Looking for customer relationship management examples to inspire your brand? This article shows you eight CRM examples and lessons to learn from each. But that’s not all.
Toward the end of the article, we highlighted the types of CRM systems and different CRM tool examples that might be helpful to you.
After reading this article, you’ll see how good CRM initiatives help to cultivate healthy customer relationships that lead to higher engagement, loyalty, customer retention, and mouth-watering LTV. Feel free to read the whole piece or use the table of contents to find specific information.
What’s your biggest challenge with customer relationship management?
Customer relationship management examples summary
- 8 Customer relationship management examples:
- Tracking customer behavior
- Automated feedback collection
- Data-driven decisions
- Personalized customer experiences
- Automated customer service relationships
- Omnichannel service
- Strong social media presence
- Marketing automation
- The 3 types of customer relationship management (CRM) systems:
- Collaborative CRM system: Aligns business activities and facilitates collaboration between marketing efforts, customer support, and sales teams. Collaborative CRM systems also make it easy for different departments to share customer data, creating a holistic approach to customer relationship management.
- Operational CRM system uses automation and data management to streamline business operations, customer interactions, sales, and marketing processes in one place.
- Analytical CRM system: This is more technical and mainly focuses on using customer data to improve customer experience and customer interactions. Analytical CRM software analyzes raw user behavior data to reveal user preferences, preferred channels, touchpoints, trends, sales forecasting, etc.
The impact of customer relationship management on your business
A good CRM is not only about building but also sustaining good customer relationships. And the benefits are enormous.
Some benefits of CRM you stand to gain include:
- Improved user engagement: CRM involves studying user behavior and optimizing interactions to meet their needs. This will lead to an increase in user engagement.
- Improved customer experience (CX): Good customer relationship equals positive experiences. With a better customer experience, you’ll also be able to build customer loyalty.
- Higher customer satisfaction: Customer satisfaction happens when you consistently meet user expectations. Your exceptional service and continuous product improvement will make this possible.
- Better decision-making: Modern CRM platforms enable businesses to gather extensive data on each customer. You can segment customers based on this data and use it to make more informed business decisions. For instance, with a CRM system in place, sales teams would make quicker decisions regarding their leads.
8 Customer relationship management examples
There are multiple ways to study and interact with customers, each with unique advantages. Below are eight CRM examples to inspire you for better customer relationship management.
CRM example 1: Tracking customer behavior
Behavior tracking is a good CRM practice. It is key to understanding your customers and how they interact with your product. You’ll uncover valuable data on purchase intent, causes of friction, etc., to see what works and what doesn’t with your existing audience.
There are different ways to analyze customer behavior, depending on the data you want to gather. You could track on-site or in-app, measure engagement with a specific feature, track the behavior of a certain user group, etc.
With all this data at hand, you’ll be in a much better position to increase customer retention and end up with more loyal customers.
CRM example 2: Automated customer feedback collection
Customer feedback lets you know what users think and feel about your product.
Feedback is also a reliable way to eliminate guesswork and collect data that will enable you to make improvements customers will appreciate.
Implement surveys like CSAT or NPS to collect qualitative and quantitative feedback, then analyze the results to extract actionable insights regarding customer expectations and preferences.
For instance, you can automatically collect feedback from customers after their trial ends:
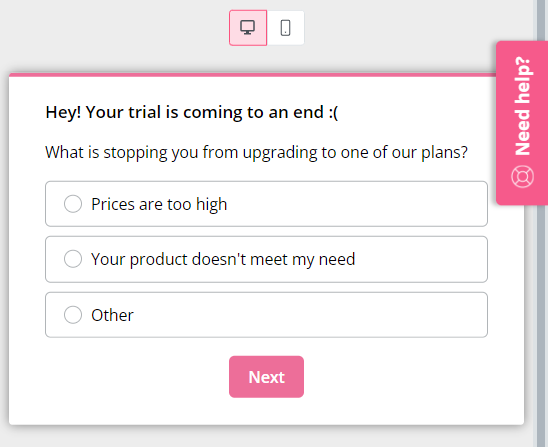
To streamline your customer relationship management efforts, use a feedback tool to automate the process of customer requests and collect feedback at scale.
