Understanding your customers isn’t just a nice-to-have—it’s a must if you want to drive product growth and retention. But too often, customer analysis ends up being a pile of disconnected data points rather than a clear roadmap for action.
To help you get better at it, in this guide, we’ll share our tried-and-true six-step process for conducting an actionable customer analysis—one that helps you make informed decisions and improve your product.
Try Userpilot Now
See Why 1,000+ Teams Choose Userpilot
What is customer analysis?
Customer analysis is the process of understanding your customers. It involves collecting quantitative and qualitative data to understand different aspects of your audience, including:
- Customer preferences.
- Their needs.
- Pressing pain points.
- Objectives and goals.
- Jobs-to-be-done (JTBDs).
The goal is to design your communications, marketing campaigns, and product strategies around your customers to make their experience with your product more enjoyable.
Why is customer analysis important?
You might think your product is the best in the world, but without tapping into your customer’s real experience, you’re just playing a guessing game.
Customer analysis is the only door available for this, and it’s essential for leading a business in the right direction. For example, customer analysis:
- Removes guesswork from decision-making: Instead of relying on gut feelings, customer analysis gives you real data to guide your choices.
- Helps prioritize the right features: Understanding customer needs ensures you focus on what truly matters, not just what seems important.
- Optimizes messaging and positioning: Knowing who your customers are and what they care about allows you to craft more effective marketing and sales strategies.
- Identifies friction points: Pinpoints where customers struggle in their journey, so you can improve the experience and increase conversions.
How to conduct customer analysis in 6 steps?
That said, here’s our process for conducting a customer analysis that not only focuses on the right data but also leads to more action:
1. Define a clear objective
The worst approach to a customer analysis is to take the data at face value. You can’t just assume you’re going to find valuable insights without any explicit intention.
So if you want to extract value from it, you first need to determine exactly what you want to achieve with your research. Are you building a new product? Tapping into a new market? Or just achieving product-market fit with your product?
How you approach this will depend on the context of your analysis, for example:
- If you’re making an analysis for stakeholders or clients, set up a discovery session to define its exact goal. This allows you to make event definitions clear, determine relevant metrics, and clarify areas of ambiguity in the analysis.
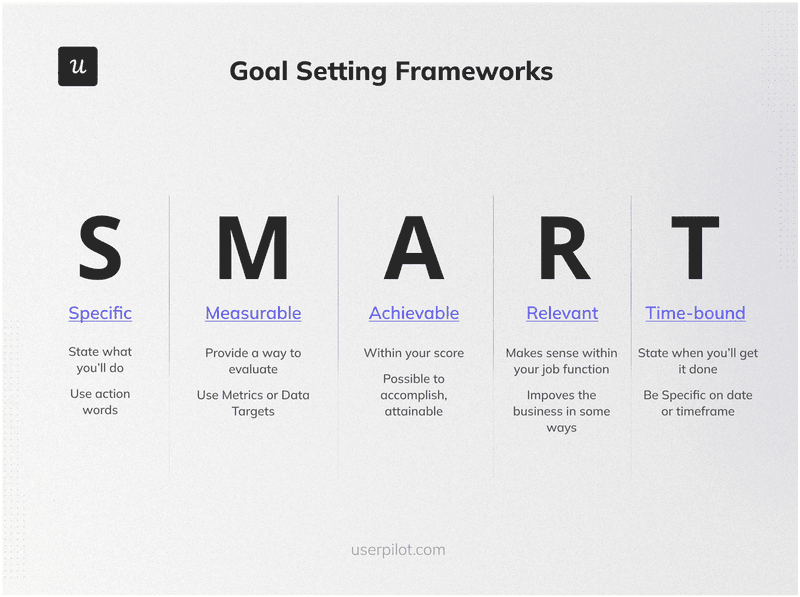
- If you’re leading the design of a product, then goal-setting frameworks such as SMART or OKRs might also be useful as templates too. The point here is to have well-defined success criteria for your analysis.
- Also, if you’re only optimizing your current product, then trace back to your main KPI and guide your analysis to improve it. It could be product adoption, DAUs, revenue, etc.
