73% of customers expect businesses to “understand their unique needs and expectations,” according to a report from Salesforce.
A customer wants and needs analysis helps you do just that.
It helps you identify the factors that shape customers’ buying decisions, which further enables you to build a product that meets customer requirements and expectations.
Thankfully, conducting this analysis is fairly straightforward with the right steps and product tools. This article explores each of these steps in detail.
Step-by-step process for carrying out a customer wants and needs analysis
Analyzing customer needs and wants can be broken down into a 7-step process. Let’s explore each step.
1. Define clear objectives to guide your analysis
This is an often overlooked but essential step in the process. Truly, it’s not a stretch to say that a misstep here or ignoring this step completely can doom your analysis from the start.
Your objectives shape your process. They tell you what you’re looking for and help you stay on track when sifting through lots of data.
When defining these objectives, ask yourself:
- What am I trying to achieve? Am I launching a new product, improving an existing one, or just trying to understand my customers?
- What information (customer pain points, preferences, motivations, etc.) do I hope to get from this analysis?
Once you’ve determined your objectives, you can begin setting your goals. A good goal should be specific and measurable.
For example, if you’re conducting a needs analysis survey to help launch a new product, you can set a goal of identifying the “top 3 unsolved customer pain points” in your niche.
P.S. The next steps are tailored to businesses with existing customers. However, these points can be adapted to businesses of any growth level.
2. Break down your audience into distinct segments
Once you’ve determined your goals, it’s time to segment your customers. The reason is simple: each user segment will have unique wants that need to be analyzed.
As a result, your target audience may differ depending on your goals—you may choose to analyze all customer segments or only a select group(s).
For example, if you want to increase the free-to-paid conversion rate, you can study the behavior of free plan customers who didn’t convert into paying ones to understand how best to convert them.
Similarly, if your goal is to improve an existing product by adding more features, you could segment users based on their goals, experience level, etc., to gain valuable insights into each segment’s needs and tailor your improvements accordingly.
3. Analyze customer behavior data to identify trends
Now that you know which customers you’re interested in, it’s time to collect data and begin your analysis.
We’ve chosen customer behavior data as the first data source as it provides valuable insights into how customers use your product and what they desire.