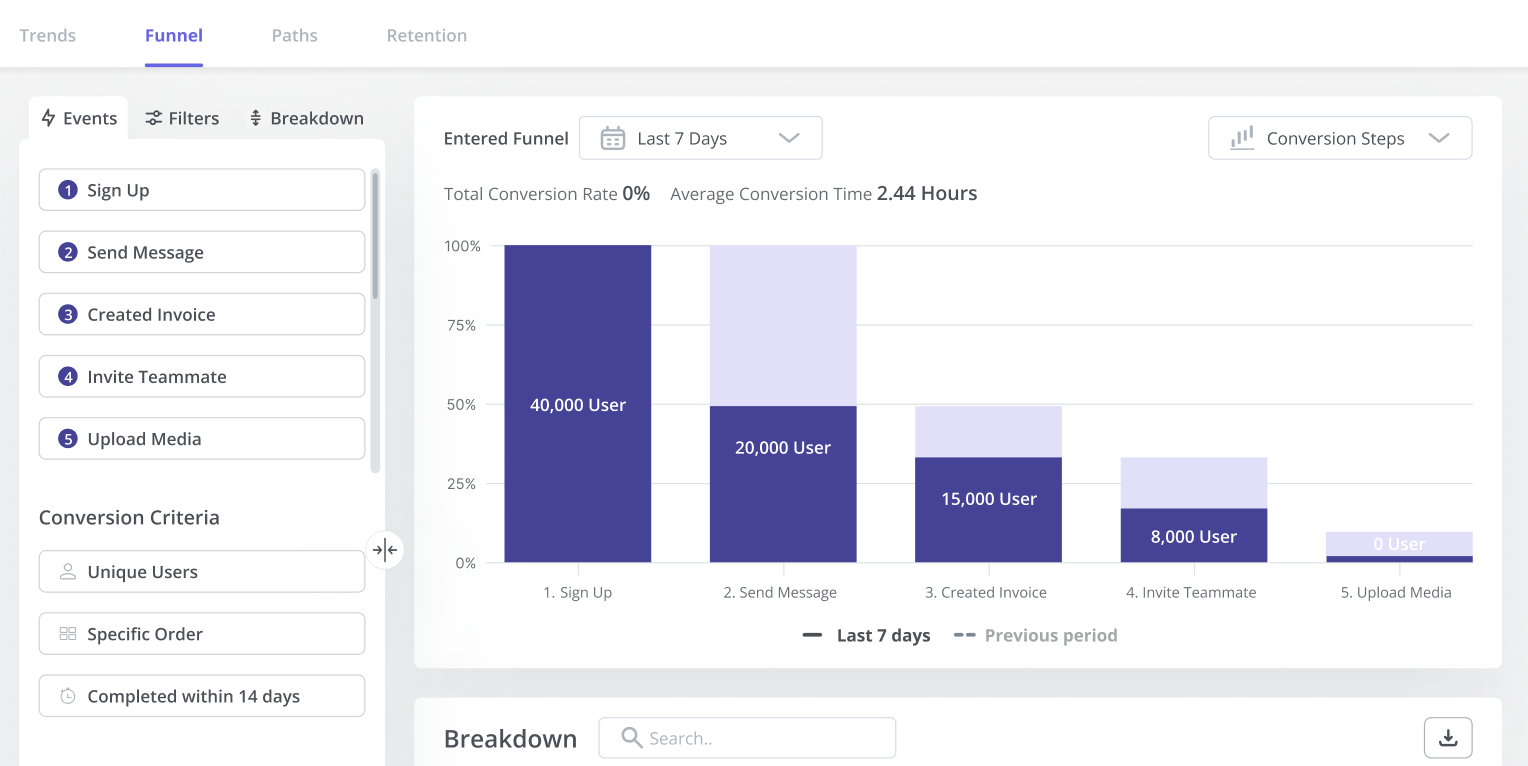
CRM example 3: Analyze customer interactions and make data-driven decisions
With enormous amounts of data widely available to businesses, it’s easier than ever to make sound decisions.
