![How to Become a Data Analyst [+Tools and Resources]](https://blog-static.userpilot.com/blog/wp-content/uploads/2024/07/How-to-Become-a-Data-Analyst-Tools-and-Resources.png)
How to Become a Data Analyst [+Tools and Resources]15 min read
Get The Insights!
The fastest way to learn about Product Growth, Management & Trends.
Data analyst’s main responsibilities
Here’s a breakdown of a data analyst’s main responsibilities and duties:
- Data collection and cleaning: Gather data from various sources (databases, spreadsheets, APIs, etc.), assess its quality, and clean it by addressing inconsistencies, errors, and missing values.
- Data analysis and interpretation: Apply statistical techniques and tools to analyze data, identify patterns, trends, and correlations, and derive meaningful insights that address business questions or problems.
- Data visualization: Create clear and impactful visualizations (charts, graphs, dashboards) to communicate data findings effectively to both technical and non-technical stakeholders.
- Reporting and presentation: Prepare comprehensive reports and presentations that summarize data analysis results, highlight key findings, and offer actionable recommendations based on data-driven insights.
However, with the rise of cloud storage and machine learning trends, you may need to handle tasks specific to certain tools, such as:
- Apply machine learning algorithms to develop predictive models, automate data analysis tasks, and gain deeper insights from complex datasets.
- Work with big data technologies (Hadoop, Spark) to process and analyze massive volumes of data.
- Utilize cloud-based data platforms (AWS, Azure, Google Cloud) for scalable data storage, processing, and analysis.
Data analyst career path
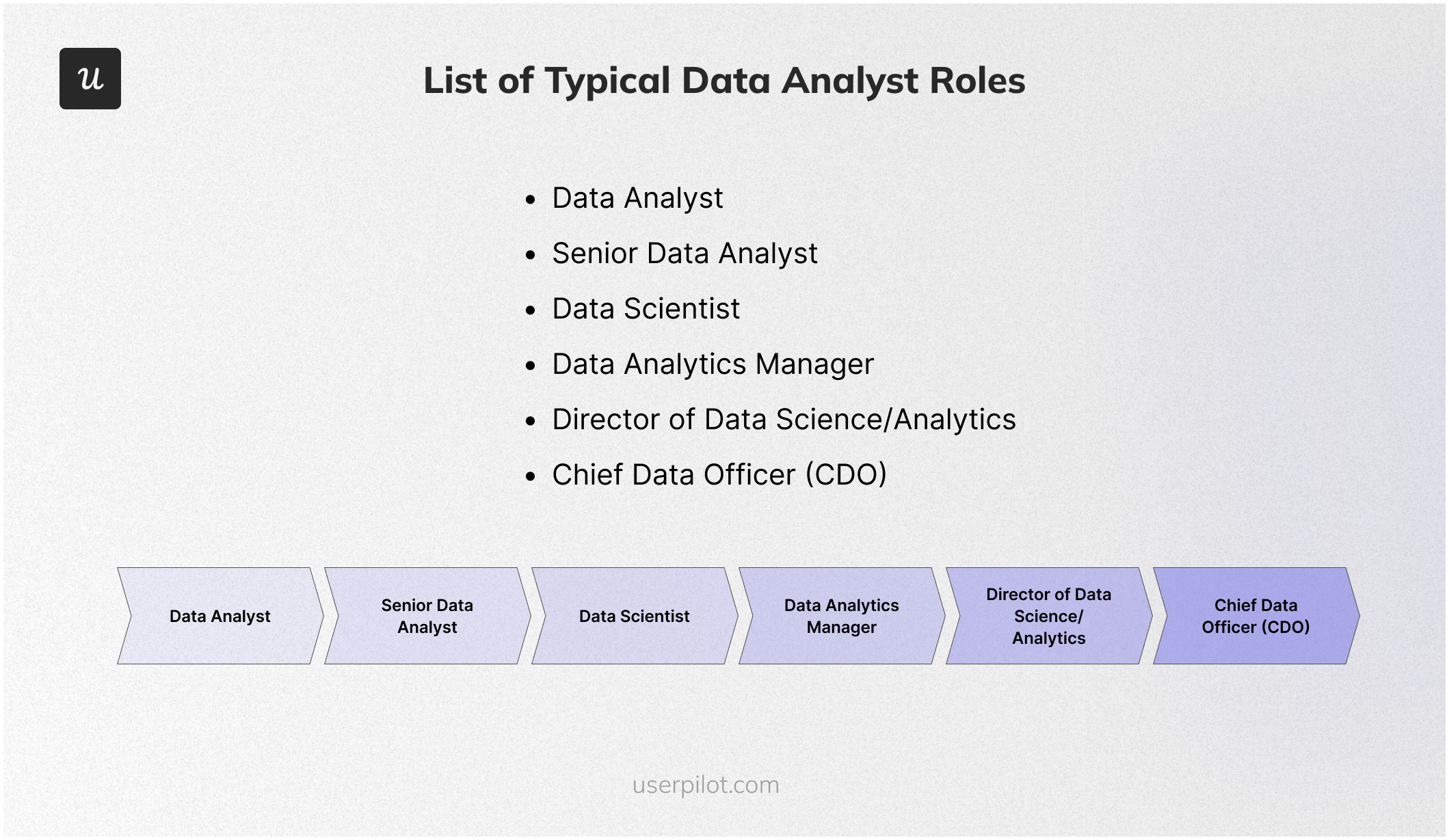
The specific paths may vary depending on your interests and the organization you work for. Nonetheless, here’s a breakdown of typical positions and growth opportunities as a data analyst:
- Data Analyst (0-3 years): Entry-level position focused on data collection, cleaning, and basic analysis. Responsibilities include creating reports, dashboards, and visualizations to support decision-making.
- Senior Data Analyst (3-5 years): Takes on more complex projects involving advanced statistical techniques and data modeling. May lead small teams of analysts and mentor junior colleagues.
- Data Scientist (5-8 years): Applies machine learning and statistical modeling to predict future trends, optimize processes, and solve business problems. Strong programming skills (Python, R) are often required.
- Data Analytics Manager (8-12 years): Oversees a team of data analysts and scientists, setting goals, managing projects, and ensuring the team’s work aligns with business objectives.
- Director of Data Science/Analytics (12+ years): Leads the entire data organization, defining the overall data strategy, developing data-driven products, and fostering a data-driven culture within the company.
