Try Userpilot Now
See Why 1,000+ Teams Choose Userpilot
What is a product designer?
A product designer is a professional responsible for creating user-friendly and visually appealing designs for products, particularly in digital applications like software and websites.
They focus on the overall user experience (UX) and user interface (UI), ensuring that the product is both functional and aesthetically pleasing.
Product designers collaborate with cross-functional teams, including product managers, developers, and stakeholders, to align design goals with business objectives.
Key tasks include conducting user research, developing wireframes and prototypes, and iterating on designs based on user feedback and testing.
As a product designer, what’s your biggest user onboarding challenge?
How do you currently measure feature adoption?
What’s your primary method for gathering user feedback for your product design?
It looks like you’re focused on building better product experiences.
Userpilot can help you improve user activation, boost feature adoption, and gather contextual feedback—without writing any code. See how top product designers are creating product experiences that users love.
What does a product designer do?
A product designer is responsible for creating intuitive and visually appealing digital product experiences.
They conduct user research to understand needs and pain points, develop wireframes and prototypes, and test these designs to gather feedback. Working closely with product managers and developers, they ensure that the final design aligns with both user requirements and business objectives.
By focusing on user experience (UX) and user interface (UI) design, they aim to deliver products that are not only functional but also enjoyable to use.
Product designer’s main responsibilities
A product designer plays a vital role in the SaaS industry, focusing on creating user-friendly and visually appealing software products.
They collaborate with cross-functional teams to ensure the design meets user needs and business objectives.
Here are the main responsibilities and duties:
- Conduct User Research: Gather insights on user needs, behaviors, and pain points through surveys, interviews, and usability testing.
- Create Wireframes and Prototypes: Develop wireframes, mockups, and interactive prototypes to visualize design solutions and iterate based on feedback.
- Design User Interfaces: Craft intuitive and visually appealing user interfaces for web and mobile applications, ensuring a seamless user experience.
- Collaborate with Cross-Functional Teams: Work closely with product managers, developers, and other stakeholders to define and implement innovative design solutions that align with product goals.
- Maintain Design Systems: Create and manage design systems and component libraries to ensure consistency and efficiency across all products.
- Conduct Usability Testing: Test designs with users to gather feedback and make necessary adjustments to improve usability and user satisfaction.
- Stay Updated with Design Trends: Keep abreast of the latest design trends, tools, and technologies to ensure the products are modern and competitive.
- Advocate for User-Centric Design: Promote user-centered design principles and best practices within the organization to ensure all products meet high usability standards.
- Iterate on Designs: Continuously refine and improve designs based on user feedback, analytics, and changing business requirements.
- Document Design Processes: Maintain clear documentation of design processes, decisions, and guidelines to ensure transparency and consistency.
These responsibilities ensure that a product designer effectively contributes to creating exceptional SaaS products that meet both user needs and business goals.
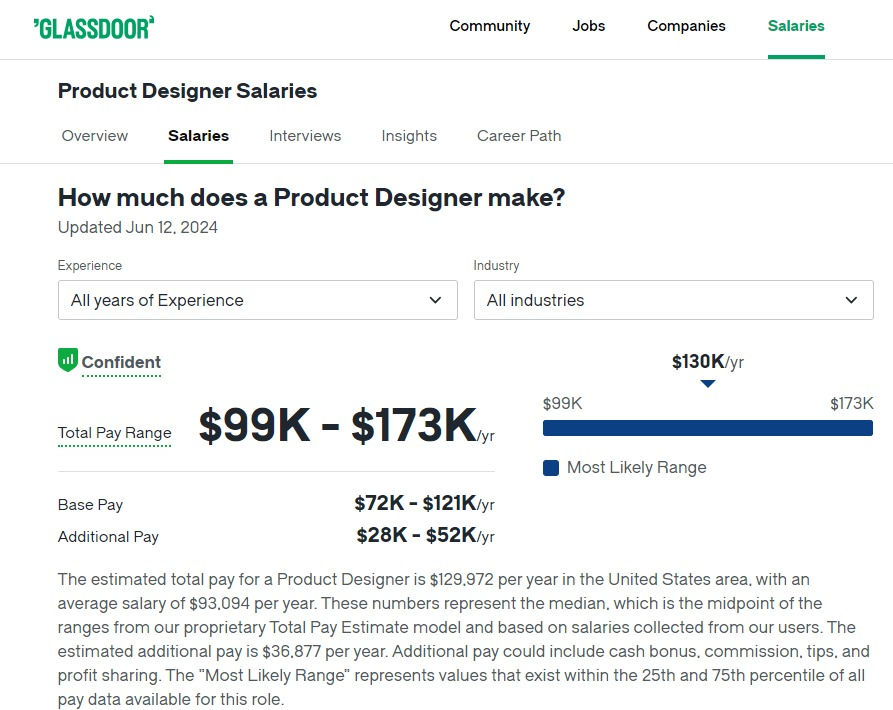
Product designer salary
Product designers play a crucial role in creating user-friendly and visually appealing digital products.