There are two ways to collect this:
Observe quantitative user data
Quantitative user data deals with numbers and measurements relating to user behavior. It helps you understand customer behavior by presenting how many, how much, or how often a “thing” happens.
For example, quantitative data can track feature usage frequency, number of app sessions, conversion rates, daily or monthly active users, etc.
You can also generate time-series data to track product usage trends. For instance, if you want to understand why customers churn, you can track drop-offs in funnel reports for churned customers.
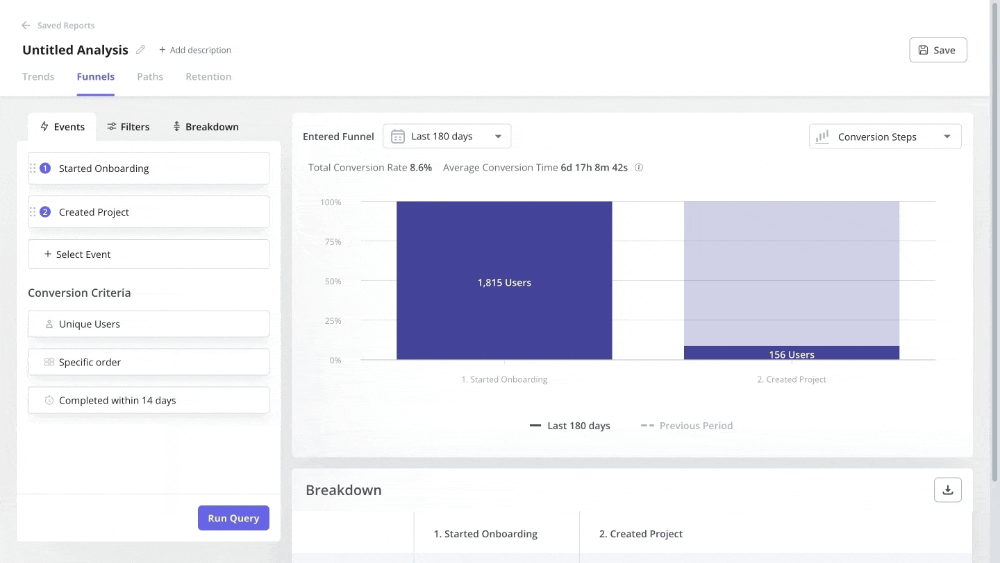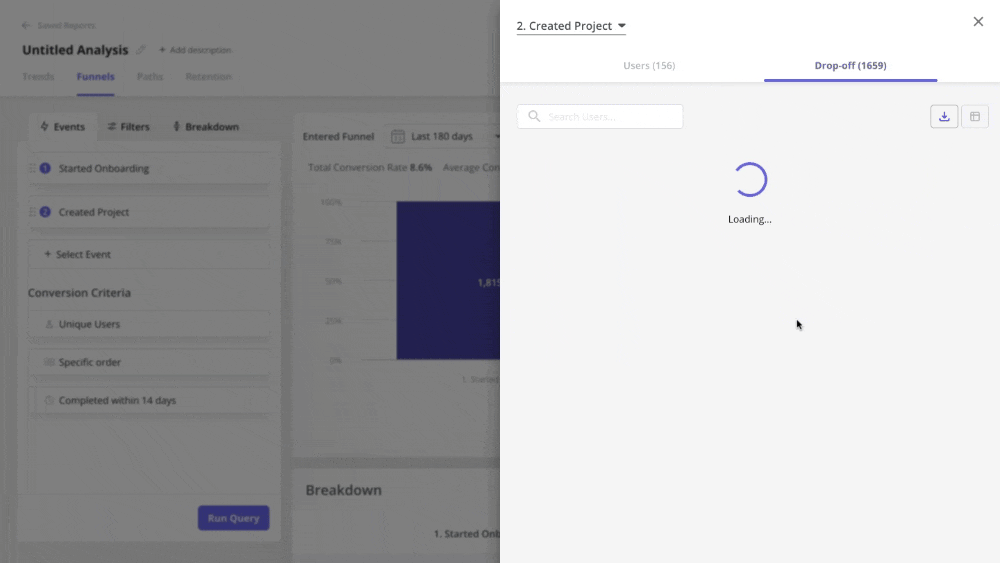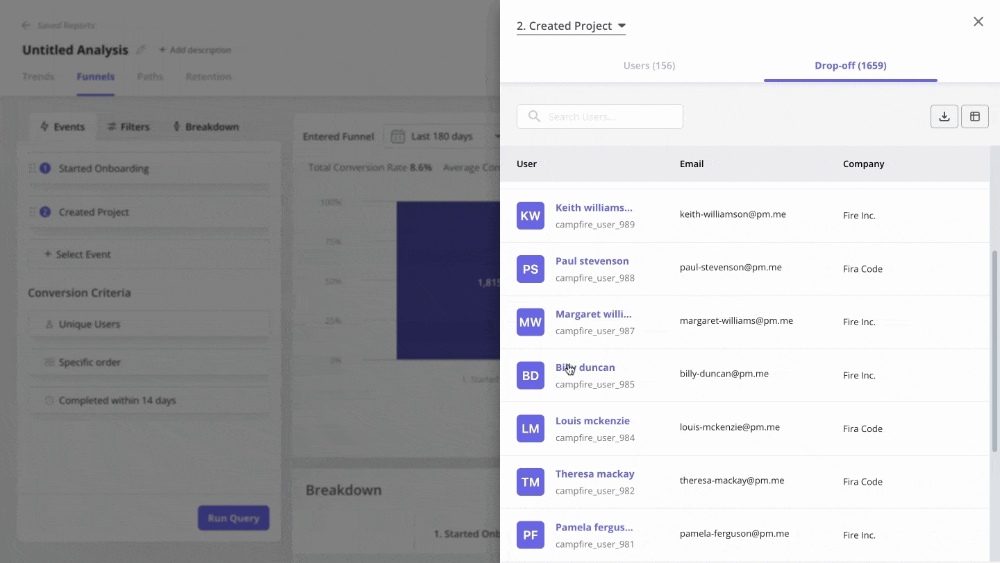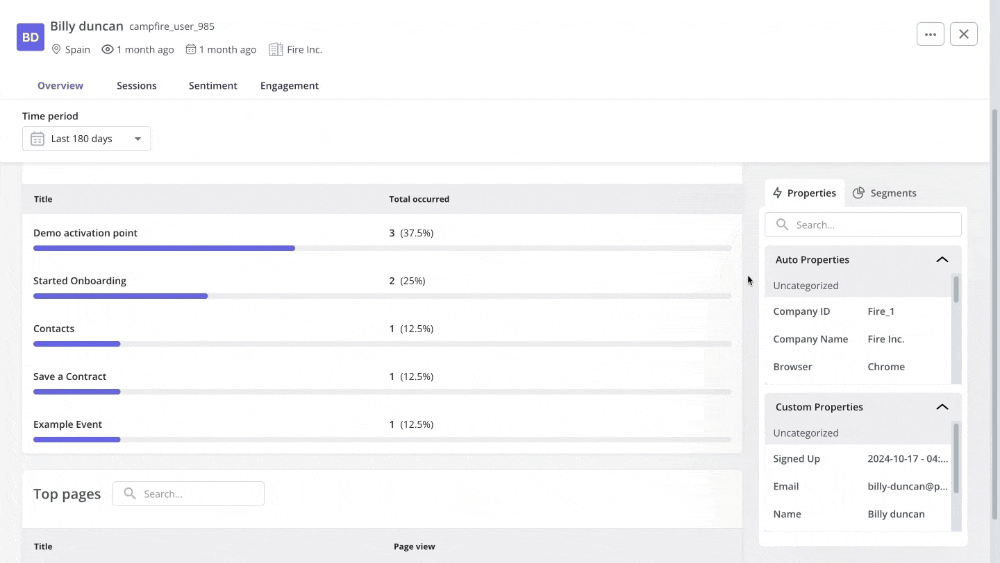
Monitor visual customer data
Visual customer data is quantitative data that is presented in a visual format. Visualizing customer data in an appealing and informative manner makes it easier to understand, interpret, and communicate.
Visual data also makes identifying patterns and trends you may have missed in raw data easier.
For example, you can use session recordings to understand user interactions on your app. This can reveal areas where users hesitate, click excessively, or abandon workflows.
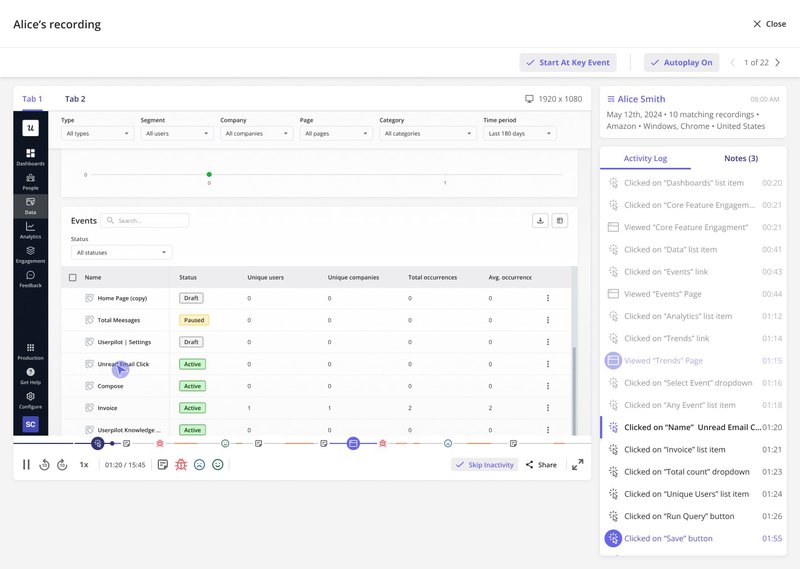
Other useful forms of visual customer data include customer journey maps, product usage dashboards, etc.
