autocapture to automatically track in-app interactions. Then create data visualizations, like funnels, paths, retention cohort tables, etc., to unearth any usage trends.
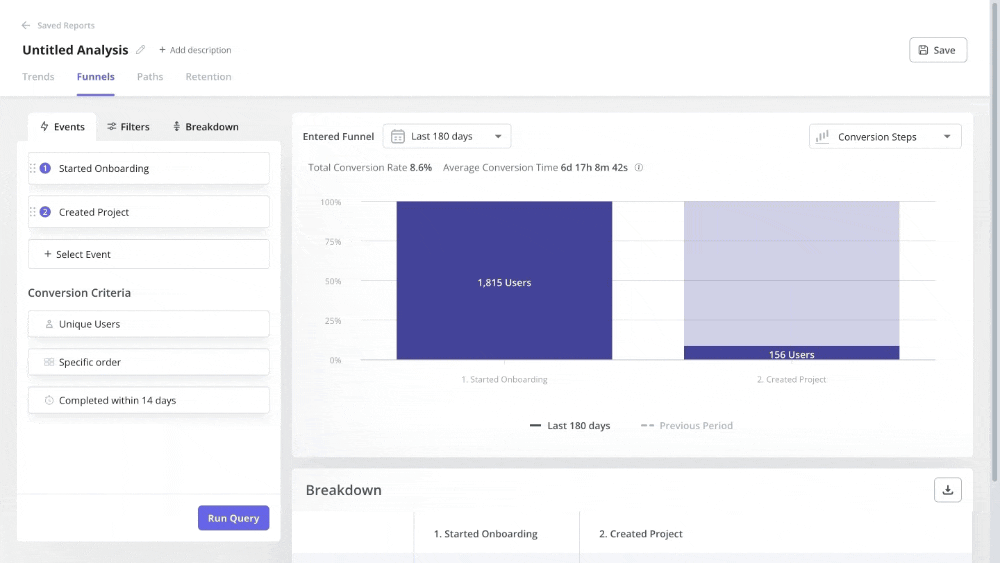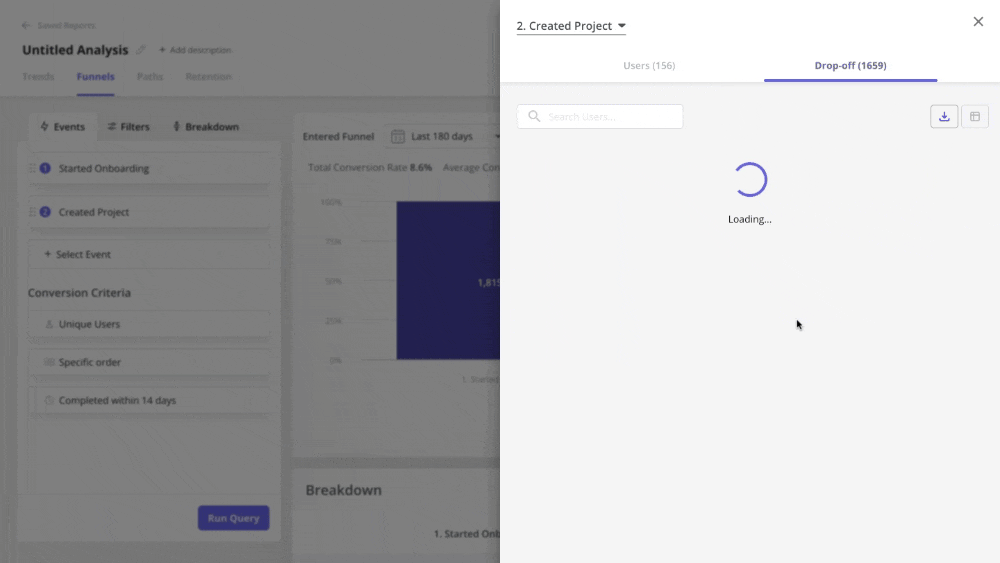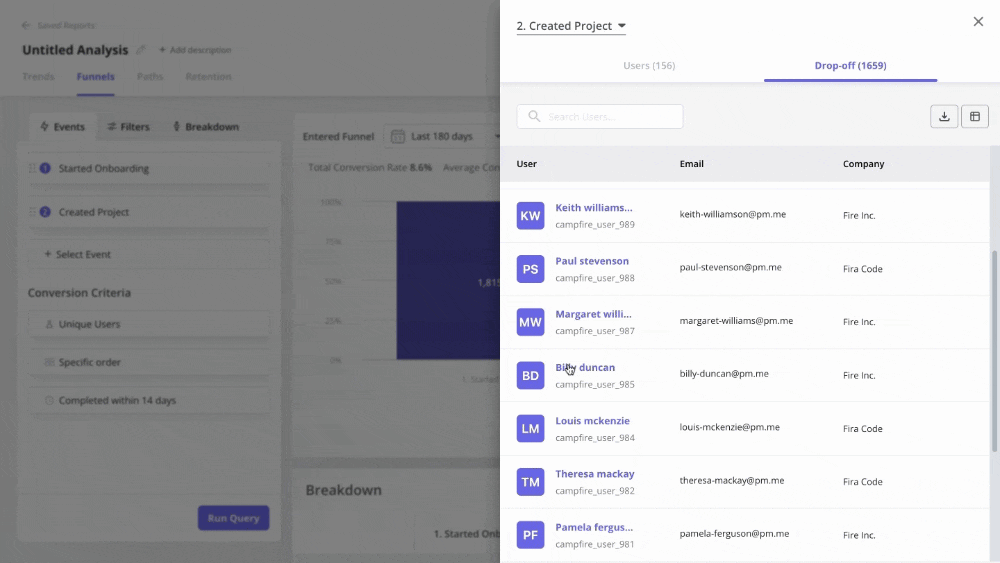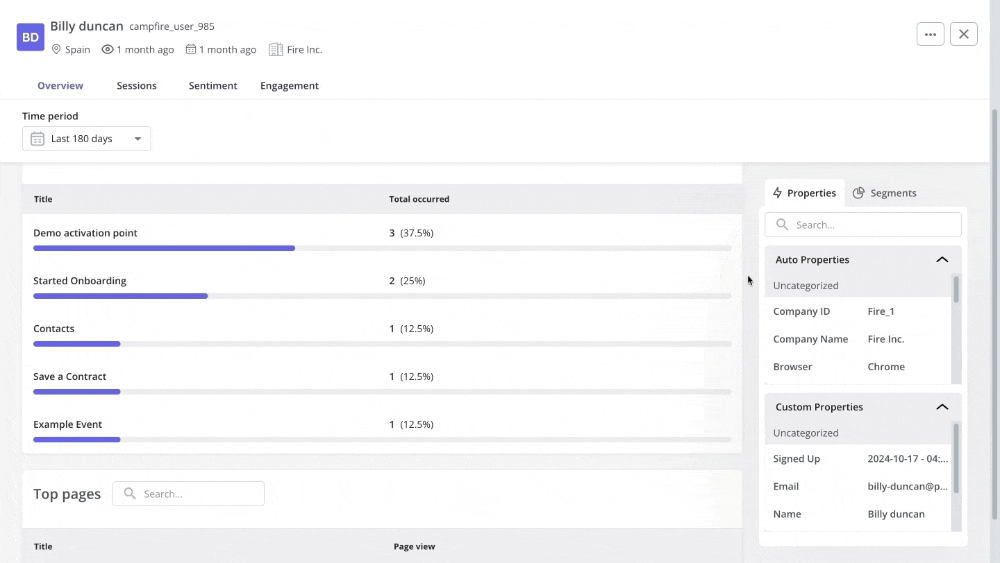