Their salaries vary based on experience, industry, and location, with certain companies offering higher compensation.
Salary by Experience Level
- Junior Product Designer: Typically earns around $72,277 per year.
- Mid-level Product Designer: The average salary is approximately $98,676 per year.
- Senior Product Designer: Generally earns about $129,579 per year.
Salary by Industry
- Technology: Product designers in the tech industry can earn between $90,000 and $140,000 per year, depending on the company’s size and location.
- Finance: Product designers in financial technology (FinTech) often see salaries ranging from $80,000 to $130,000 annually.
- Healthcare: Salaries typically range from $75,000 to $125,000 per year in the healthcare industry.
- Retail: Product designers in the retail sector might earn between $70,000 and $110,000 annually.
Salary by Location
- San Francisco, CA: Average salaries range from $81,000 to $200,000 per year.
- New York, NY: Salaries typically range from $64,000 to $168,000 per year.
- Seattle, WA: Product designers earn between $68,000 and $157,000 annually.
- Toronto, Canada: Salaries range from CA$51,000 to CA$108,000 per year.
- London, UK: Average salaries range from £23,000 to £93,000 annually.
Highest Paying Companies
- Meta (Facebook): Known for offering high salaries, with product designers earning between $150,000 and $250,000 annually.
- Stripe: Provides competitive compensation, often ranging from $140,000 to $230,000 per year.
- Pinterest: Product designers at Pinterest can earn between $130,000 and $220,000 annually.
- LinkedIn: Offers salaries typically ranging from $120,000 to $210,000 per year.
These figures highlight the significant variation in salaries based on experience, industry, and location, providing a comprehensive overview for aspiring and current product designers.
For more detailed and updated information, visiting specific salary websites like Glassdoor and PayScale is recommended.
