What is a localization manager?
When businesses begin to scale, one of the things they begin to do is the international market, and that’s where a localization manager comes in. A localization manager helps a company enter the international market by adapting the company’s product and content to the language and culture of the global audience. A localization manager oversees the localization strategy implementation process from beginning to end while maintaining quality.
Localization manager’s main responsibilities
The responsibilities and duties of a localization manager are multifaceted. They are directly in charge of bringing a product to a regional market. Here is a list of their responsibilities:
- Overseeing the translation project from start to finish. This includes the company’s content, visuals, and entire messaging.
- Beyond just translating, they also ensure that all communication gaps are filled and the messaging resonates well with the global audience.
- Overseeing all tasks assigned to translators and external agencies involved in the translation process, thereby ensuring quality delivery.
- Collaborating with other teams involved in the localization process ranging from legal, product, and marketing to IT.
- Researching the global market and identifying gaps and opportunities to leverage for growth.
- Manages the budget allocated to the localization process, pays external agencies such as translation agencies, and keeps track of the budget.
- Keep accurate track of the localization process and report progress to company stakeholders.
- Optimization of tech tools such as localization tools to ensure smooth and efficient translation.
- Serving as a quality assurance personnel and ensuring the standard of the content is maintained through the translation process.
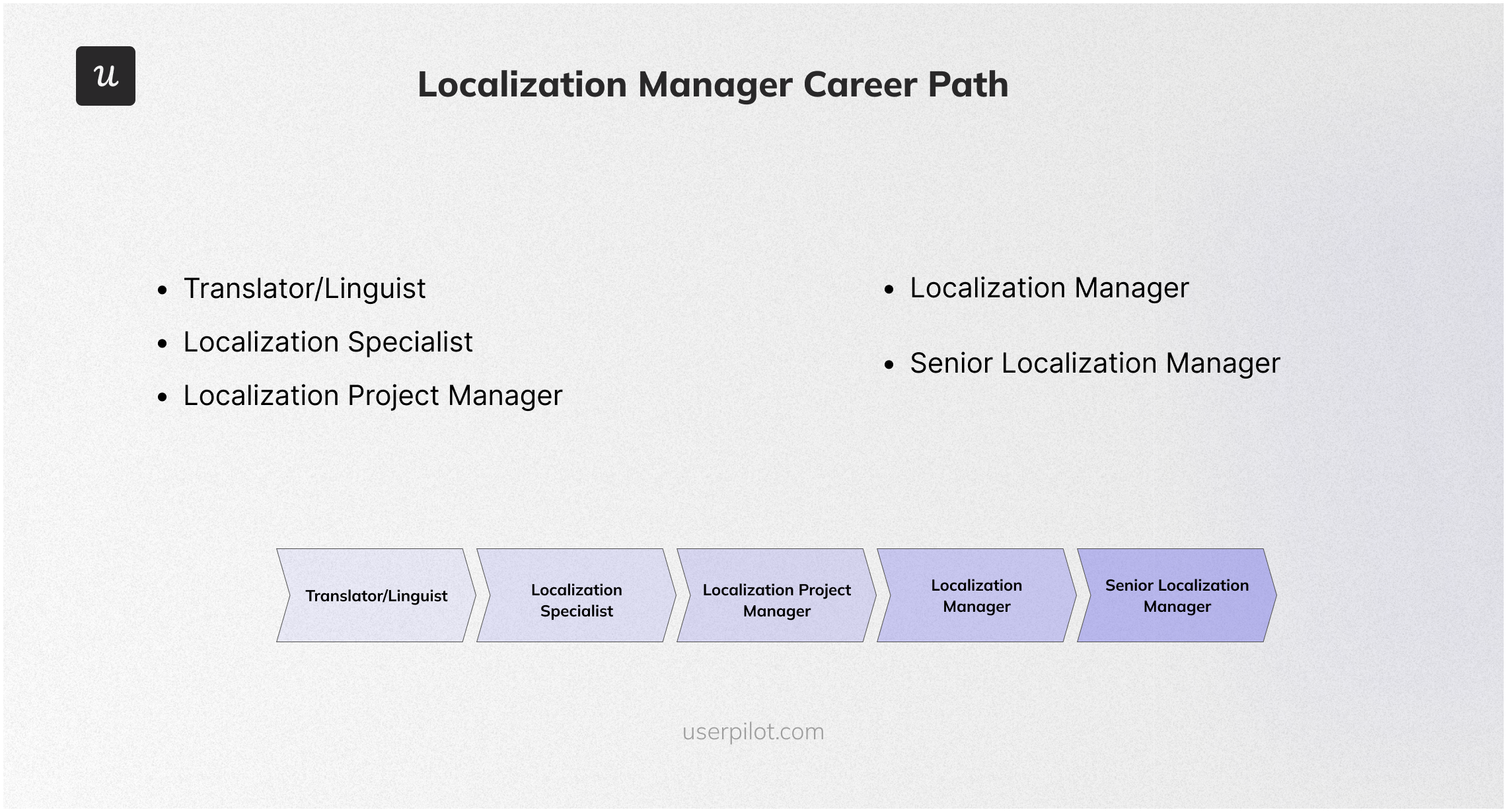
Localization manager career path
The career path for a localization manager is an interesting one when you are enthusiastic and excited about learning. With constant upskilling and as your years of experience increase, you begin to move up the career ladder, and your income does the same. Here is a typical career path for a localization manager:
- Entry-Level Positions (Translator or Linguist): Most localization managers start as translators or linguists. In this role, you help translate the company’s content into the language of the target audience. Proficiency in the audience’s language is, therefore, very important for this role.