Aiming too high will easily overwhelm you, so I recommend keeping this objective short and clear. For example, let’s say you’re developing a new feature that’s meant to be used by DevOps engineers. Then, your objective here could be to analyze this segment to learn about their current pain points, most impactful JTBDs, and their sentiment toward your product.
How well do you truly know your customers?
Customer analysis is the foundation of a successful product. Take this 4-step assessment to see if you’re leveraging the right data to drive engagement.
2. Break down your audience into distinct segments
Not every customer is made equal. That’s why you should first start creating the customer segments that you’re going to target your analysis on.
For this, trace back to your main objective and think of:
- Which data is relevant to my goal?
- What are the unique problems that these customers face?
- What data do I already have on this?
- Which dataset can I use to investigate those unique problems?
If you did the first step well, then this task is going to be pretty intuitive. For instance, if your goal is to increase free-to-paid conversion rates, then you know you have to segment freemium users before you can start analyzing them.
💡 Pro tip: For non-technical product managers, I highly recommend using an all-in-one tool like Userpilot. Not only because it doesn’t require coding, but because it will bring all the other tools you’ll need for this analysis (e.g., in-app surveys, behavior reports, autocaptured events, session replays, etc.).
3. Analyze customer behavior data to identify patterns
Once you know the segment you’re investigating, you can start exploring behavioral data to find:
- Patterns in their usage of your product.
- Recurrent events that correlate with churn or customer retention.
- Behaviors that repeatedly bring more results to users.
There are two methods you can follow for this:
a. Observe quantitative user data
When I mention quantitative data, I mean hard data that quantifies specific events that are (mostly) triggered by users.
It’s the best way to track user behavior and correlate recurrent actions with real problems. You need it to identify sources of churn, spot friction points, and define what the customer journey looks like in your product.
Now, there are too many methods for analyzing customer data, but our favorites are the analyses you can perform with Userpilot, including:
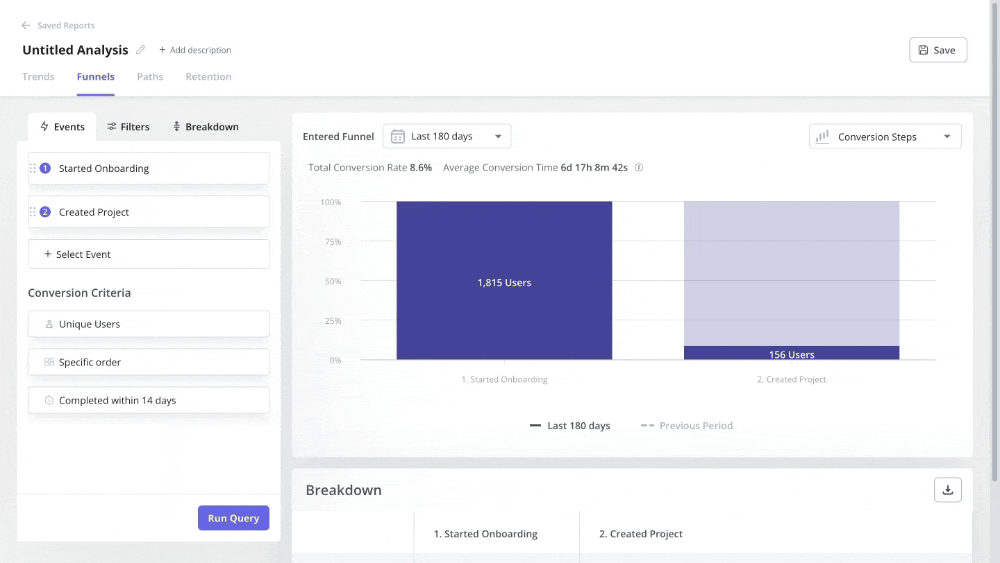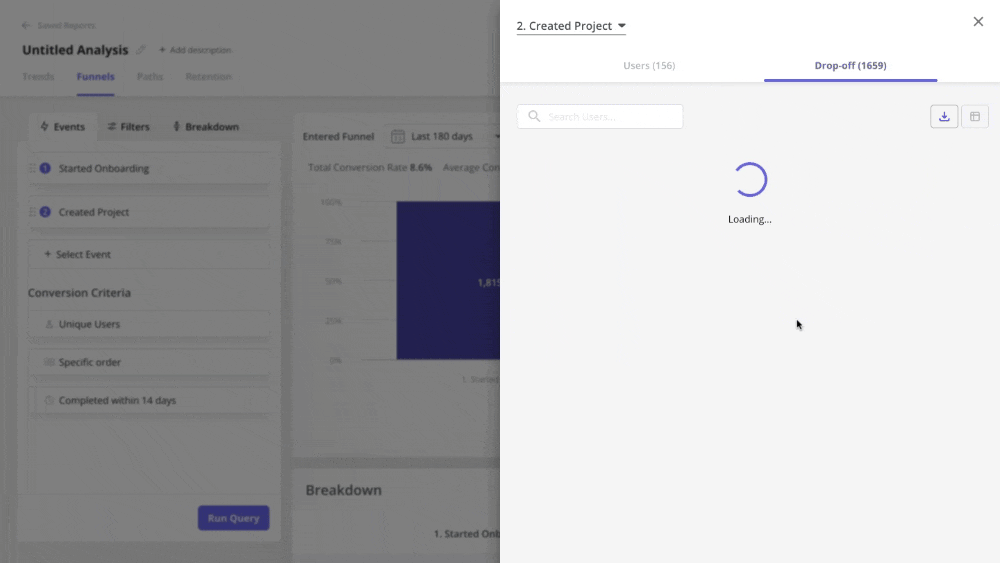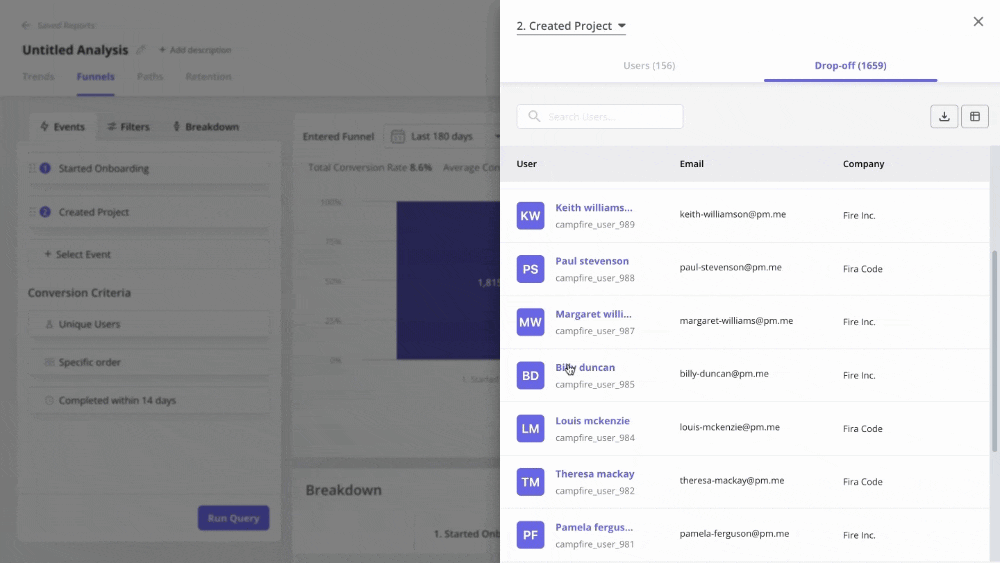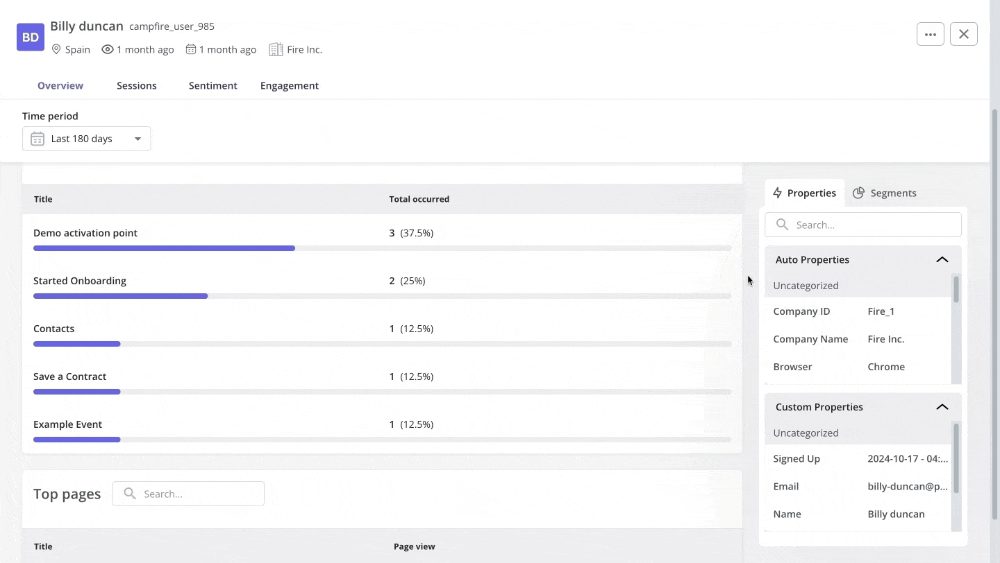
- Performing funnel analysis to observe how users navigate through their journey.
- Using path analysis to compare how different types of users navigate your product.
- Conducting cohort analysis to compare the in-app behavior of different groups of users.
- Analyzing trend reports to explore what behaviors are becoming more or less common.