Customer data will help to spot trends, analyze performance, predict user behavior, and much more. These will allow you to get actionable business insights and make smarter decisions to build good customer relationships and drive business growth.
CRM example 4: Personalized customer experiences
This is one of the most important customer relationship management examples in SaaS. From reaching a prospect with a targeted marketing message to nurturing them through personalized support and closing a sale, your company should focus on delivering tailored interactions during different stages of the customer lifecycle.
Personalization makes customers feel seen and understood and helps improve customer satisfaction, leading to a strong bond between them and the company.
Begin your personalization of customer journey by segmenting users according to similar customer information, characteristics, or behavior.
A good example of this is HubSpot. When a company signs up for HubSpot, the platform tracks its interactions, such as which tools they use most (e.g., CRM, marketing automation, or sales tools), and how they engage with content on the HubSpot website or webinars. HubSpot then segments businesses based on industry, company size, and usage patterns.
For instance, if a small business frequently uses HubSpot’s CRM tool but has not explored the marketing automation tool, HubSpot might send a personalized email highlighting how marketing automation could benefit small teams. This email would include relevant case studies, tutorials, and pricing models suited to the business’s specific needs, creating a customized experience that encourages deeper product adoption and engagement.
This personalized approach helps HubSpot demonstrate value to each business, leading to higher customer satisfaction and long-term retention.
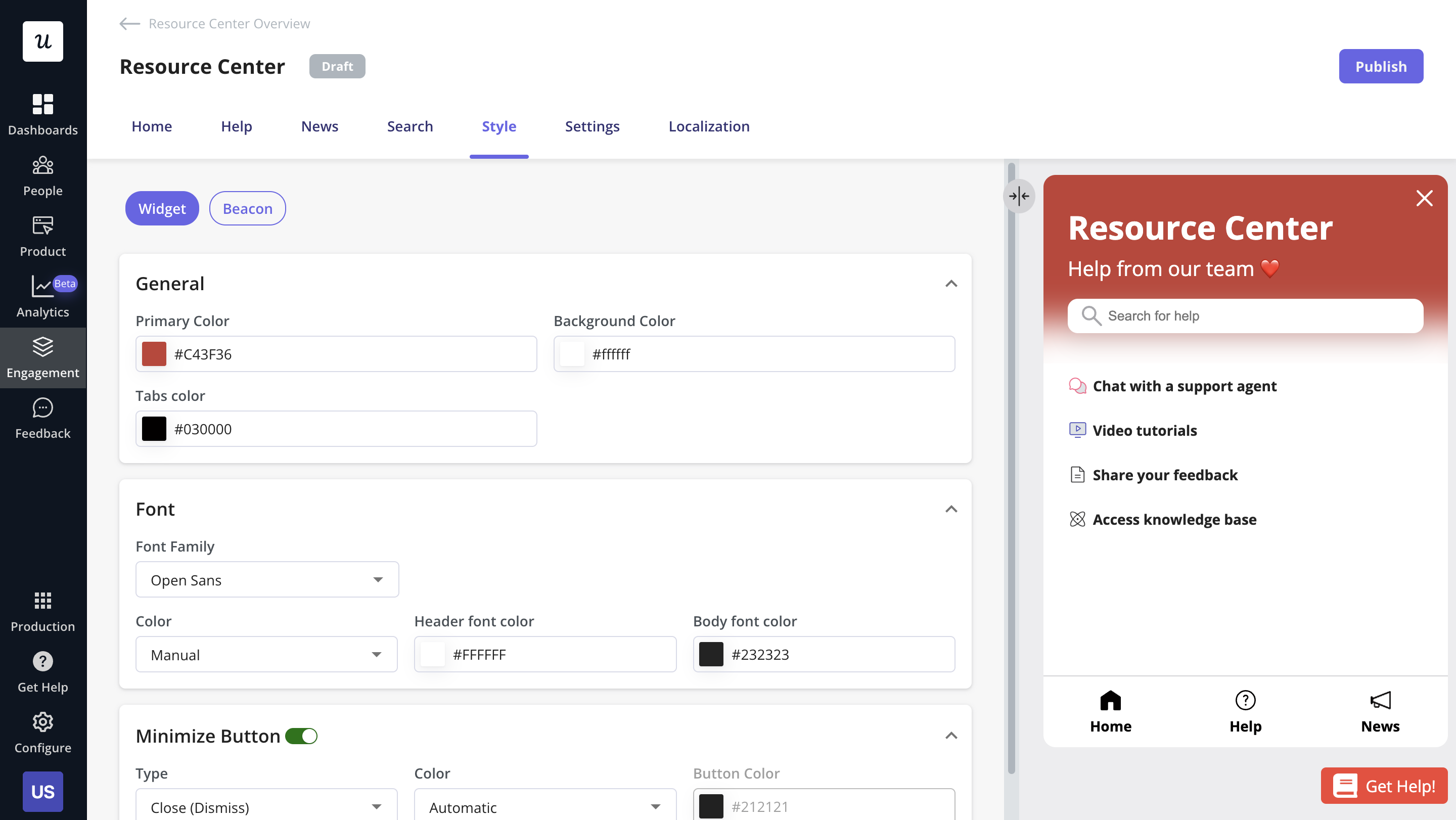
CRM example 5: Automated customer support
In simple terms, automating customer support is using technology to enhance your customer service.
Your support will be fast and available 24/7—which is what modern customers want.
Automated customer service doesn’t just make your users happy; it also reduces support costs since it means fewer human agents.
Chatbots are popular among SaaS companies that are big on CS automation, and it’s something you might want to consider for effective customer relationship management.