- Localization specialist: The localization specialist edits translated content and ensures quality assurance. They also have an in-depth understanding of the target audience and ensure there is a product and content fit.
- Localization Project Manager: As you upskill and get your project management certificates, you can progress to the role of a localization project manager. In this role, localization projects are assigned to you, and you are responsible for their success.
- Localization Manager: The localization manager is in charge of implementing a localization strategy. They manage workflow and ensure all localization projects are going as planned.
- Senior Localization Manager: After some years of more hands-on experience as a localization manager, you can move up the ropes to a senior localization manager, where you have more responsibilities. The senior localization manager carries out the market research, comes up with the localization strategy, and ensures the implementation process goes as planned.
How to become a localization manager?
You do not need to go to school to become a localization manager. Although it is not compulsory, most companies ask for a degree in translation or project management. Other related courses are business administration, international relations, and language-related courses.
If you do not have a degree in any of the above courses, you can take related certification courses on well-recognized platforms like Coursera and learn the needed skills. Learning how to use translation and project management tools such as Trello, Asana, and Notion will also be a plus. Meanwhile, you should also take short courses on soft skills such as management, communication and teamwork.
Although a localization manager would not be the one to do the translation work, a solid grasp of the languages involved will be crucial in getting the job done. Also, the journey to being a localization manager is a deliberate process. You can start as a translator or a project manager. From there, you can climb up the ladder by making the right connection, getting hands-on experience in localization, and proving your capacity.
What skills should a localization manager have?
The localization manager role is multifaceted. It requires a fine blend of technical and soft skills. It also requires analytical and a good grasp of linguistics and international relations skills. Here is an outline of the skills required for a localization manager:
- Project management skills: As a project manager, you oversee different projects and ensure their success. You need to know how to relate with people and manage them to get the work done.
- Communication skills: A localization manager will interact with quite several people: the product team, marketing team, sales team, and even external agencies. They must be able to communicate effectively with everyone they are working with.
- Organization skills: A localization manager will be overseeing some people and projects at the same time. They must pay great attention to details and be well-organized. A great project management tool such as Trello, Notion, or Asana will be handy in this case.
- Stronger leadership and people management skills: A localization manager is essentially a people manager. They lead the people involved in the localization process to get things done. It can be a little dicey in a remote team when people are spread abroad in different locations.
- Tech-savvy: Being tech-savvy is essential for a localization manager, as you need to operate technical localization tools to achieve your goal. You should also be able to assess and pick the right tool to get the job done.
- Understanding of international terrain: A localization manager needs to have an understanding of the international terrain to ensure a smooth localization.
- Quality-oriented: A localization manager is a quality assurance manager. They ensure that the company’s content is maintained.
Best certifications for localization manager
If you haven’t got any clue about how to get started, here are some options gaining recognition, along with insights across hiring platforms regarding valuable skills for a localization manager:
Localization Certifications:
- Certified Localization Professional (CLP) (Localization Institute): This certification, offered by a leading industry organization, validates your understanding of core localization processes, workflows, and best practices. It demonstrates expertise to potential employers.
- Global Professional in Localization (GLoc) Certification (Globalization & Localization Association (GALA)): Similar to the CLP, this certification from another well-respected organization validates your knowledge of core localization concepts and best practices. Earning it showcases your competency.
Project Management & Business Certifications (Valuable for Localization):
- Project Management Professional (PMP) Certification (Project Management Institute (PMI)): Localization projects often involve complex workflows and managing teams across regions. This certification equips you with project management methodologies in the localization field.
- Certified Business Analysis Professional (CBAP) Certification (International Institute of Business Analysis (IIBA)): Localization managers often analyze existing content and workflows for improvement. This certification validates your business analysis skills, which is important for localization managers.
Language & Cultural Certifications:
- American Translators Association (ATA) Certification: Earning an ATA certification in your target language demonstrates fluency and translation expertise, a valuable asset for localization managers.
- Graduate Certificate in Translation Studies: This advanced program equips you with in-depth knowledge of translation theory and cultural nuances, crucial for successful localization (offered by various universities).