- Chief Data Officer (CDO): A C-suite executive responsible for the company’s data assets and strategy. This role is typically found in larger organizations with mature data functions.
Alternative paths:
- Business intelligence analyst/developer: If you enjoy building dashboards and reports, this could be a good fit. Requires strong visualization skills and an understanding of data warehousing concepts.
- Data engineer: If you’re passionate about building data pipelines and infrastructure, this is a technical route. Requires strong programming and cloud skills.
How to become a data analyst?
Starting a data analyst career can be approached from a few different directions. Traditionally, a bachelor’s degree in a quantitative field like statistics, math, or computer science was a prerequisite.
However, the field is evolving, and we acknowledge the growing acceptance of alternative paths.
Here’s a roadmap to get you started:
- Build your foundation: Regardless of your educational background, self-learning is key. Online courses and boot camps offer a compressed introduction to data analysis. Explore platforms like Coursera or edX to develop core skills in SQL – a query language for extracting data from databases, and Python or R – popular programming languages used for data manipulation and analysis.
- Consider certifications: Earning industry-recognized certifications like Google’s Data Analytics Professional Certificate or Microsoft’s Data Analyst certification can validate your capabilities to potential employers, especially if you’re bypassing a traditional degree.
- Get hands-on experience: Look for internship opportunities. They provide valuable real-world experience and can help you identify areas of interest within data analysis. Sites like LinkedIn or Glassdoor can be great resources for finding internship postings geared toward data analysis.
- Contribute to open-source projects: Participating in open-source projects on platforms like GitHub allows you to collaborate with other data enthusiasts, build your portfolio, and showcase your problem-solving abilities to recruiters.
- Network with data professionals: Some of the big names to follow on Linkedin include Cassie Kozyrkov, Steve Nouri, Ben Rogojan, etc. You can learn from them while also eyeing for industry meetups or online communities to connect with other data analysts.
What skills should a data analyst have?
As a data analyst, you should prepare yourself to learn new tools, techniques, and technologies throughout your career.
As a starting point, here’s a realistic breakdown of the essential skills you need to succeed as a data analyst:
Must-have technical skills:
- SQL: This is the absolute backbone of data analysis. You need to be proficient in querying databases, manipulating data, and performing aggregations.
- Data cleaning: Real-world data is messy. You’ll spend a lot of time cleaning, transforming, and preparing data for analysis. Python and R are popular languages for this.
