Tracking revenue on a spreadsheet is easy, but understanding the underlying factors influencing revenue growth rate is a different ball game. By the end of this article, you will be equipped to do that.
As you read on, you will learn:
- How to properly define revenue growth rate.
- The formula to calculate growth rate and what good growth looks like.
- Related metrics that impact your revenue and how to use the insights to turn your product into a growth engine.
Get The Insights!
The fastest way to learn about Product Growth, Management & Trends.
What is revenue growth rate?
Revenue growth is the increase in a company’s total revenue or income over a specific period, typically calculated quarterly or annually.
For SaaS products, achieving sustainable revenue growth is often a top-level goal, aligning with broader business objectives like market expansion, profitability, and shareholder value. It serves as a key performance indicator (KPI) for evaluating the effectiveness of various business strategies.
Why is tracking revenue growth rate important?
Revenue tracking goes beyond financial record-keeping. The insights you generate when you regularly calculate revenue growth are pivotal in steering the strategic direction of your business and optimizing your revenue growth strategy.
Here are three reasons you should always know your numbers:
- Measure business growth
Financial performance evaluation serves as a barometer for assessing your business’s overall health and vitality.
By analyzing revenue growth over specific periods, your company will gain insights into the effectiveness of marketing campaigns, customer retention initiatives, and product enhancements.
- Improve business valuation
Your company’s valuation is tied closely to its revenue performance, especially because you’re a subscription business.
Investors and potential acquirers scrutinize revenue growth as a key factor in evaluating the attractiveness and sustainability of a business. Consistent and substantial revenue growth signals to investors that your company is on a trajectory of success. It enhances your perceived value, potentially leading to more favorable investment opportunities, partnerships, or acquisition deals that drive scalability.
- Spot anomalies in revenue flow and take corrective action
Anomalies in revenue flow, whether sudden spikes or unexpected dips, can be early indicators of underlying issues, but you won’t know this if you don’t measure revenue often.
Regular tracking allows you to swiftly identify these anomalies, enabling proactive corrective action. Whether it’s addressing customer churn, refining marketing strategies, or adapting to market shifts, the ability to spot irregularities will empower your company to navigate several challenges. This helps users see the ROI of using your tool and boosts your overall revenue growth rate.
Revenue growth rate formula
Now that you’ve seen the importance of tracking revenue growth, how do you begin? Use this simple revenue growth formula.

For example, if your total revenue for Q1 2023 was $100,000, and you had $120,000 in Q2 2023, your company’s revenue growth rate would be:
= ($120,000−$100,000/$100,000) × 100
= ($20,000/$100,000) × 100
= 0.2 × 100
= 20%
What is a good revenue growth rate?
Revenue growth rate varies by industry and company stage. For example, startups typically start with lower revenue figures, making it easier to achieve high percentage growth rates even with relatively small increases in revenue.
Mature companies may experience more stable but moderate revenue growth rates. They have likely captured a significant portion of their target market, and growth becomes more about retaining existing customers and optimizing operations.
Research by the team at Bessemer proves this. According to their study, companies with ARR between $1-10MM experience up to 200% revenue growth rate, while more mature ones with over $100MM+ have growth rates of around 60%. On average, most companies have a YoY growth rate of around 70% regardless of growth stage.
Relevant metrics that affect revenue growth
SaaS revenue is complex and multifaceted, with many factors affecting the bottom line. This section shows you the most important metrics shaping growth and how to measure them.
Customer acquisition cost (CAC)
CAC represents the average cost incurred to acquire a new paying customer. It encompasses expenses related to marketing, sales, and any other activities involved in attracting and onboarding new customers.
To calculate CAC, divide the total cost of customer acquisition over a specific period by the number of new customers acquired during that same period.

Suppose your company spent $50,000 on marketing and sales last month and acquired 100 new customers. Your CAC would be $500 per customer.
CAC = ($50,000 / 100 customers) x 100 = $500/customer
Churn rate
The churn rate measures the percentage of customers who stop using your product or service over a specific period. High churn can erode revenue gains. Monitoring churn helps identify weaknesses in customer retention strategies and prompts corrective action.
To calculate your churn rate, divide the number of lost customers in a period by the number of active customers at the beginning of the period and multiply by 100.

If your company had 1,000 active customers at the beginning of the month and lost 50 customers during the month, your churn rate would be:
(50 customers / 1,000 customers) x 100 = 0.05 x 100 = 5%
Monthly recurring revenue (MRR)
Your MRR represents the total predictable revenue your company expects to generate from recurring payments in a single month. This metric provides a clear picture of your company’s financial health, allowing for accurate revenue forecasting and identifying trends in subscription revenue.