4. Supplement insights with qualitative data
Quantitative data may answer the what but not the why behind the numbers. This is where qualitative customer data becomes useful.
There are three main ways to collect this data:
Trigger surveys with open-ended questions
In-app surveys enable your target audience to provide their thoughts on different matters. Note, however, that you need open-ended survey questions to get qualitative customer feedback.
So, instead of offering users a “Yes/No” or rating-scale question, open-ended questions allow customers to express their thoughts, feelings, and experiences using their own words.
It includes questions like, ‘What did you dislike about your customer service experience?’, ‘What feature(s) would you like us to add to our product?’, etc.
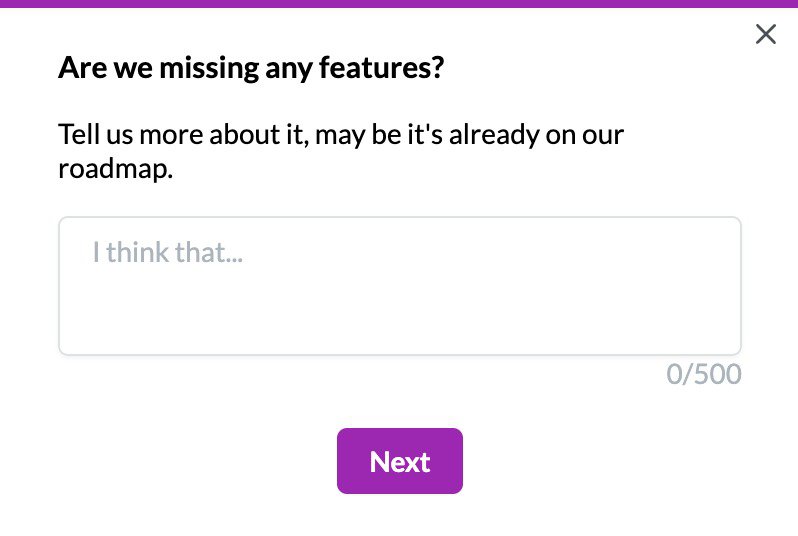
This is ideal for 3 key reasons:
- It provides rich, nuanced insights into why a customer feels a certain way.
- Customers may raise concerns or provide suggestions you haven’t considered.
- Because they target users already using your product, in-app surveys are scalable and cost-effective.
Despite these advantages, though, these surveys typically have low response rates. This can make them ineffective sources of aggregate customer feedback.
Conduct interviews and focus groups
Interviews and focus groups present an opportunity to speak directly with customers and dive deeper into their pain points, motivations, and behaviors.
For example, you can conduct interviews with a select group of users (say, NPS detractors) to understand their frustrations with a product feature.
During the interview, the interviewer can ask follow-up questions to understand the customer’s complaint. They can also observe facial expressions and other non-verbal cues to understand customer emotions.
The same is true of focus groups. A moderator can observe how individuals interact and note how customer opinions and attitudes evolve within a group setting.
Review customer support interactions
Customer support interactions provide a direct window into customer problems and frustrations.
Unlike surveys, you don’t have to spend time waiting to gather customer feedback. Simply collate existing support tickets, chat logs, or email threads over the period of interest.
Then, analyze the tickets to identify recurring problems and common pain points. You can also analyze the tone and language used in the ticket to understand customer emotions and satisfaction levels.
For example, you can analyze interactions with the customer service team by churned customers to identify the most common reasons for customer churn.