- Data visualization: You need to be able to turn data into insights through clear and compelling visualizations. Tableau and Power BI are popular tools, but understanding the principles of good design is key. To save time, you can also choose no-code options like Userpilot.
- Statistical foundations: You don’t need to be a statistician, but you need a solid grasp of basic concepts like hypothesis testing, distributions, and regression.
- Spreadsheet proficiency (Excel/Google Sheets): Basic spreadsheets are still incredibly useful for quick analysis, data cleaning, and ad-hoc reporting.
Additional valuable skills:
- Python or R: These programming languages are incredibly versatile for data manipulation, analysis, and automation.
- Machine learning basics: Even if you’re not aiming for a machine learning role, understanding basic concepts like regression and classification can be very valuable.
Soft Skills (Equally Important!):
- Curiosity and problem-solving: Data analysis is all about asking the right questions and finding creative solutions.
- Critical thinking: You need to be able to evaluate data sources, analyze results, and draw logical conclusions.
- Communication and collaboration: You’ll often be working with teams, explaining technical concepts to non-technical stakeholders, and presenting your findings.
- Attention to detail: Data is precise; even small errors can have big consequences.
If you are seeking opportunities for advancement, it is highly recommended to acquire skills related to cloud and big data technologies. Additionally, developing expertise in a specific domain can be beneficial.
Best certifications for data analysts
To better decide which certification to go for, you should always consider costs and time investment. Plus, conduct careful research to see whether the certifications you’re interested in are valued by employers in your target industry or region.
Nonetheless, here are a few widely-recognized certifications to help you get started:
- Google Data Analytics Professional Certificate: This beginner-friendly certificate from Google covers the fundamentals of data analysis, including data cleaning, visualization, and analysis using spreadsheets, SQL, and R programming. It’s a great starting point for those new to the field or seeking to formalize their skills.
- Microsoft Certified: Azure Data Scientist Associate: For analysts working with Azure, this certification validates your ability to build and deploy machine learning models on the Azure platform. It covers data preparation, model training, and deployment, demonstrating your expertise in cloud-based data science.
- Certified Analytics Professional (CAP): CAP is a vendor-neutral certification that covers the entire analytics process, from framing business problems to communicating results. It’s a comprehensive credential that demonstrates your ability to apply analytics to real-world challenges.
- Cloudera Certified Associate (CCA) Data Analyst: If you work with big data technologies like Hadoop and Spark, the CCA Data Analyst certification proves your ability to perform essential data analysis tasks in a distributed environment.
Best resources for data analysts
In this section, we’ll explore some of the best resources for data analysts, including educational books, insightful blogs, and other resources designed to help you excel in your career and keep up with industry advancements.
Best books for data analysts
Data is everywhere, and the ability to analyze it is a highly sought-after skill. If you’re taking your first steps in data analysis, building a strong foundation is crucial.
These recommended books offer a practical and accessible way to learn the essentials, from basic concepts to more advanced tools and techniques:
- “Naked Statistics: Stripping the Dread from the Data” by Charles Wheelan: A fun and accessible introduction to statistics, explaining complex concepts in a way that’s easy to understand.
- “Storytelling with Data: A Data Visualization Guide for Business Professionals” by Cole Nussbaumer Knaflic: Highly recommended for mastering the art of presenting data in a clear, concise, and engaging manner.
- Practical Statistics for Data Scientists: 50+ Essential Concepts Using R and Python” by Peter Bruce, Andrew Bruce, and Peter Gedeck: Covers essential statistical concepts with practical examples in R and Python, making it a great resource for data analysts who are comfortable with programming.
- “SQL Practice Problems: 57 beginning, intermediate, and advanced challenges for you to solve using a “learn-by-doing” approach” by Sylvia Moestl Vasilik: A practical guide to mastering SQL with hands-on exercises, perfect for data analysts who need to work with databases.
- “Designing Data-Intensive Applications” by Martin Kleppmann: A comprehensive guide to building scalable and reliable data systems, covering topics like data storage, distributed systems, and batch processing.
Best webinars for data analysts
As a data analyst, you need to constantly update your skills and knowledge to keep up with the fast-paced world of data. Webinars offer a convenient way to do just that, allowing you to learn new techniques, tools, and industry trends from the comfort of your own desk.
So, here’s a list of useful webinar sources that you should keep an eye on:
- Userpilot Events: Userpilot’s webinars often focus on product analytics, user onboarding, and behavior-driven insights. They’re excellent for analysts interested in the intersection of data and user experience.
