Make Better Decisions with Actionable Product Analytics
Understand user behavior across the product journey with powerful custom reports, and answer every product question - without any coding.
Get a demo with one of our product specialists today
Join 1,000+ Companies Accelerating Product Growth With Userpilot.



Turn complex data into clear, actionable takeaways
Get real-time insights into user actions and product adoption data.

Funnel analysis
See where users drop off and optimize conversions
Spot bottlenecks and optimize onboarding and key flows to boost conversions.
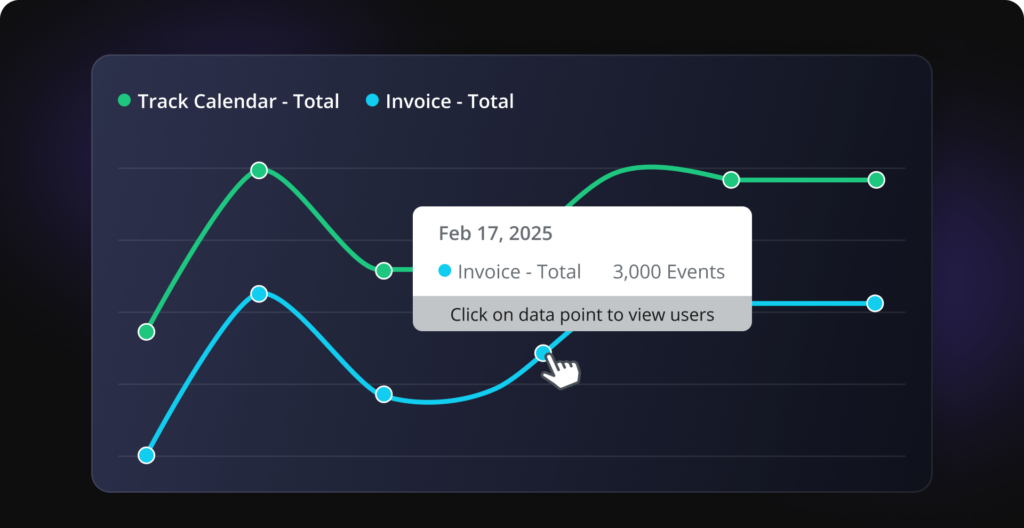
Trend analysis
Spot trends and predict user behavior
Track growth trends, feature spikes, and areas for improvement to make proactive decisions.

Path analysis
Understand how users navigate your product
See the exact paths users take, uncover popular features, and identify unexpected behaviors to enhance engagement.
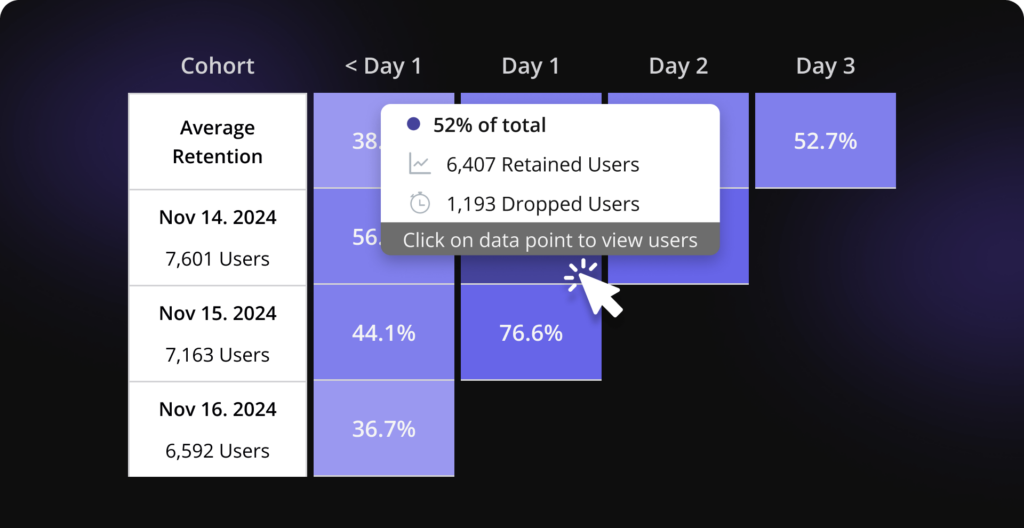
Retention (cohort) analysis
Track user retention and long-term engagement
Group users by behaviors and track how segments perform over time to improve retention and understand product stickiness.