P.S. By now, you should have a list of all the pain points and frustrations you identified in steps 3 and 4. If you don’t already have one, pause and create it. You can include the number of times a complaint was made to help your next step.
5. Prioritize customer needs based on impact and feasibility
Okay, I’m sure by now you’re itching to start addressing these customer issues. But there’s one last step before you get there—ranking (prioritizing) your findings.
The reason is simple: Not every complaint or frustration is worth your limited time and resources. So, you must focus on the most impactful and feasible solutions that deliver the highest ROI to you and your customers.
Thankfully, prioritization doesn’t have to be driven by gut feeling or guesswork. In fact, there are several prioritization frameworks that can guide this process, including:
The RICE framework
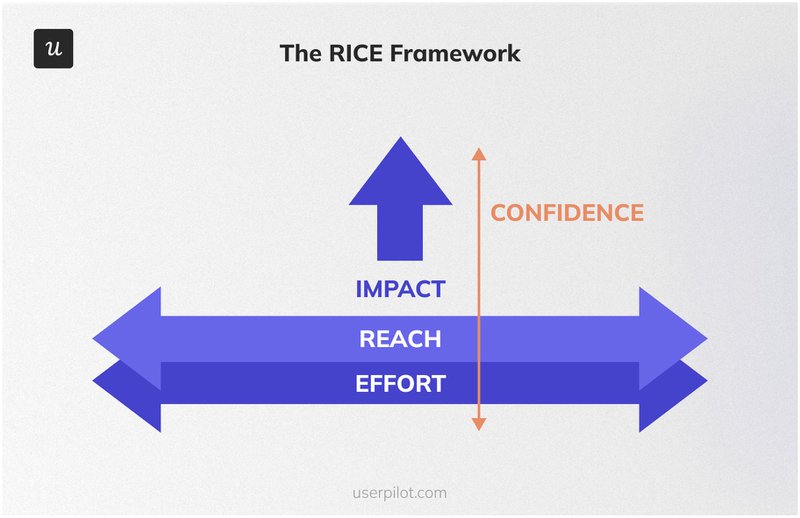
RICE stands for Reach (the number of users affected by the solution), Impact (the solution’s effect on user behavior), Confidence (the level of certainty in the estimated reach and impact), and Effort (the estimated time and resources required to address the problem).
The model directly measures the reach and impact (on key product metrics) of suggested changes. It also prevents over-prioritizing features that are overly complex or time-consuming to develop.
Value vs. effort framework
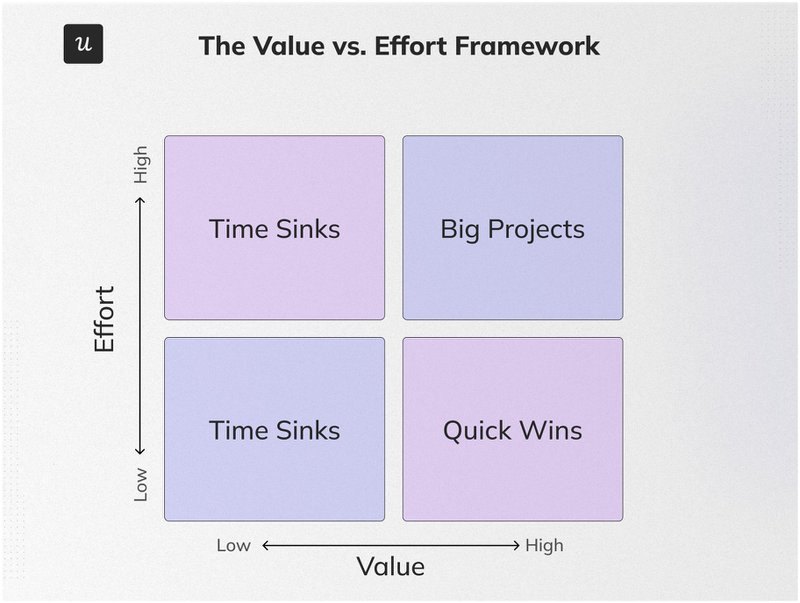
This model provides a simple and intuitive visual representation of the trade-offs between value and effort.