- BrightTALK: This platform hosts a massive selection of webinars on various topics, including data analysis, business intelligence, and data science. You can filter by your interests and level of expertise.
- DataCamp: While primarily known for its courses, DataCamp also offers webinars on specific data analysis techniques, tools, and career development.
- Orbit Analytics: Their webinars delve into reporting, BI, and data analytics, often focusing on Oracle-related tools and solutions.
Best blogs for data analysts
By reading insightful articles, tutorials, and case studies, analysts can expand their knowledge, learn new techniques, and gain inspiration from industry leaders.
With that in mind, here are a few suggestions from us:
- Userpilot Blog: Userpilot’s blog delves into product analytics, user onboarding, and behavior-driven insights. They offer actionable advice on how to use data to understand and improve the user experience, making it a valuable resource for analysts focused on product growth.
- Kaggle Blog: Kaggle is a renowned platform for data science competitions and collaboration. Their blog features insightful articles, tutorials, and interviews with top data scientists. It’s a go-to resource for learning about cutting-edge techniques and real-world applications.
- KDnuggets: This blog focuses on news and tutorials related to data science, machine learning, and artificial intelligence. It offers a mix of technical and non-technical content, making it suitable for both beginners and experienced analysts.
- DataCamp Blog: DataCamp’s blog complements its online courses with insightful articles on data analysis, visualization, and career advice. Their content is known for its clarity and practical approach, making it ideal for both beginners and experienced.
Best podcasts for data analysts
Podcasts offer a convenient and engaging way to learn on the go, whether you’re commuting, exercising, or simply relaxing. Here we include a list of useful podcasts that can make your data analyst life a bit easier:
- The Analytics Power Hour: This podcast features casual conversations among experienced data analysts and scientists about industry trends, tools, and challenges. You can find it on popular platforms like Spotify, Apple Podcasts, and Google Podcasts.
- Not So Standard Deviations: Hosted by Roger Peng and Hilary Parker, this podcast delves into the world of data science, covering topics from statistics and programming to career advice. It’s known for its in-depth discussions and thought-provoking interviews with experts in the field.
- DataFramed: Hosted by Hugo Bowne-Anderson, this podcast features interviews with industry leaders about data science, machine learning, and artificial intelligence. It explores the broader impact of data science on society and different industries.
- Data Skeptic: This podcast explores the science behind data, covering topics like statistics, machine learning, and data analysis. It offers a mix of mini-episodes and longer interviews that cater to both beginners and experienced professionals.
- Women in Data Science: Features interviews with women working in data science, providing valuable insights and career advice. (Available on Apple Podcasts).
Best tools for data analysts
Data analysts rely on a suite of powerful tools designed to collect, process, analyze, and visualize data. So here’s a list of the top tools that every data analyst should consider:
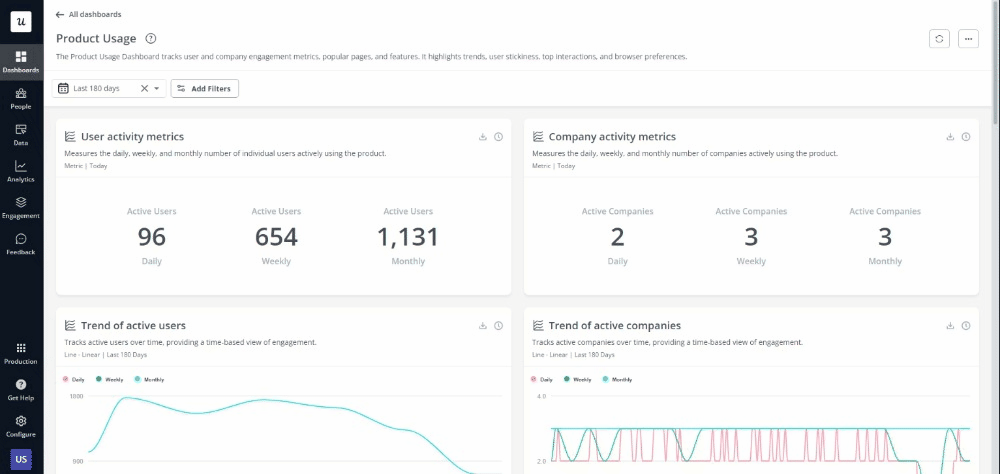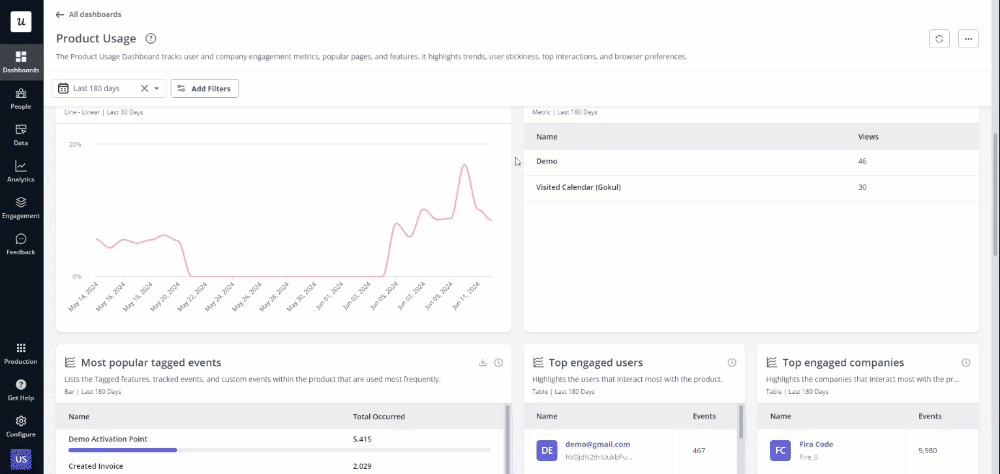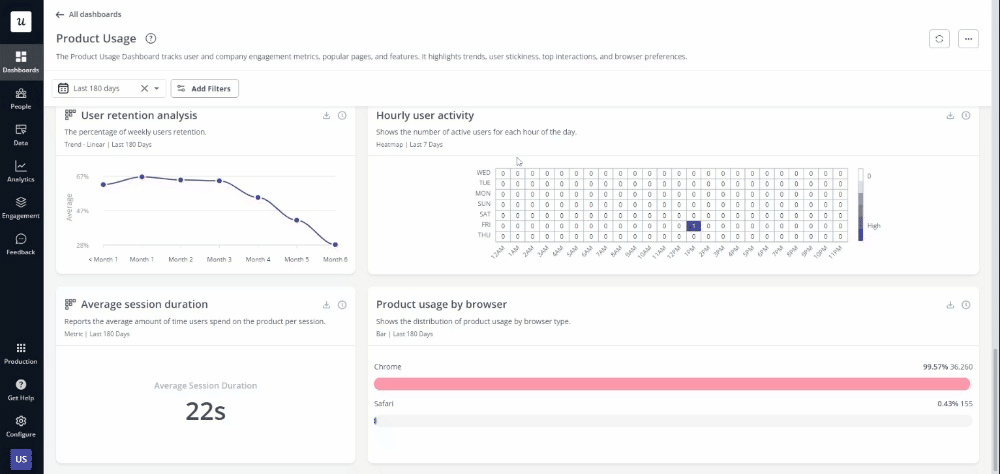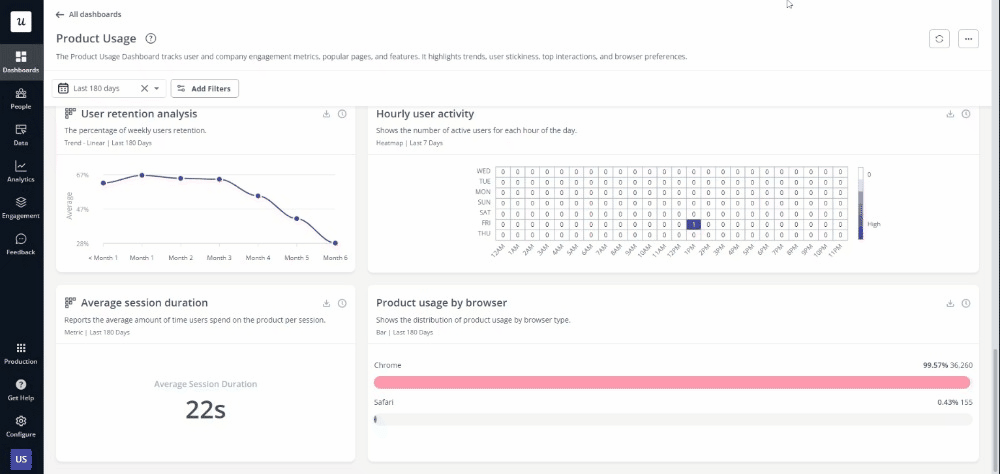
- Userpilot (Best for no-code product analytics): Userpilot is a no-code product analytics tool that helps product managers and data analysts understand user behavior and track product adoption. It provides features like metrics dashboards, reports (funnel, path, trend, cohort), user feedback, etc. This tool can help foster cross-team communication, bridging the gap between technical and non-technical teams.