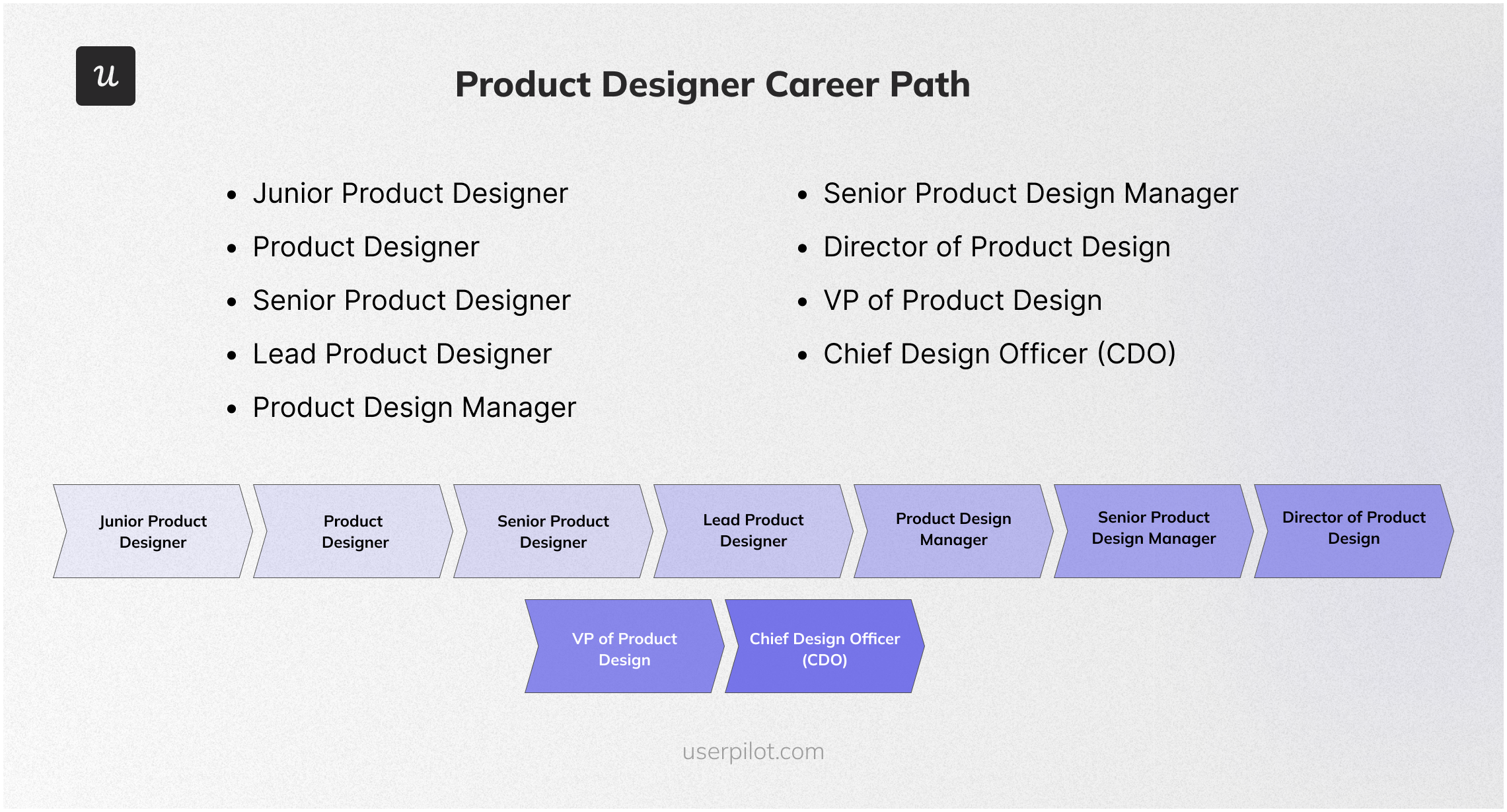
Product designer career path
A career in product design typically involves progressing through various roles that build on each other in terms of responsibility, expertise, and leadership.
Here’s a typical career progression for a product designer, from junior roles to senior leadership positions:
- Junior Product Designer – Assists senior designers, creates basic design components, and supports user research. Focus on learning design tools, building a strong portfolio, and seeking feedback to improve your skills.
- Product Designer – Involved in designing product interfaces, conducting usability tests, and collaborating with cross-functional teams. Take on more complex projects, deepen your understanding of UX principles, and start leading smaller design initiatives.
- Senior Product Designer – Leads major design projects, mentors junior designers, and plays a key role in strategic design decisions. Enhance leadership skills, contribute to design systems, and build strong relationships with product managers and developers.
- Lead Product Designer – Oversees the design team, ensures design consistency across projects, and aligns design goals with business objectives. Develop project management skills, drive innovation within the team, and engage in high-level strategic planning.
- Product Design Manager – Manages the design team, coordinates design projects, and ensures alignment with business goals and user needs. Enhance leadership and managerial skills, stay updated with industry trends, and focus on optimizing team performance and design processes.
- Senior Product Design Manager – Manages larger design teams, oversees multiple projects, and plays a critical role in company-wide design strategy. Develop a vision for the design department, influence company design culture, and mentor upcoming leaders within the team.