b. Visualize customer behavior with session replays
Although behavioral data can effectively tell you what’s happening, it has difficulty showing you how.
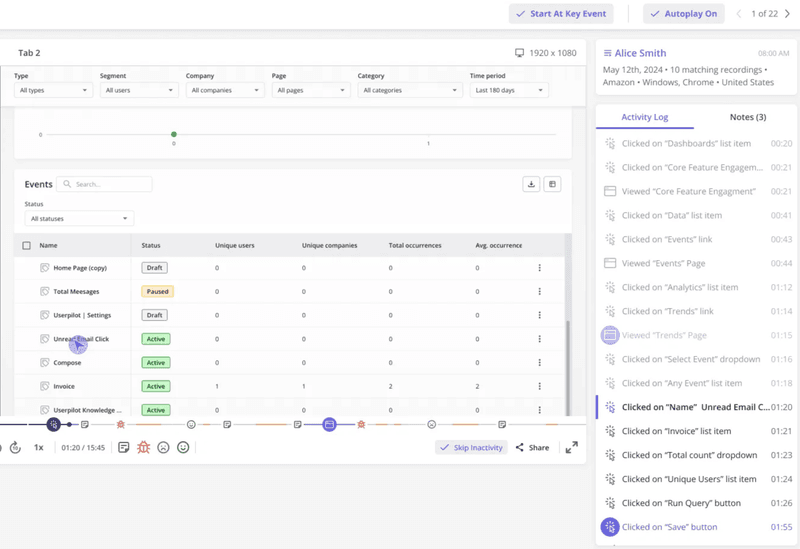
That’s where visual analytics methods like session recordings come in and add context to quantitative data. You can tell what elements are causing friction, or what interfaces are overly complicated.
By reconstricting interactions with real users, you can see where and why users hesitate, rage-click, or give up on the task, making it easier for you to promptly address them.
4. Supplement insights with qualitative feedback data
While behavioral data answers the what, qualitative feedback tells you the why.
And to do this, there’s simply no tool that can get to your customer’s brain. All you can do is ask them.
So with that said, here are three of the most essential ways to get qualitative data:
a. Trigger surveys with open-ended questions
Unlike other types of surveys, open-ended surveys create an opportunity to gather more detailed feedback at scale.
Their response rates tend to be lower because they take more time to answer, but considering how cheap it is to set them up, it’s hard to incur any loss from it.
For instance, if you’re investigating free trial users for a new feature, then you can use a customer feedback tool like Userpilot to automatically ask them if there’s a feature they wish your product had.