- Tableau (Best for data visualization): Tableau is a data visualization tool that allows users to create interactive dashboards and reports. This can help data scientists identify trends and patterns in their data that would be difficult to see in a spreadsheet.
- Power BI (Best for business intelligence): Power BI is a business intelligence tool from Microsoft. It allows users to connect to a variety of data sources, create reports and dashboards, and share insights with others.
- Google Charts (Best for simple data visualization): Google Charts is a free data visualization tool from Google. It allows users to create a variety of charts and graphs, such as bar charts, line charts, and pie charts.
- Amplitude (Best for product analytics): Amplitude is a product analytics tool that helps businesses track user behavior and understand how users interact with their products. It provides features like funnels, user paths, and cohort analysis.
- Heap (Best for digital analytics): Heap is a digital analytics tool that automatically captures all user interactions on a website or app. This makes it a good option for businesses that want to track every user interaction, even if they don’t know what specific data points they are interested in yet.
- Mixpanel (Best for user behavior and predictive analytics): Mixpanel can help data scientists by providing them with a wealth of data on user behavior. This data can be used to improve product design, marketing campaigns, and overall user experience.
- Qualtrics (Best for survey research): Qualtrics can help data scientists by providing them with a way to collect data from a large number of people. This data can be used to identify trends and patterns in customer or employee sentiment.
- Optimal Workshop (Best for user research): Optimal Workshop is a user research tool that helps businesses conduct user testing and gather feedback from users. It provides features like card sorting, tree testing, and surveys.
- UserTesting (Best for user testing): UserTesting is a platform specifically designed for conducting remote user testing. Users can be recruited through the platform itself, allowing data scientists to gather feedback from a diverse range of people.
Data analyst FAQs
Is a data analyst an IT job?
Data analysis is often considered a hybrid role that bridges the gap between IT and business. While data analysts use technical skills and tools (like SQL, Python, and various data visualization platforms) to work with data, their primary focus is on extracting insights that can be used to inform business decisions.
What is a data analyst’s job description?
A data analyst’s job revolves around transforming raw data into actionable insights that drive business decisions. They collect, clean, and organize data from various sources, then utilize statistical techniques and tools to analyze it. Their work is essential for understanding customer behavior, optimizing business operations, and identifying new growth opportunities.
What do you need to become a data analyst?
Here’s a general roadmap that can give you an idea of how to become a data analyst:
- Develop foundational skills: Gain proficiency in mathematics, statistics, and computer science.
- Learn essential tools and technologies: Master programming languages like SQL, Python, or R, and data visualization tools like Tableau or Power BI.
- Gain practical experience: Work on real-world projects, internships, or freelance gigs to build your portfolio.
- Earn a degree or certification: Consider a bachelor’s degree in a relevant field or pursue industry-recognized certifications (e.g., Google Data Analytics, Microsoft Azure Data Scientist Associate).
- Network and build relationships: Connect with other data professionals through online communities, conferences, and job fairs.
- Apply for entry-level positions: Look for junior data analyst, data analyst intern, or business analyst roles to gain experience.
Is a data analyst a good career?
Yes, data analysis is a promising career choice for many. With the ever-increasing reliance on data across industries, the demand for skilled data analysts is high and projected to grow steadily in the coming years. This translates to competitive salaries and abundant job opportunities. Plus, data analysis offers a versatile skillset applicable across diverse sectors, providing flexibility and potential for career advancement.
Conclusion
Becoming a successful data analyst requires dedication, continuous learning, and a proactive approach to developing relevant skills.
By following the outlined steps and leveraging the resources available, you can effectively navigate your career path and achieve your professional goals.
We hope this guide has provided you with valuable insights and practical advice to help you on your journey to becoming a proficient and impactful data analyst!
Looking into tools for data analysts? Userpilot is an all-in-one product platform with engagement features and powerful analytics capabilities. Book a demo to see it in action!