Why choose Userpilot analytics?
See results from day one with data autocapture and event tagging
Track user data with a no-code solution
With autocapture and event-tagging, track user behavior instantly. No need to chase developers to track events!
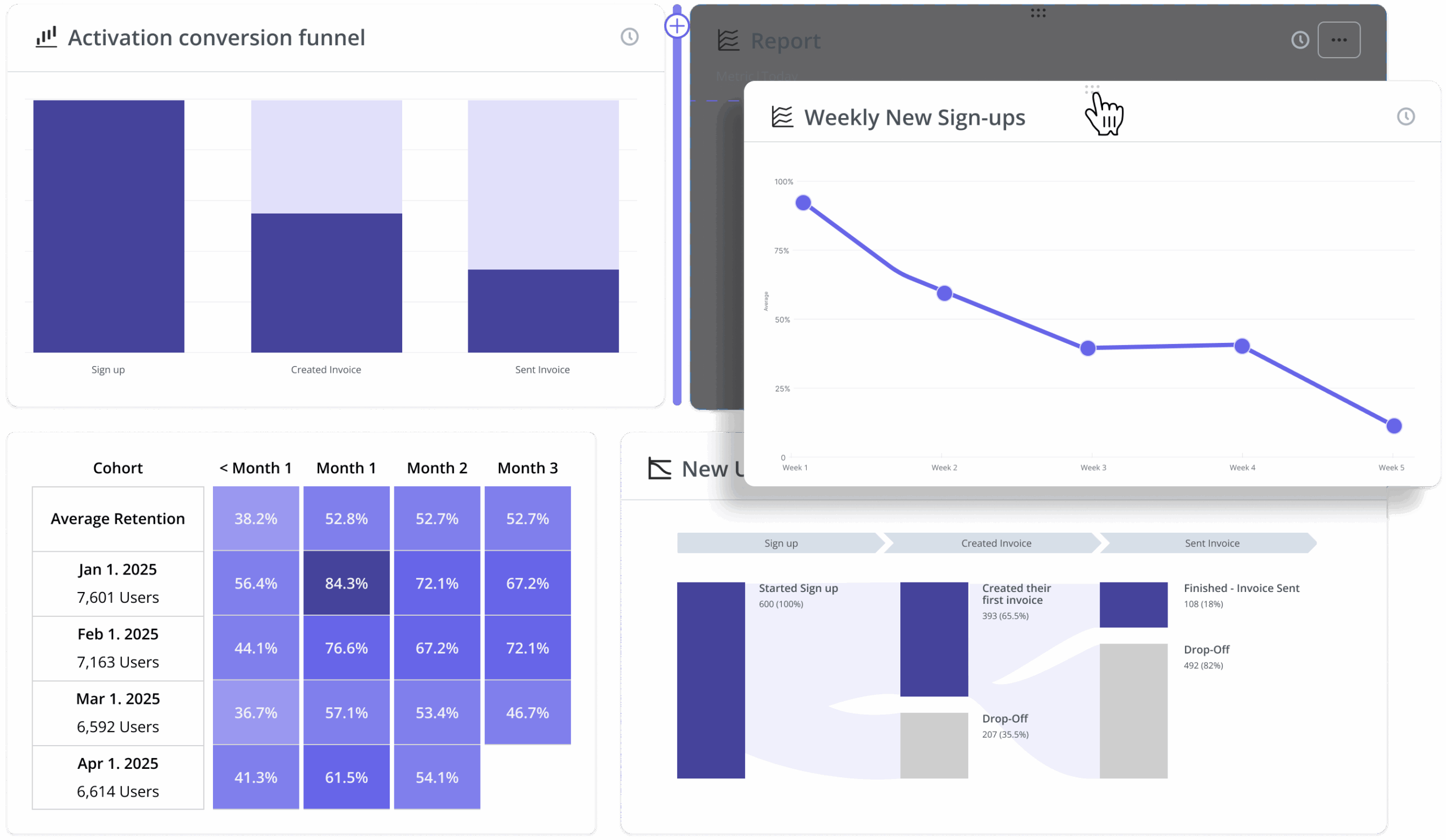
Stay on top of your metrics with custom analytics dashboards
Monitor key metrics at a glance
Use our pre-defined dashboards or build custom ones to track key metrics like product usage, activation, and feature adoption—all at a glance.