The image below illustrates how a chatbot uses prompts to solve user problems.

Aside from bots, self-service resource centers are another way to automate support. These are collections of helpful resources available to customers at all times to make sure they are never stranded.
CRM example 6: Omnichannel customer experience
Even if you’re super responsive, providing support on one channel only won’t cut it. Every user has a channel they prefer to use for communication. Asking them to switch to your preferred method will add friction to the user experience. So it’s best to be flexible by providing multiple communication channels.
Most SaaS businesses integrate web, in-app, social media, and email as their main communication channels. But choosing the right ones for you will depend on your audience. Test various channels and analyze user responses before deciding which ones to stick with.
Keep in mind that multichannel support doesn’t automatically make it omnichannel. Being omnichannel means your platforms are integrated, and the customer can switch from one to another seamlessly—that’s what you should aim for.
Also, consider customer touchpoints across the different user journey stages when designing your omnichannel customer experience strategy.
CRM example 7: Strong social media presence
We can’t discuss customer relationship management examples without mentioning social media—the 21st-century powerhouse of customer relationship building.
From connecting with long-lost friends to finding love, people use social media daily to build quality relationships.
Business isn’t left out; most people depend on social media for building profitable customer and client relationships now.
You can’t afford to be absent on social media. Utilize it to connect with customers, deliver product updates, listen to what people say about your brand, and so on.
Several B2B businesses with strong social media presence you can look up to are HubSpot, Salesforce, and Slack. They actively engage with their audiences on platforms like LinkedIn and Twitter through thought leadership, product updates, and customer success stories.

CRM example 8: Marketing automation
So far, we’ve only talked about support automation, but your customer relationship marketing efforts could also be automated to save time and increase efficiency. The right automation tools can help you create effective workflows and reduce repetitive tasks.
