Whether you’re a seasoned professional or new to the field, understanding the nuances of data analysts is essential for success.
In this guide, we’ll delve into the core responsibilities, salary insights, essential skills, and more, providing you with the knowledge and tools you need to excel as a data analyst.
Try Userpilot Now
See Why 1,000+ Teams Choose Userpilot
TL;DR
- A data analyst is a problem-solver who uses their technical skills to uncover valuable insights from data. They act as translators, transforming raw data sets into clear and actionable information that businesses can use to make better decisions.
- According to Glassdoor, the average base salary for a data analyst in the United States is $76,293 per year. However, salaries can range widely based on experience level:
- 2 to 4 years (Data Analyst): $82,288 per year
- 5 to 7 years (Senior Data Analyst): $109,880 per year
- Looking into tools for data analysts? Userpilot is an all-in-one product platform with engagement features and powerful analytics capabilities. Book a demo to see it in action!
What is a data analyst?
A data analyst is a problem-solver who uses their technical skills to uncover valuable insights from data. They act as translators, transforming raw data sets into clear and actionable information that businesses can use to make better decisions.
What does a data analyst do?
A data analyst collects, cleans, and interprets data to answer questions or solve problems. They work in many different industries, from business and finance to healthcare and government.
Data analyst’s main responsibilities
Here’s a breakdown of a data analyst’s main responsibilities and duties:
- Data collection and cleaning: Gather data from various sources (databases, spreadsheets, APIs, etc.), assess its quality, and clean it by addressing inconsistencies, errors, and missing values.