Next, dig deeper into this data by capturing session replays, which enable you to focus on individual user behavior.
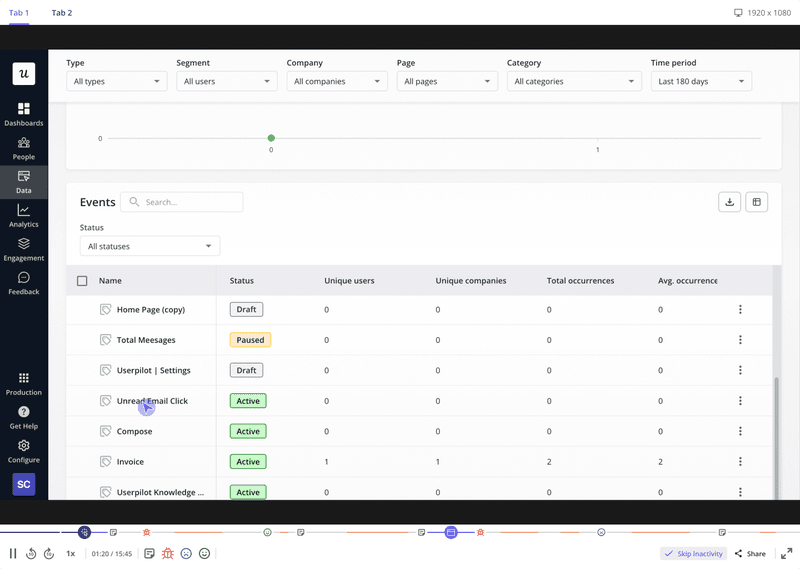
You can also use feedback surveys to collect qualitative insights into user actions, their needs and wants, and pain points.