Best analytics tool I have ever worked with
It is the most useful analytics tool I have ever seen in software industry. It has many good features like survey forms, onboarding tools, funnels, integrations etc. and also it is very easy to use as it is beginner friendly.
Anandkumar P.
Information Technology and Services Company
Userpilot helps us uncover growth patterns
Userpilot helps us learn where to focus and understand what our users are doing. The most important thing is to track user behavior as they interact with our product, and link that back to upgrading from free to paid, and to retention, so that we can identify the patterns exhibited by our most valuable customers v. our least.
Sue M.
FeedXL Horse Nutrition Calculator
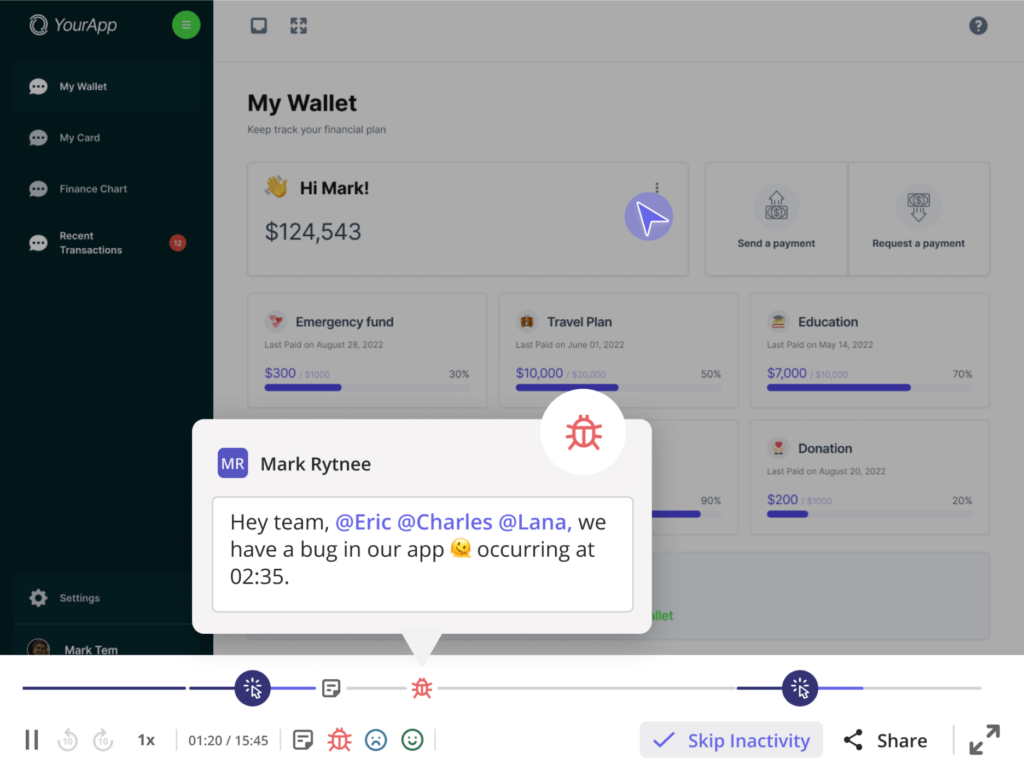
Go beyond the data—understand the 'why' with session replay
Replay user journeys for deeper insights
Session replays show exactly what users do in your product, giving you the full context to uncover frustrations and opportunities for improvement.