- Data analysis and interpretation: Apply statistical techniques and tools to analyze data, identify patterns, trends, and correlations, and derive meaningful insights that address business questions or problems.
- Data visualization: Create clear and impactful visualizations (charts, graphs, dashboards) to communicate data findings effectively to both technical and non-technical stakeholders.
- Reporting and presentation: Prepare comprehensive reports and presentations that summarize data analysis results, highlight key findings, and offer actionable recommendations based on data-driven insights.
However, with the rise of cloud storage and machine learning trends, you may need to handle tasks specific to certain tools, such as:
- Apply machine learning algorithms to develop predictive models, automate data analysis tasks, and gain deeper insights from complex datasets.
- Work with big data technologies (Hadoop, Spark) to process and analyze massive volumes of data.
- Utilize cloud-based data platforms (AWS, Azure, Google Cloud) for scalable data storage, processing, and analysis.
Data analyst salary
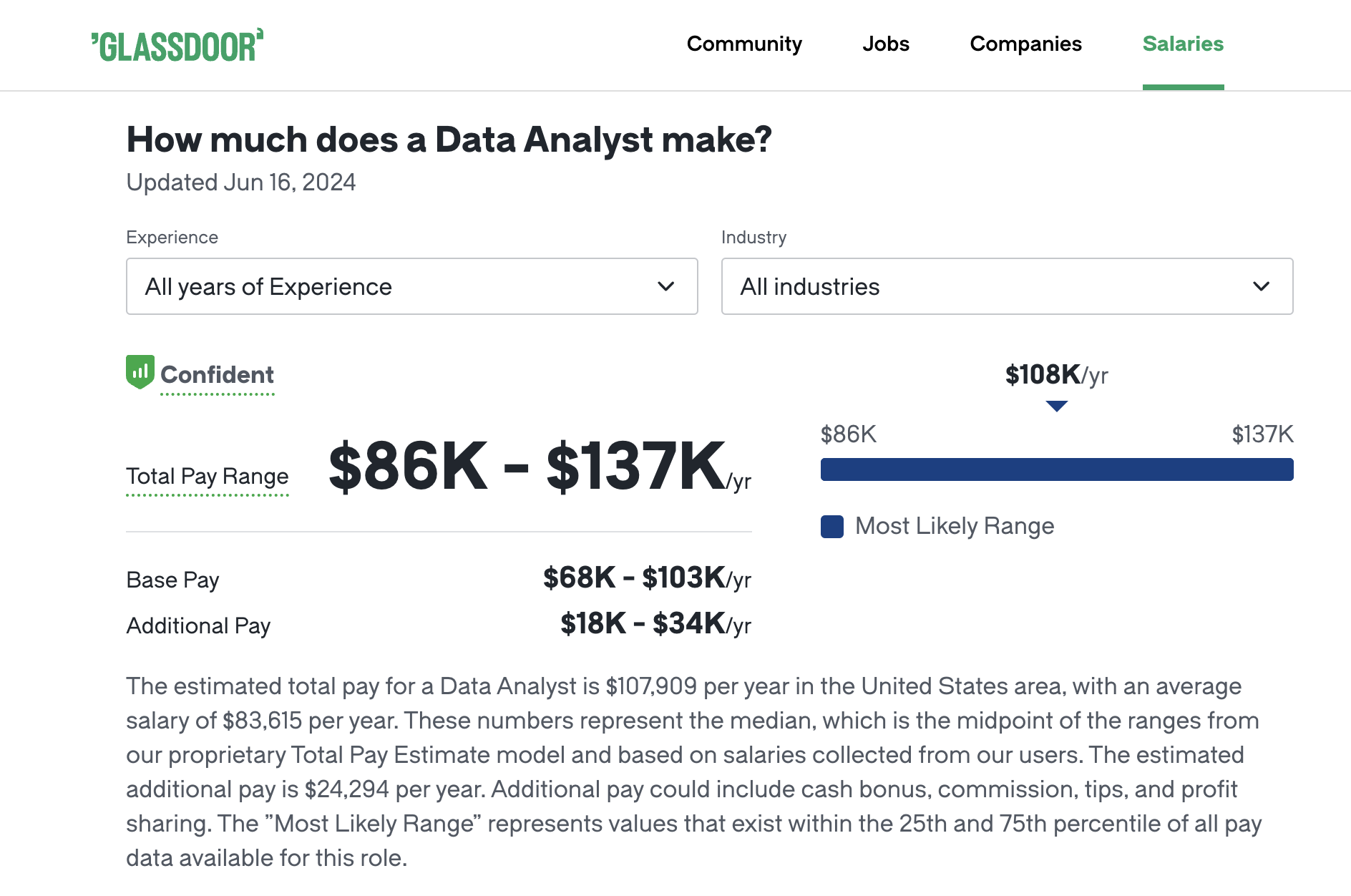
According to Glassdoor, the average base salary for a data analyst in the United States is $76,293 per year. However, salaries can range widely based on experience level:
- 2 to 4 years (Data Analyst): $82,288 per year
- 5 to 7 years (Senior Data Analyst): $109,880 per year
In addition, data analyst salaries tend to be higher in major tech hubs and metropolitan areas with a high cost of living. For example:
- San Francisco Bay Area: $90,000 – $130,000+ per year
- New York City: $80,000 – $120,000+ per year
- Seattle: $85,000 – $125,000+ per year
Salaries in smaller cities or rural areas may be lower than the national average.
Apart from these main factors, your skill set, educational background, and the specific company you work for can also influence your salary. Having expertise in in-demand tools and technologies like Python, SQL, or machine learning can boost your earning potential.