To calculate MRR, multiply the Average Revenue per Account by the number of paying accounts in a month. Your calculation should cover monthly subscriptions, annual subscriptions prorated to a monthly amount, and any other recurring payments.

If your company has 100 customers paying a monthly subscription of $50 each, your MRR would be $5,000.
Average revenue per user (ARPU)
ARPU measures the average revenue generated per user or customer. This metric helps assess the overall revenue potential of each customer segment, guiding pricing strategies and identifying upselling opportunities to boost your company’s growth rate.
To calculate ARPU, divide your total monthly recurring revenue by the number of active customers for a given month.

If your company generates $5,000 in MRR and has 100 active customers, your ARPU would be $50 per customer.
Customer lifetime value (LTV)
Customer Lifetime Value (LTV) estimates the total revenue your company expects to generate from a single customer throughout their relationship with you. LTV helps gauge the long-term value of acquiring and retaining customers, guiding investment decisions and customer relationship management strategies.
Calculate LTV by dividing the ARPA by the customer churn rate.

For example, if your ARPA in the last month was $4,000 and the customer churn rate was 2% or 0.02, your LTV in the previous month was $(4,000/0.02) or $200,000.
Burn rate
Burn rate measures how quickly your company is spending its available capital.
Monitoring this metric is crucial for financial planning. A high burn rate without corresponding revenue growth can lead to financial instability, while a low burn rate may indicate conservative spending that could be hindering growth.
To calculate your net burn rate, subtract operating expenses in a given period from your revenue. Divide the result by your starting capital and multiply by 100.

Suppose your company has the following financials for a given period.
- Revenue: $300,000
- Operating Expenses: $200,000
- Starting Capital: $1,000,000
Net Burn Rate = (($300,000 – $200,000) / $1,000,000) x 100
= ($100,000 / $1,000,000) x 100
= 10%
The assessment of what constitutes a “good” burn rate can depend on various factors, including your company stage, growth strategy, and market conditions, but always aim to keep it moderate.
Retention rate
Retention rate measures the percentage of customers who continue using your product or service over a given period. A high retention rate indicates your company is successfully keeping its customers and generating recurring revenue.
Use this formula to calculate your net revenue retention rate:

Suppose your company has the following data for a given period.
- Starting MRR: $100,000
- Downgrade MRR: $5,000
- Churn MRR: $10,000
- Expansion MRR: $8,000
- Starting Capital: $1,000,000
Your Net Revenue Retention Rate = (($100,000 – $5,000 – $10,000 + $8,000) / $1,000,000) x 100
= ($93,000 / $1,000,000) x 100
= 9.3%
Expansion revenue
Expansion revenue measures the additional revenue generated from existing customers through upsells, cross-sells, or upgrades. Identifying opportunities for expansion revenue is essential for maximizing the value of existing customers.
To calculate your expansion MRR rate, subtract the expansion MRR at the beginning of the month from your expansion MRR at the end. Divide the result by the previous revenue and multiply by 100.

Imagine your company has the following data:
- Expansion MRR at the beginning of the month: $20,000
- Expansion MRR at the end of the month: $30,000
- Previous period revenue: $150,000
Your Expansion MRR rate = (($30,000 – $20,000) / $150,000) x 100
= ($10,000 / $150,000) x 100
= 6.67%
How to track revenue growth rate with Userpilot
Userpilot is a product growth platform that comes with ready-made analytics dashboards and in-app experience builders. It allows product teams to monitor product performance, take steps to increase product engagement, and improve retention – all without knowing how to code.