Receive data from other sources with bulk import APIs
You can easily import historical user data from other platforms to Userpilot. This includes data related to user and company identification, page views, and custom events.
Userpilot APIs also help improve the data stack’s security since they require your unique API key for request authentication.
Unify business and product data for better decision-making
Lastly, save time when unifying data in your chosen BI tool by relying on Userpilot’s automation instead of manual processes that come with a poorly designed modern data stack.
For instance, filter data by date range, user, company, event type, or predefined segments, then export automatically in JSON or CSV format.
Plus, to reduce any duplicates or outdated information, set sync frequency to update data every few hours. This helps ensure data consistency across your systems.
Here’s what this process would look like in action:
- Product usage data tracked with Userpilot is transferred to cloud storage platforms, like Amazon S3, Google Cloud, Microsoft Azure, etc.
- Next, this data undergoes the Extract, Transform, Load (ETL) process where raw data is cleaned and organized.
- The now-processed data is then stored in data warehouses like Amazon Redshift, Snowflake, or Databricks.
- Finally, the data is transferred to BI tools, like Power BI, Looker, or Tableau, where your business decisions are made.

Embrace the post-modern data stack era
The modern data stack could not deliver. It’s riddled with too many problems — large overhead costs, significant set-up times, data quality and consistency concerns, and increased security threats.
So what’s the next step then?
We think it’s time to move on to the “post-modern” data stack by investing in fewer tools and choosing all-in-one solutions instead. These will help reduce the operational complexity associated with maintaining a fragmented toolset, lower costs, and avoid siloes.
Looking for the right all-in-one platform to get you started? Book a free Userpilot demo and see how easily you can unify product and business data throughout your data stack.
FAQs about modern data stack
What’s a modern data stack?
A modern data stack is a collection of cloud-based tools created to work together to collect, store, transform, and analyze data.
Plus, since they require less technical assistance to set up, they provide a great way to democratize data access throughout the organization.
What is the difference between traditional and modern data stack?
The main difference between traditional and modern data stacks lies in their architecture and scalability.
A traditional data stack relies on on-premise solutions and hand-coded data pipelines. This increases the complexity and skill needed to set up and scale one.
In contrast, modern data stacks use cloud-based tools and cloud data warehouses. Offering data scientists and product teams greater scalability, easier setup, and more automated data management.
How does a modern data stack work?
The modern data stack is a mix of several tools, each associated with a specific level of the data pipeline, from collection to analytics.
There are typically 6 layers the data stack needs to function. These include data sources (event streams, CRM, etc.), data transformation tools, centralized storage (cloud data warehouses or lakes), data analytics and visualization software, and monitoring policies.
What are the key components of a modern data stack?
All modern data stacks include these basic components:
- Sources: Internal and external systems that generate raw data.
- Data ingestion & integration: Collect data and apply data transformation tools to extract high-quality data for analytics.
- Storage: Unify data assets in centralized storage, like data warehouses or lakes.
- Data analysis: Process transformed data into usable formats.
- Data visualization: Create reports, dashboards, predictive models, etc. for data-driven decision-making.
- Governance: Implement data privacy, security, and compliance policies.
FAQ
What’s a modern data stack?
A modern data stack is a collection of cloud-based tools created to work together to collect, store, transform, and analyze data.
Plus, since they require less technical assistance to set up, they provide a great way to democratize data access throughout the organization.
What is the difference between traditional and modern data stack?
The main difference between traditional and modern data stacks lies in their architecture and scalability.
A traditional data stack relies on on-premise solutions and hand-coded data pipelines. This increases the complexity and skill needed to set up and scale one.
In contrast, modern data stacks use cloud-based tools and cloud data warehouses. Offering data scientists and product teams greater scalability, easier setup, and more automated data management.
How does a modern data stack work?
The modern data stack is a mix of several tools, each associated with a specific level of the data pipeline, from collection to analytics.
There are typically 6 layers the data stack needs to function. These include data sources (event streams, CRM, etc.), data transformation tools, centralized storage (cloud data warehouses or lakes), data analytics and visualization software, and monitoring policies.
What are the key components of a modern data stack?
All modern data stacks include these basic components:
- Sources: Internal and external systems that generate raw data.
- Data ingestion & integration: Collect data and apply data transformation tools to extract high-quality data for analytics.
- Storage: Unify data assets in centralized storage, like data warehouses or lakes.
- Data analysis: Process transformed data into usable formats.
- Data visualization: Create reports, dashboards, predictive models, etc. for data-driven decision-making.
- Governance: Implement data privacy, security, and compliance policies.