Data analyst career path
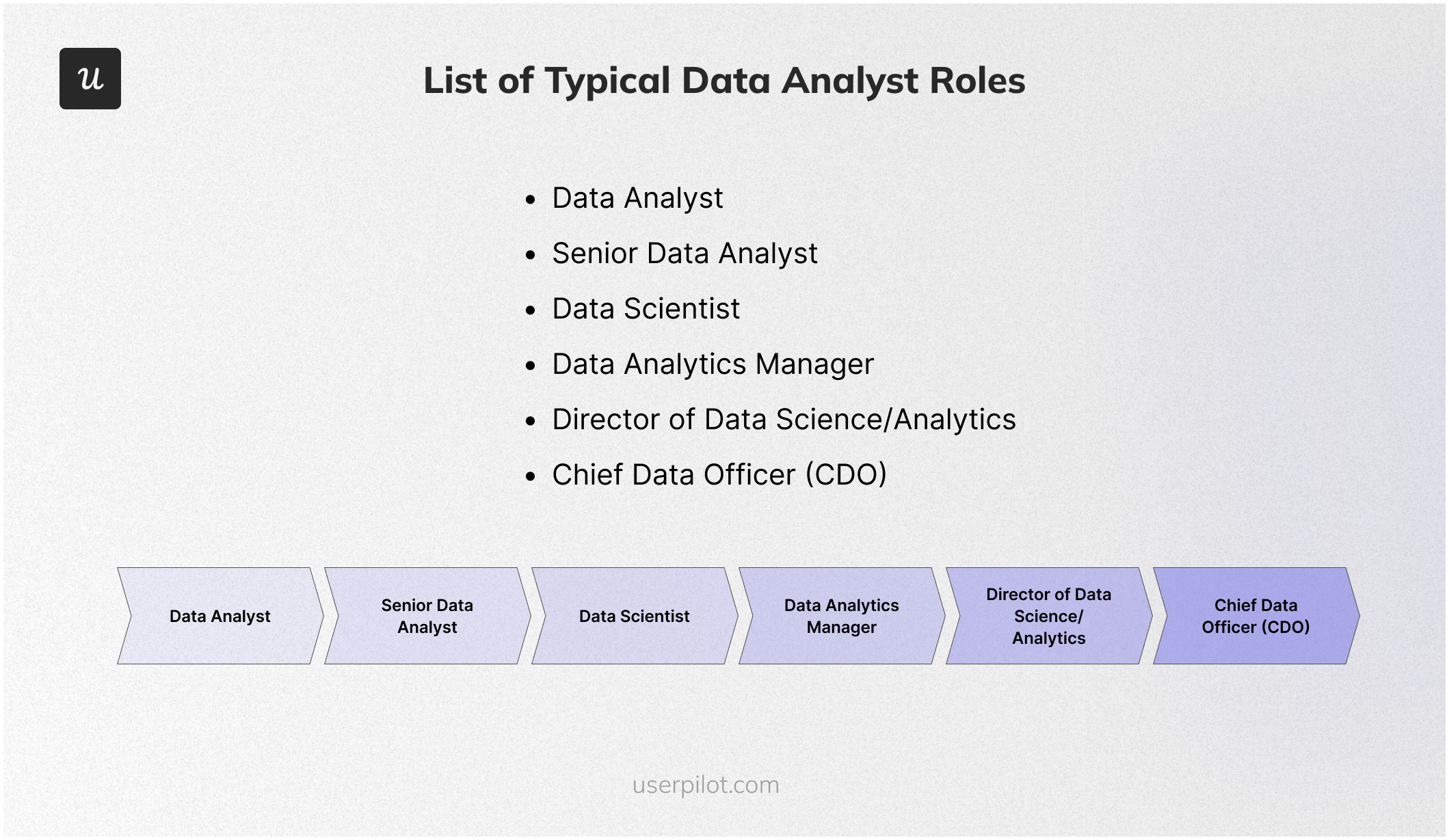
The specific paths may vary depending on your interests and the organization you work for. Nonetheless, here’s a breakdown of typical positions and growth opportunities as a data analyst:
- Data Analyst (0-3 years): Entry-level position focused on data collection, cleaning, and basic analysis. Responsibilities include creating reports, dashboards, and visualizations to support decision-making.
- Senior Data Analyst (3-5 years): Takes on more complex projects involving advanced statistical techniques and data modeling. May lead small teams of analysts and mentor junior colleagues.
- Data Scientist (5-8 years): Applies machine learning and statistical modeling to predict future trends, optimize processes, and solve business problems. Strong programming skills (Python, R) are often required.
- Data Analytics Manager (8-12 years): Oversees a team of data analysts and scientists, setting goals, managing projects, and ensuring the team’s work aligns with business objectives.