“Effort” here refers to everything from the time and resources taken to build the feature to the time taken (if necessary) to update other features for compatibility. Meanwhile, “value” measures the product’s usefulness to customers and the overall business strategy.
The model, therefore, easily highlights “quick wins”—solutions that deliver high value with low effort. It also highlights “time sinks”—solutions that deliver low value with high effort.
The Kano model
The Kano model categorizes customer needs into 3 groups:
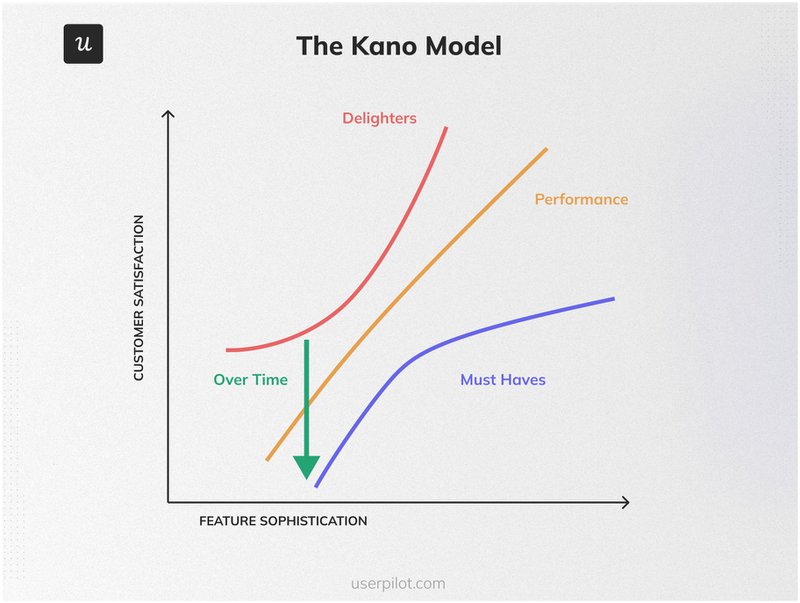
- Basic features: These are “must-have” product features necessary for your product to function. Customers generally expect these features and take them for granted.
- Performance features: These features improve the performance of your product in some capacity. They directly correlate with customer satisfaction and can cause dissatisfaction when absent.
- Excitement features: Also known as “delighters”, these unexpected features make your product more enjoyable to use. They yield dramatic customer delight and give you a competitive advantage.
6. Implement changes and measure their success
Finally, it’s time to start working on your proposed changes. Your goal should be to address customer needs and improve your product or services satisfactorily.
But your work doesn’t stop when you roll out the changes.
Instead, you need to track the metrics relevant to your goals to gauge the success of your initiatives. Then, create a custom dashboard with these metrics and share it with relevant stakeholders.