Common use cases for marketing automation include lead management, content planning and distribution, social media scheduling, etc.
Most marketing automation tools will also include analytics to help businesses keep track of campaign performance.
What are the 3 types of CRM systems?
There are essentially three types of customer relationship management systems, each with its own uniqueness.
Knowing the different types will help you decide on the right CRM tool, so let’s briefly go over them.
Collaborative CRM system
This CRM system aligns business activities and facilitates collaboration between marketing, customer support, and sales teams.
Collaborative CRM systems also make it easy for different departments to share customer data, creating a holistic approach to customer relationships. This function is useful to large teams, especially ones that are spread across multiple locations.
Additionally, collaborative CRM platforms track customer interactions and decide the best communication channels for each user.
Operational CRM system
The main goal of this system is to streamline business operations, customer interactions, sales, and marketing processes all in one place.
Operational CRMs are the most common because they are used when companies aim to understand and nurture users at every point in the customer lifecycle.
Analytical CRM system
This is more technical and mainly focuses on using customer data to improve the user experience. Analytical CRMs analyze raw user behavior data to reveal customer preferences, preferred channels, touchpoints, trends, sales forecasting, etc.
This CRM system is most useful to mid-size and large companies that need to analyze huge data volumes.
FAQ
What is customer relationship management?
Customer relationship management (CRM) refers to the strategies, processes, and technologies used to build and maintain relationships with customers.
The key to effective CRM and customer communication is tailoring your approach to the different stages of the customer lifecycle. Your users will feel valued, and you’ll increase your customer retention rates.
What are some examples of CRM?
Some examples of CRM tools include Salesforce, HubSpot, Zoho CRM, Pipedrive, and Freshsales. These tools help businesses manage customer relationships, sales, and support processes by providing features like contact management, lead tracking, and marketing automation.
What are the four types of customer relationship management?
The four main types of CRM are:
- Operational CRM: Focuses on automating sales, marketing, and service processes to streamline business operations (e.g., HubSpot).
- Analytical CRM: Analyzes customer data to provide actionable insights for better decision-making (e.g., Zoho Analytics).
- Collaborative CRM: Facilitates communication and collaboration between different teams and departments, ensuring a unified approach to customer service (e.g., Microsoft Dynamics 365).
- Strategic CRM: Focuses on long-term customer engagement and satisfaction, prioritizing customer-centric strategies.
What are the 5 models of CRM?
The five CRM models include:
- IDIC Model: Identify, Differentiate, Interact, and Customize. Focuses on personalizing customer interactions.
- QCI Model: Focuses on customer acquisition, retention, and optimizing customer lifetime value.
- CRM Value Chain Model: Emphasizes building customer value through relationships and supply chain optimization.
- Payne’s Five-Process Model: Focuses on building a comprehensive CRM strategy, covering customer acquisition, retention, and development.
- Gartner’s 8-Building Block Model: A more detailed model that focuses on leadership, strategy, and building a customer-centric culture within the business.
What is the CRM process with an example?
The CRM process involves identifying leads, nurturing relationships, converting prospects into customers, and maintaining long-term customer engagement.
For instance, a company using Salesforce might capture leads through web forms or social media integrations. These leads are then segmented and nurtured with personalized email campaigns using Salesforce’s marketing automation. When a lead is ready to purchase, the sales team uses Salesforce’s CRM to track the deal progress and close the sale. Post-purchase, Salesforce Service Cloud helps manage customer support tickets, while automated satisfaction surveys and loyalty programs keep customers engaged and encourage repeat business. This ensures a seamless experience from lead to loyal customers.
How to improve customer relationship management?
To improve customer relationship management, focus on personalizing interactions, leveraging CRM tools to automate processes, and using data-driven insights to better understand customer needs. Enhance communication through omnichannel support, actively gather and act on customer feedback, and continuously improve the customer journey to foster long-term loyalty and satisfaction.