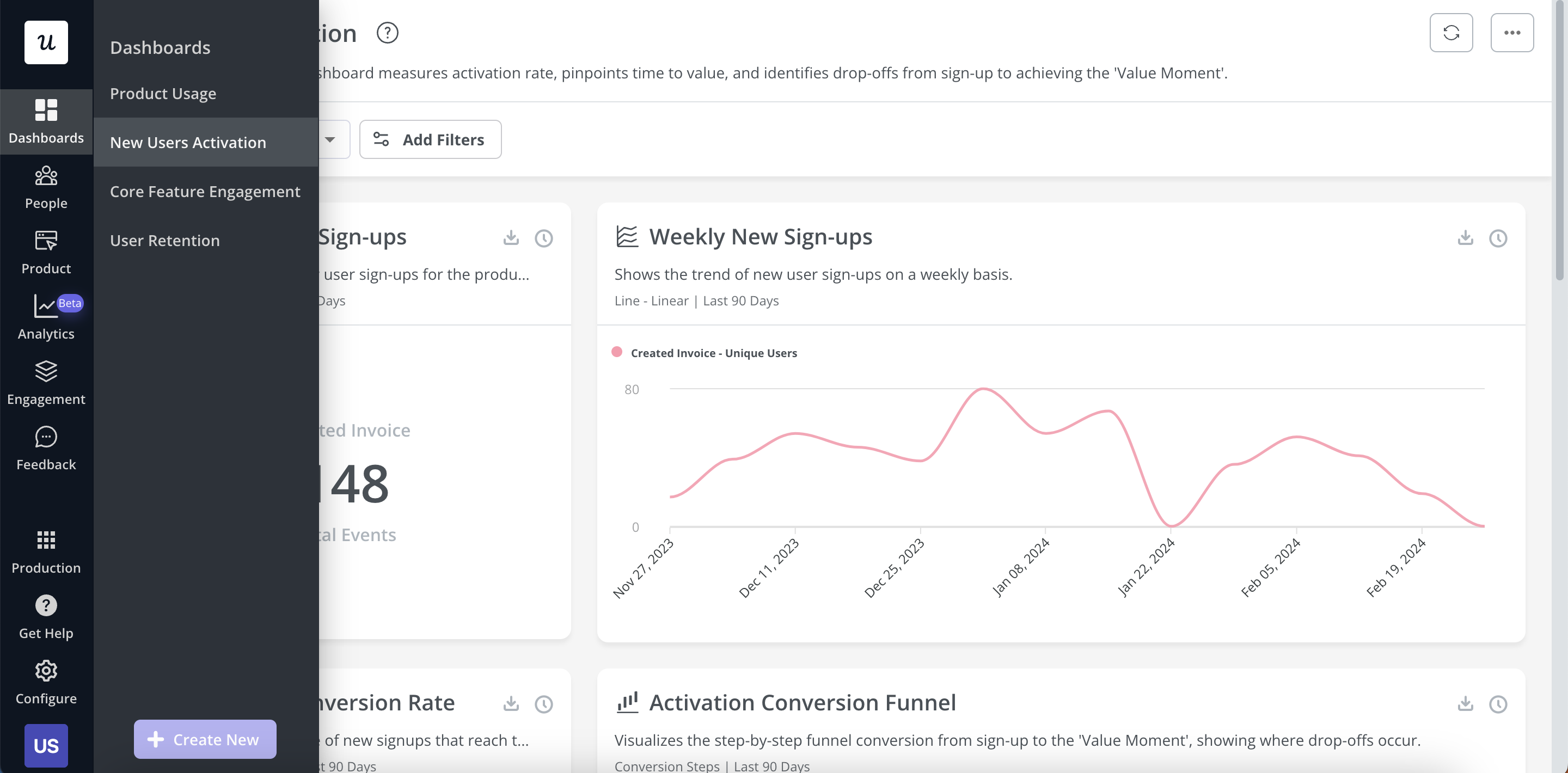
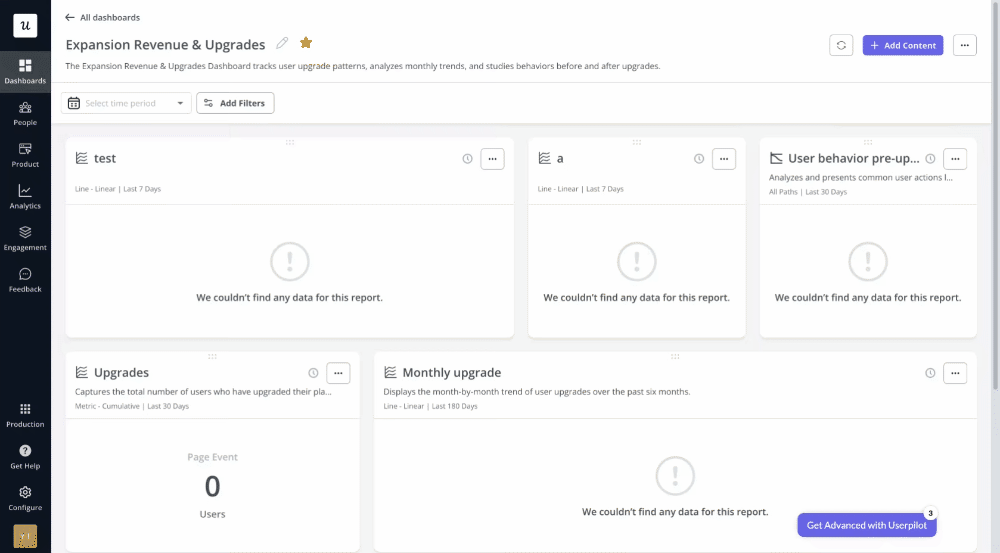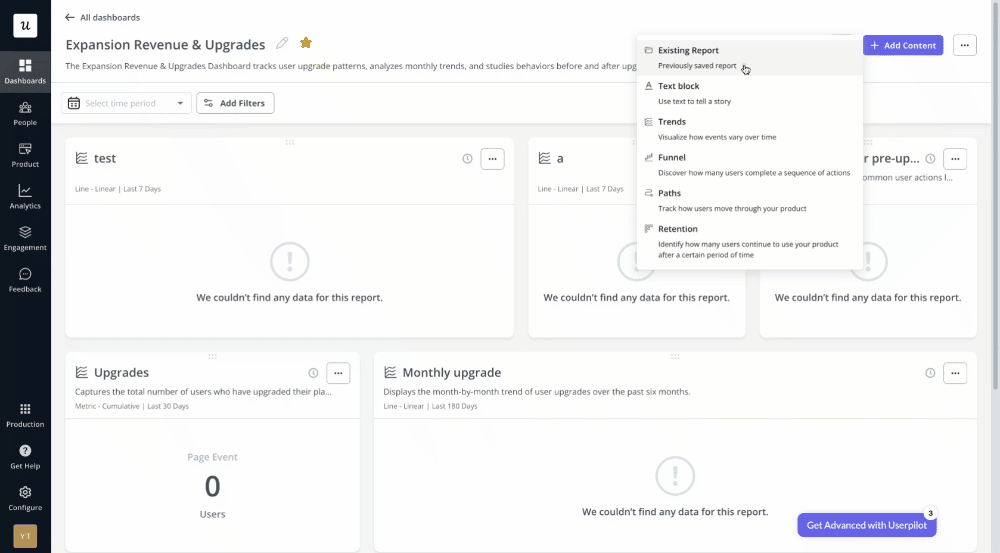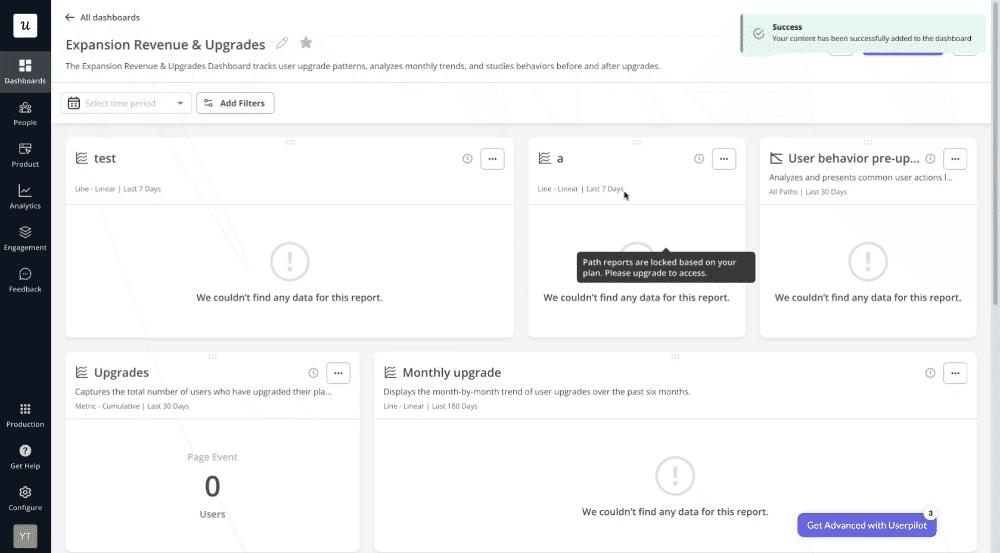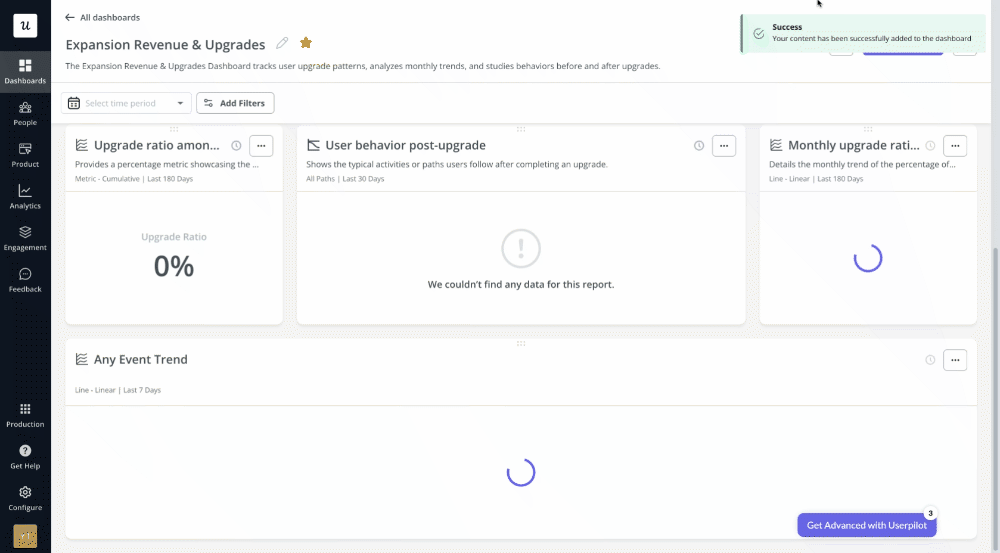
With Userpilot, you can take advantage of the premade dashboards:
- Product usage dashboard
- New users’ activation dashboard
- Core feature engagement dashboard
- User retention dashboard
Types of analytics dashboards available in Userpilot currently.