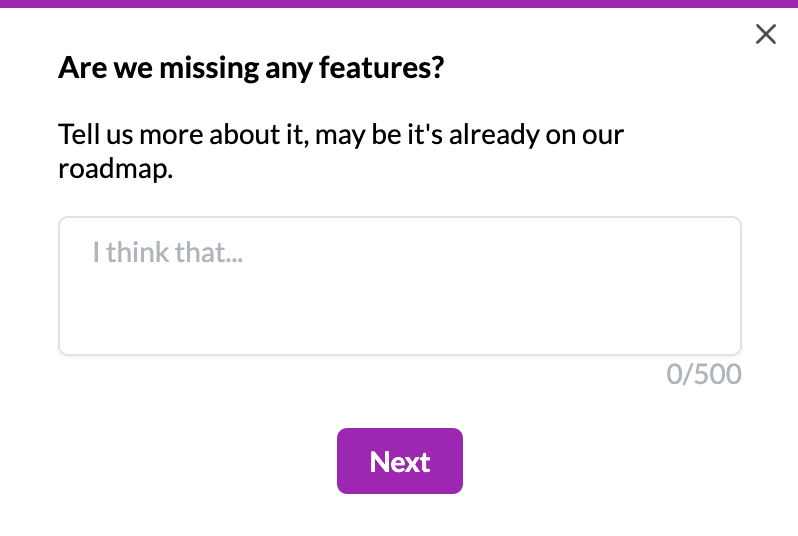
Userpilot lets you customize in-app mobile surveys with any type of question and trigger, helping you gather this valuable feedback directly from your mobile users.
b. Conduct 1-on-1 interviews and focus groups
If the insights you’re looking for are too specific, there won’t be another way to get it without interviewing your existing customers.
And although this is the most time-consuming method, it’s also the most fruitful. Nothing can beat the depth of insights you can get from having conversations with a customer (compared to just sending a single-question survey).
There are two ways to approach this:
- 1-on-1 interviews. Where you or your team host a meeting with a single customer to ask about their experiences with your product, their major obstacles, and potential opportunities for improvement. The insights here are more personal, and there’s a chance to tap into deeper customers’ emotions.
- Focus groups. Here you meet with a small group of target customers to talk about their thoughts, feelings, and experiences with your product. It must be a structured conversation, so you’ll need a moderator to guide the talk. You also get more ideas and perspectives here compared to 1-on-1 interviews.
c. Review customer support interactions
Customer support interactions can be a gold mine of customer data. It compiles pretty much all the possible problems your existing customer base may face and their possible causes.
This can include support tickets, chat logs, or email threads. With these, you can observe which categories receive the most tickets, identify the most recurrent issues, and come up with solutions to prevent them.
5. Prioritize customer needs based on impact and feasibility
After gathering a lot of data from customers, you’ll realize that most of it isn’t actionable. Many of the insights you get might be superficial or might represent problems that are not worth solving.
So the goal of this step is to prioritize issues with the most business impact, scrap information that doesn’t serve you right now, and slowly add the building blocks of a cleaner data environment.
For this, you must weigh the impact of each customer’s needs based on their value (the result you get from addressing it), effort (resources required to solve a problem), and risk (uncertainty around the effectiveness of the solution).
How you approach your prioritization system will depend on your business. But, there are some frameworks you can use as templates to get started, such as:
- RICE scoring. Where you weigh the value of an idea based on its reach, impact, confidence, and effort.
- Kano model. Which compares the priority of different ideas based on their potential to delight customers vs. their implementation costs.
Whether you follow a framework or not, the end goal is to make sure to separate the actionable insights from the least important information (what has a low impact on your business).
6. Put everything together in an actionable report
Now that you’ve gathered data and curated the most impactful insights, it’s time to pull everything together into a report.
Many people just add basic market research, like demographics, psychographics, and behavioral data. But I believe a report is more useful if you focus on the most actionable data points and their potential solutions.