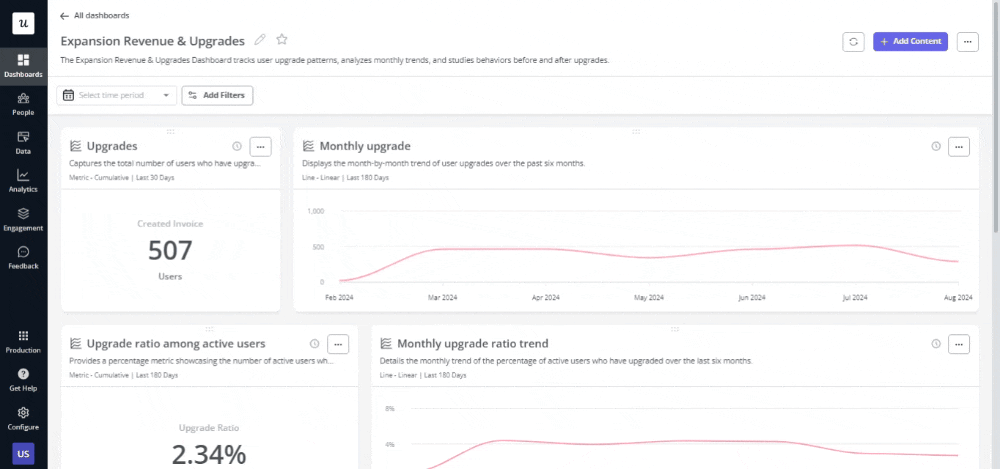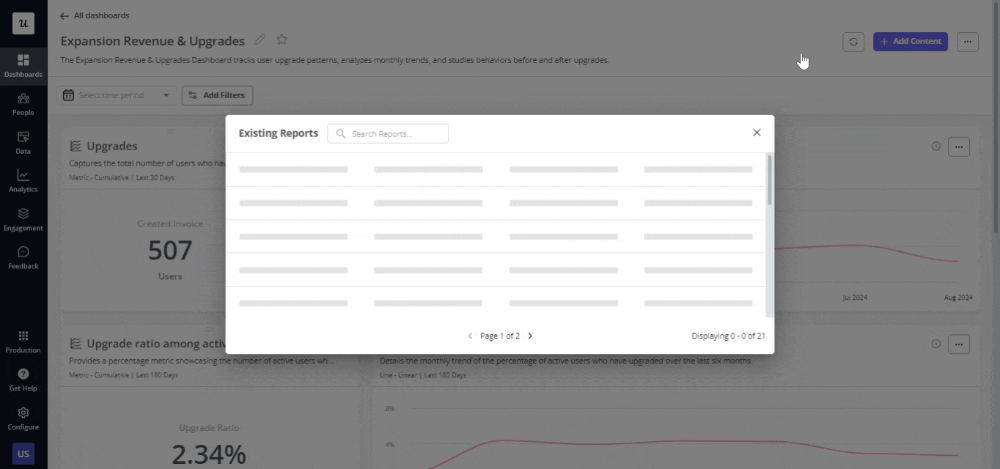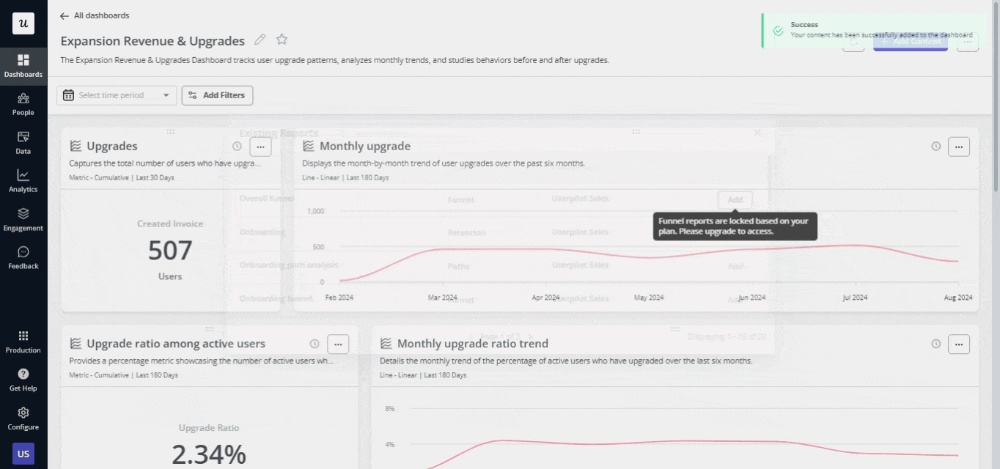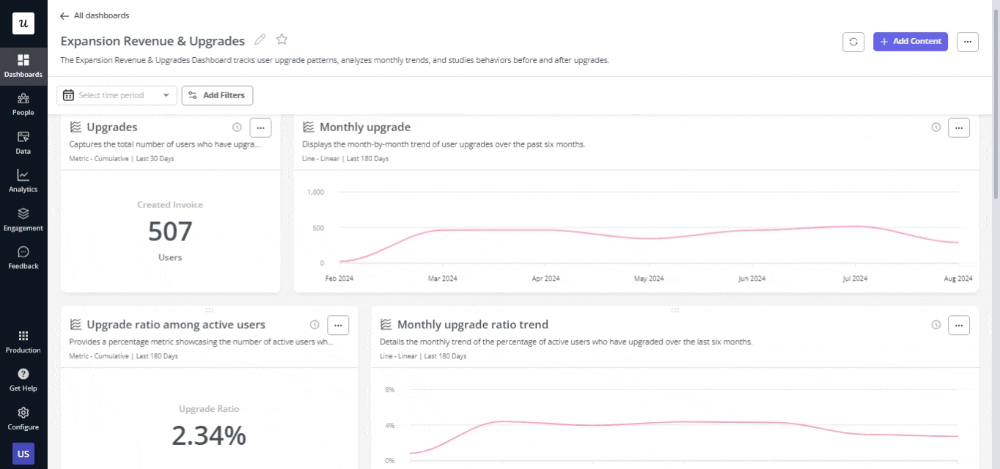
This will help you identify areas where you may have missed the mark so you can correct it accordingly.
7. Make it an ongoing process by iterating regularly
Now, the key to achieving lasting customer loyalty lies in the recognition that customer needs are not static—they evolve. So, it’s crucial that you regularly (quarterly or bi-annually) review these needs.
An easy way to do this is to continuously collect and analyze customer feedback (via in-app surveys and a feedback widget) to spot any major changes in customer needs.
Then, rank these needs again and address them accordingly. This will lead to enhanced customer satisfaction and continued loyalty.
Ready to gather customer needs?
Customer needs analysis is a must for any product manager. It helps you build emotional connections with customers, leading to better sales, revenue, and retention.
To succeed, though, you’ll need the right product. Userpilot empowers you to streamline the process, providing tools for collecting valuable customer data, gathering customer feedback, and acting on it.
Ready? Get a Userpilot demo and learn how to accommodate your customer needs and improve your product.
FAQ
What is a customer wants and needs analysis?
A customer wants and needs analysis is a data-driven evaluation of what customers desire from a product or service and what problems they’re trying to solve.
What is the difference between customer needs and customer wants?
A need is something essential, required, and vital, while a want is something desirable.