- Director of Data Science/Analytics (12+ years): Leads the entire data organization, defining the overall data strategy, developing data-driven products, and fostering a data-driven culture within the company.
- Chief Data Officer (CDO): A C-suite executive responsible for the company’s data assets and strategy. This role is typically found in larger organizations with mature data functions.
Alternative paths:
- Business intelligence analyst/developer: If you enjoy building dashboards and reports, this could be a good fit. Requires strong visualization skills and an understanding of data warehousing concepts.
- Data engineer: If you’re passionate about building data pipelines and infrastructure, this is a technical route. Requires strong programming and cloud skills.
Best practices for being a great data analyst
Data analysis is a multi-stage process, with each step contributing to the overall quality of the insights. With that in mind, we’ve outlined several best practices to make your job easier along the way:
- Define clear objectives: Every analysis should have a goal. What questions are you trying to answer? What decisions will the insights inform? Having a clear target keeps your analysis focused and avoids getting lost in the data
- Understand the business context: Don’t analyze data in a vacuum. Learn the industry, the company’s goals, and how your analysis fits in. Talk to stakeholders to understand their needs.
- Embrace iteration: Data analysis is rarely a linear process. Be prepared to revisit your approach, refine your questions, and try different techniques as you gain insights.
- Document everything: Keep thorough records of your data sources, cleaning steps, analysis methods, and findings. This ensures transparency and reproducibility.
- Automate when possible: To save time and reduce errors, repetitive tasks can be automated with scripts (Python, R).
- Choose the right tools for the job: There are many data analysis tools – both code (i.e. Amplitude, Heap, etc.) and no code options (i.e. Userpilot), but you can choose the one that best suits the task. For example, you can use Userpilot to visualize data and generate actionable insights leveraging reports such as funnel, path, etc.
- Focus on actionable insights: Don’t just present numbers, but tell a story with your data. Translate your findings into clear recommendations for action.
- Communicate effectively: Tailor your communication to your audience. Use simple language, visualizations, and narratives to make your findings accessible to everyone. This is where no-code options like Userpilot become useful when it works for both technical and non-technical teams.
Data analyst FAQs
Is a data analyst an IT job?
Data analysis is often considered a hybrid role that bridges the gap between IT and business. While data analysts use technical skills and tools (like SQL, Python, and various data visualization platforms) to work with data, their primary focus is on extracting insights that can be used to inform business decisions.
What is a data analyst’s job description?
A data analyst’s job revolves around transforming raw data into actionable insights that drive business decisions. They collect, clean, and organize data from various sources, then utilize statistical techniques and tools to analyze it. Their work is essential for understanding customer behavior, optimizing business operations, and identifying new growth opportunities.
What do you need to become a data analyst?
Here’s a general roadmap that can give you an idea of how to become a data analyst:
- Develop foundational skills: Gain proficiency in mathematics, statistics, and computer science.
- Learn essential tools and technologies: Master programming languages like SQL, Python, or R, and data visualization tools like Tableau or Power BI.
- Gain practical experience: Work on real-world projects, internships, or freelance gigs to build your portfolio.
- Earn a degree or certification: Consider a bachelor’s degree in a relevant field or pursue industry-recognized certifications (e.g., Google Data Analytics, Microsoft Azure Data Scientist Associate).
- Network and build relationships: Connect with other data professionals through online communities, conferences, and job fairs.
- Apply for entry-level positions: Look for junior data analyst, data analyst intern, or business analyst roles to gain experience.
Is a data analyst a good career?
Yes, data analysis is a promising career choice for many. With the ever-increasing reliance on data across industries, the demand for skilled data analysts is high and projected to grow steadily in the coming years. This translates to competitive salaries and abundant job opportunities. Plus, data analysis offers a versatile skillset applicable across diverse sectors, providing flexibility and potential for career advancement.
Conclusion
We hope this guide has provided you with valuable insights into the roles, responsibilities, and rewards associated with this role.
Looking into tools for data analysts? Userpilot is an all-in-one product platform with engagement features and powerful analytics capabilities. Book a demo to see it in action!