- Director of Product Design – Sets the overall design direction for the company, collaborates with top executives, and ensures the design vision aligns with the company’s mission. Focus on strategic leadership, expand your influence across departments, and drive the company’s design innovation.
- VP of Product Design – Responsible for the entire design organization, driving design excellence and contributing to the overall business strategy. Strengthen executive leadership skills, maintain a forward-thinking design vision, and foster a culture of creativity and innovation.
- Chief Design Officer (CDO) – Top-level executive overseeing all design aspects of the company, ensuring cohesive design strategy across all products and services. Focus on visionary leadership, drive company-wide design integration, and champion design as a core business value.
Each step in this career path builds on the previous one, emphasizing continuous learning, leadership, and strategic thinking to progress to higher levels of responsibility and influence in the field of product design.
Best practices for being a great product designer
To excel as a product designer, adopting key practices can significantly enhance your design process and the quality of your work.
- Empathize with Users: Invest time in understanding the users’ needs, behaviors, and pain points. Conducting thorough user research and usability testing ensures that your designs are user-centric and solve real problems effectively.
- Collaborate Effectively: Foster strong collaboration with cross-functional teams, including product managers, developers, and stakeholders. Open communication ensures that design goals align with business objectives and technical constraints, resulting in cohesive and successful products.
- Iterate Based on Feedback: Embrace an iterative design process. Regularly test your designs with users, gather feedback, and make necessary improvements. This approach helps in refining the user experience and achieving optimal design solutions.
- Stay Updated with Trends: Keep abreast of the latest design trends, tools, and technologies. Continuous learning allows you to bring fresh ideas and innovative solutions to your projects, keeping your designs modern and competitive.
- Develop Strong Communication Skills: Clearly articulate your design concepts, decisions, and rationale to team members and stakeholders. Effective communication fosters better understanding, alignment, and collaboration, leading to more successful design outcomes.
- Focus on Accessibility: Ensure that your designs are accessible to all users, including those with disabilities. Incorporate accessibility guidelines and best practices to create inclusive products that provide a good user experience for everyone.
- Maintain Consistency: Create and adhere to design systems and style guides. Consistency in design elements such as typography, colors, and layouts helps in building a cohesive and professional product experience.
By integrating these best practices into your daily workflow, you can enhance your effectiveness as a product designer and contribute to creating exceptional user experiences.
Product designer FAQs
- Is product design the same as UX design? Product design encompasses UX design but also includes other aspects such as UI design, interaction design, and even some elements of product strategy and development. While UX design focuses specifically on the user’s experience and interaction with the product, product design takes a more holistic approach, covering the overall look, feel, and functionality of the product.
- Is product designer a good career? Yes, product design is a rewarding career that offers opportunities for creativity, innovation, and impact. Product designers are in high demand, especially in tech industries, and they play a crucial role in creating user-friendly and aesthetically pleasing products that meet business goals. The field offers competitive salaries and opportunities for growth and advancement.
- Does product design require coding? While coding is not a primary requirement for product designers, having a basic understanding of coding can be beneficial. Knowledge of HTML, CSS, and JavaScript can help designers better communicate with developers, understand technical constraints, and create more feasible and efficient designs.
- Who earns more, UX or product designer? Salaries for UX designers and product designers can vary depending on the company, location, and level of experience. Generally, product designers tend to earn slightly more than UX designers because their role often encompasses a broader range of responsibilities, including both UX and UI design, as well as some aspects of product strategy.
- Can I be a product designer without a degree? Yes, it is possible to become a product designer without a degree. Many successful product designers have built their careers through self-study, online courses, boot camps, and practical experience. A strong portfolio showcasing your design skills and creativity is often more important than formal education in this field.
Conclusion
We hope this guide has provided you with valuable insights into the roles, responsibilities, and rewards associated with this role.
Looking into tools for product designers? Userpilot is an all-in-one product platform with engagement features and powerful analytics capabilities. Book a demo to see it in action!