So, customer needs are essential for the product to be functional and solve the core problem. On the other hand, customer wants are desirable features that improve the customer experience but aren’t vital for basic functioning.
For example, a project management app needs to support task management, collaboration, progress tracking, and report generation. But, a project manager may also want the app to be visually appealing, gamified, and AI-powered.
What are the different types of customer needs?
Customer needs analysis can reveal several categories of needs, including:
- Functional needs: These are practical, tangible needs that establish value. They encompass the product’s core features, usability, and pricing.
- Social needs: These needs affect the perception of a product or service. They include needs like good customer service and transparency which lead to positive brand recognition.
- Emotional needs: These needs impact how the customer feels about your product. Features like personalization, gamification, fast response times, etc., create a positive user experience and feelings of enjoyment.
- Performance needs: These relate to the product’s efficiency, speed, and effectiveness. It encompasses features like fast loading times, reliability and uptimes, integrations, etc.
Why should you analyze customer needs and wants?
Knowing and understanding customer needs is at the center of every successful SaaS business. Amongst other things, it helps:
- Enhance product-market fit: Identifying customer needs allows you to build a product that meets customer requirements.
- Improve customer satisfaction and retention: A product that addresses customer’s needs sufficiently enjoys better customer satisfaction and retention levels.
- Drive revenue growth: Satisfied customers refer others via word-of-mouth marketing and are more willing to become repeat (or big-ticket) buyers.