Best resources for localization managers
To become a better localization manager and excel in your role, you need access to resources, including podcasts, books, webinars, and blogs.
Best books for localization managers
- The Culture Map: Breaking Through the Invisible Boundaries of Global Business By Erin Meyer: This is a book for localization managers that helps understand the international market and how to expand.
- The Language of Localization by Katherine Brown-Hoekstra: This book defines the terminology in localization that every localization manager needs to know and cites references for future reading. If you are just getting started in localization, this book is a must-read.
- Take Your Company Global: The New Rules of International Expansion by Nataly Kelly: In the book, Nataly Kelly, Chief Growth Officer at Rebrandly, explains the new ways to take your company global.
- A Practical Guide to Localization by Bert Esselink: In the book, Bert Esselink, a localization expert with years of experience shares practical tips on translation and how to localize software products.
- The Art of the Global Gateway by John Yunker: This book explains how you can produce localized website content that drives traffic, leads, and sales. It is a must-read for localization managers looking to produce localized content that sells.
Best webinars for localization managers
- Userpilot Webinars: If you are a SaaS product looking to take your market to the international market, the Userpilot webinar is one to bookmark because of its practical insights.
- Blend Webinars: Blend webinars are practical and insightful interviews with leaders in global companies and one every localization manager should bookmark.
- Braahmam Webinars: In the webinar series, Braahmam shares tips around translation and how to optimize your localized website content for search.
- Lokalise Webinars: The Lokalise webinar helps you grow your knowledge on localization and stay abreast of trends.
- Phrase Webinars: The webinar covers a wide range of topics related to localization, ranging from translation to building a localization workflow. It is a webinar series every localization manager should look into.
Best blogs for localization managers
- Userpilot Blog: The Userpilot Blog is a goldmine for localization managers who want to carry out localization in-app effectively, especially for a SaaS company looking to expand.
- Blend Blog: The Blend Blog is another valuable resource for localization managers. It contains valuable and well-researched content that helps you level up your localization career.
- The DayBlog: If you’re looking to stay updated on trends in the localization industry, the DayBlog allows you to stay on top of current happenings in the industry.
- Clearly Local Blog: The Clearly Local blog shares insights around localization.
- Localize Blog: The Localize Blog is a resource that touches on different topics related to localization. If you want to widen your scope of localization, you should check it out.
Best podcasts for localization managers
- Blend Podcast: The Blend podcast primarily features interviews with people in the localization industry where insights on localization are being shared.
- Translastars Podcast: The Translastars podcast is mostly about how to become a better translator.
- Marketing Tips for Translators: This podcast provides insights on how you can market yourself as a translator. Knowing how to market yourself well can help you get the most from your career.
- The Language Worker by Rita Prazeres Gonclaves: Rita is an expert in the language and localization industry and shares insights on translation and localization on the podcast.
- Wordbee Podcast: The Wordbee podcast is a series of interviews with localization experts, where they discuss matters on localization and share their insights.
Best tools for localization managers
Tools are a very important part of localization because they make your work easier and more efficient. Here are five best tools for a localization manager:
- Best tool for product analytics (Userpilot): Userpilot helps with user research and has a localization functionality that helps your localization process by offering automatic localization of in-app messaging.
- Best tool for project management (Notion): Notion keeps all your projects in one place, helping you manage them effectively.
- Best tool for business intelligence (Power BI): You need to carry out market research on your location and report findings to stakeholders. Power BI is a business tool that comes in handy here.
- Best tool for translation (Weglot): Weglot helps you translate effectively. With Weglot, you can also order professional translation services.
- Best tool for content localization (Motionpoint): Unlike other translation tools, Motionpoint has actual human translators that translate your content. This means more accuracy and better quality translation.
Localization manager FAQs
- What skills do you need to be a localization manager?
Communication, planning and organization, project management, managerial skills, and an understanding of the international terrain are the skills needed to become a localization manager.
- What is localization management?
Localization management is about planning, organizing, and executing an organization’s plan to expand to international markets.
- What is a localization role?
This is a localization manager role that requires you to oversee and execute the localization projects of a company. This includes a wide range of activities, such as managing the translation project, ensuring the brand voice and messaging are maintained, and working with freelancers and other contractors on the project.
- How to become a localization manager?
You can become a localization manager by taking courses on Project Management and Translation. When you get your certificates, you can start by applying for entry-level roles in the industry.
Conclusion
Becoming a successful localization manager requires dedication, continuous learning, and a proactive approach to developing relevant skills.
By following the outlined steps and leveraging the resources available, you can effectively navigate your career path and achieve your professional goals.
We hope this guide has provided you with valuable insights and practical advice to help you on your journey to becoming a proficient and impactful localization manager!
Looking into tools for localization managers? Userpilot is an all-in-one product platform with engagement features and powerful analytics capabilities. Book a demo to see it in action!