This means getting creative and designing your report based on the objective you set in step one. Here are the basics you can start with:
- User persona. Define the basic characteristics of the segment you analyzed, then include their most relevant needs, pain points, and jobs-to-be-done. The goal is to make it easier for everyone in your team to get familiar with the target user.
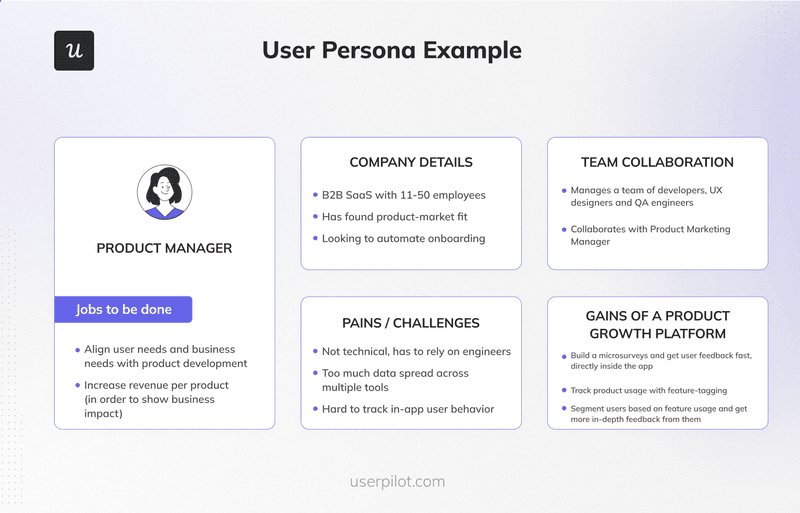
- A brief explanation of the problems. Along with the evidence you collected from the analysis (both quantitative and qualitative), and their potential impact on business KPIs (like revenue).
- Suggested solutions. Describe what the best solution is, its risks, and the metric you’re going to use to measure success.
So, rather than just compiling unrelated information, this structure gives a storytelling flavor to your report, making it easier to digest and receive buy-in from leadership if needed.
Empower your product strategy with customer analysis
Customer analysis is the foundation for building products that people love and stick around for. Without deeply understanding your customers, you’re just guessing—and guesswork won’t help your business grow.
Userpilot not only gives you the tools to collect valuable quantitative and qualitative data from your customers but also enables you to act on data. Book a demo, and we’ll show you how Userpilot can help you with customer analysis and data-driven decision-making.
FAQs about customer analysis
What are the three components of customer analysis?
In simpler terms, performing customer analysis can be dissected into three main components, including:
- Customer segmentation. A clear definition of the customers you’re analyzing.
- Quantitative data. Information about what your customers are doing.
- Qualitative data. Information on why your customers behave the way they do.
The rest of the elements in a customer data analysis are either branches of one of these (e.g. user monitoring) or serve as extra context to them.
What is the importance of customer analysis?
A customer analysis fills the gap between your customer and your business. Without it, your company would rely solely on assumptions and gut feelings during product development.
Some of the many reasons to conduct a customer analysis include:
- Being able to improve your product based on your users’ real obstacles.
- Finding potential causes of churn and coming up with strategies to prevent it.
- Designing your brand voice, marketing efforts, and messaging strategy according to your customers’ language.
- Building features that address users’ JTBDs and needs.
FAQ
What are the three components of customer analysis?
In simpler terms, performing customer analysis can be dissected into three main components, including:
- Customer segmentation. A clear definition of the customers you’re analyzing.
- Quantitative data. Information about what your customers are doing.
- Qualitative data. Information on why your customers behave the way they do.
The rest of the elements in a customer data analysis are either branches of one of these (e.g. user monitoring) or serve as extra context to them.
What is the importance of customer analysis?
A customer analysis fills the gap between your customer and your business. Without it, your company would rely solely on assumptions and gut feelings during product development.
Some of the many reasons to conduct a customer analysis include:
- Being able to improve your product based on your users’ real obstacles.
- Finding potential causes of churn and coming up with strategies to prevent it.
- Designing your brand voice, marketing efforts, and messaging strategy according to your customer’s language.
- Building features that address users’ JTBDs and needs.