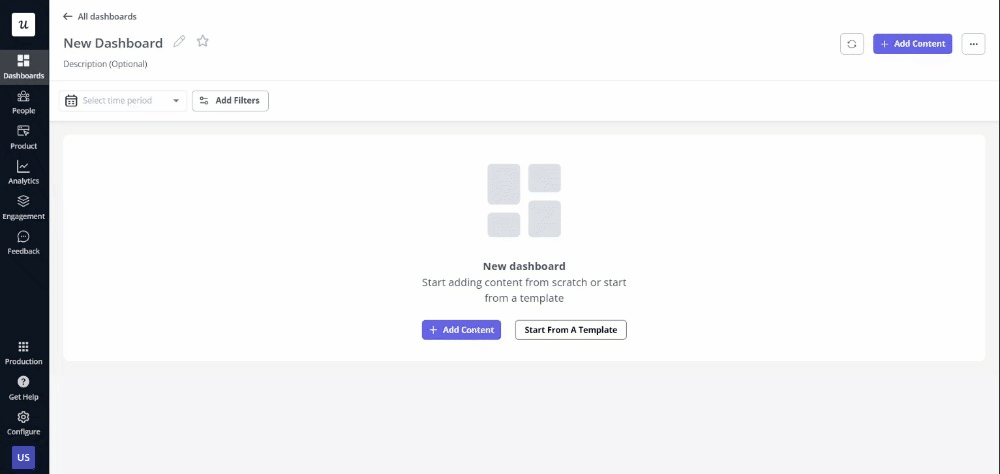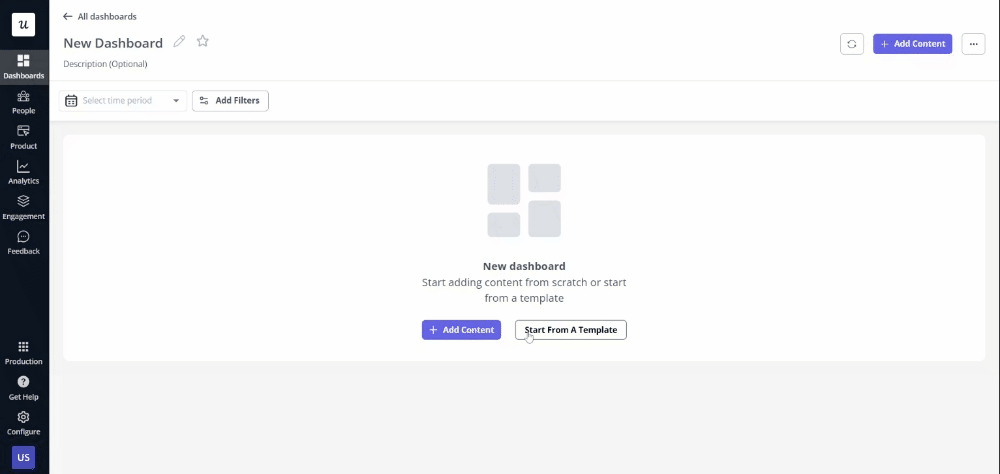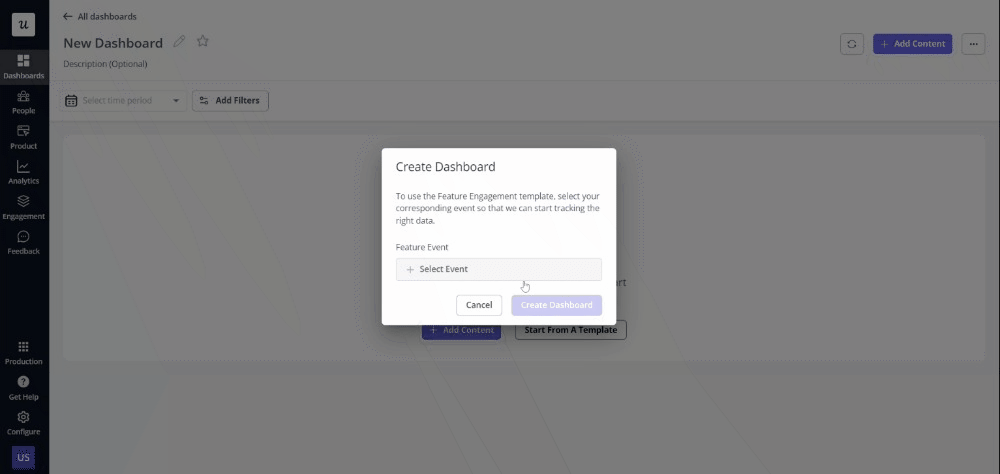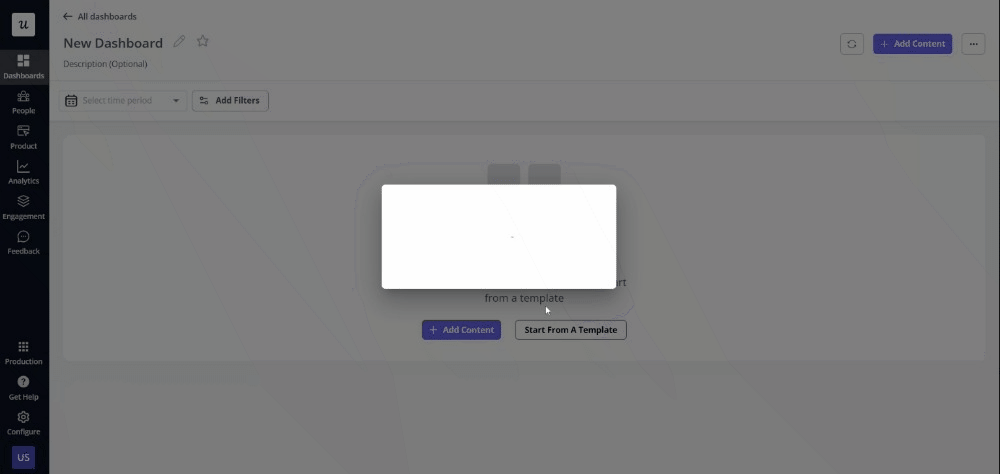
With Userpilot, you can create your analytical dashboards from scratch or use an existing template.
Create custom analytics dashboards with ease.
Achieve the perfect visual presentation with complete control over report placement, resizing, and order. You can also add context, insights, and layout descriptions using our new WYSIWYG text block integration.
Conclusion
To improve your revenue growth rate, start with your current users. Dig into their in-app behaviors and product usage patterns to see how you can prompt account expansion and boost ARPU. From there, you can look into devising user acquisition and retention strategies.
Userpilot can help you do all these. Our product growth platform has the robust features you need to speed up revenue growth rate through adoption, engagement, retention, and account expansion. Book a demo now to discuss your needs with our team.





![9 Practical Strategies to Reduce App Churn [+ How to Measure Churn Rate] cover](https://blog-static.userpilot.com/blog/wp-content/uploads/2025/06/9-practical-strategies-to-reduce-app-churn-how-to-measure-churn-rate_87f6e28e73dfeceea8751264731d1406_2000-1024x670.jpg)