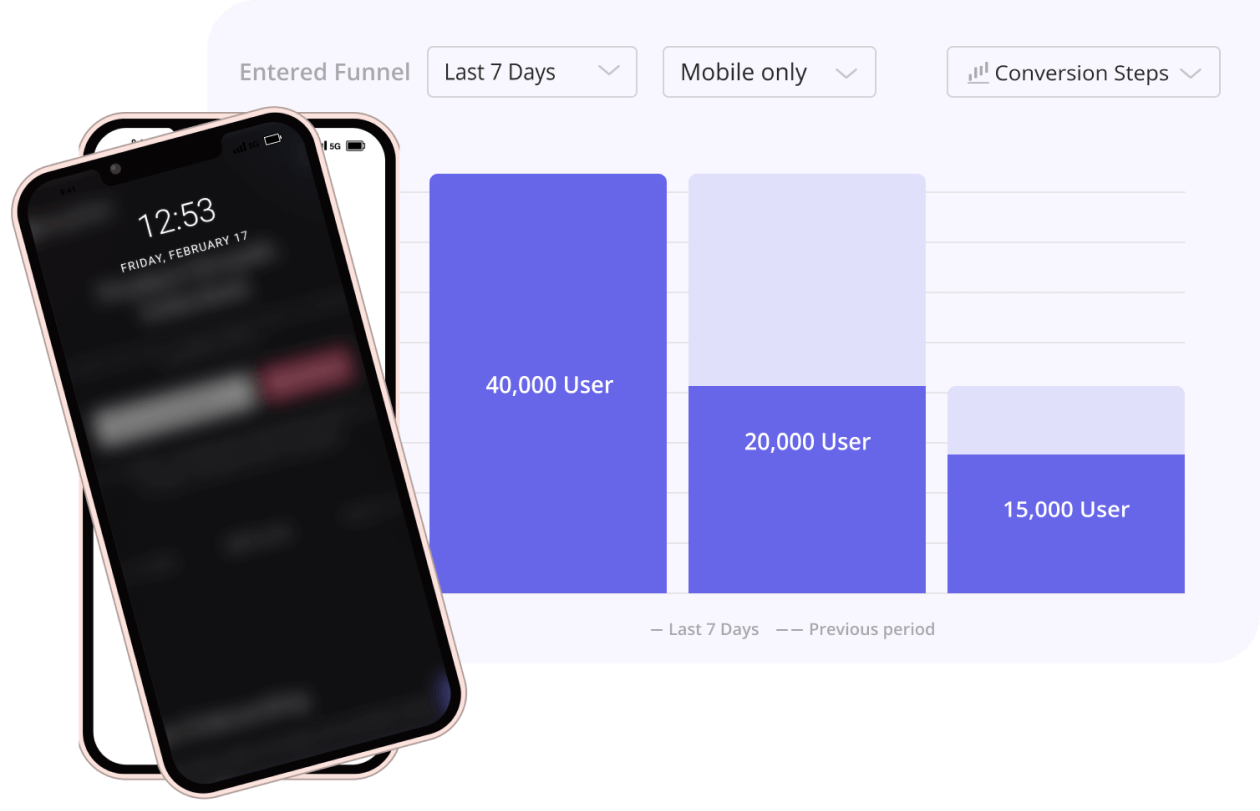
Unify data across mobile app and desktop for complete user insights
Get a holistic view of user behavior across platforms
Userpilot unifies mobile and desktop data, giving you a complete view of user behavior across platforms to make smarter, data-driven decisions.
Consolidate your data across platforms and tools
Get a holistic view of user behavior across platforms
Userpilot unifies mobile and desktop data, giving you a complete view of user behavior across platforms to make smarter, data-driven decisions.
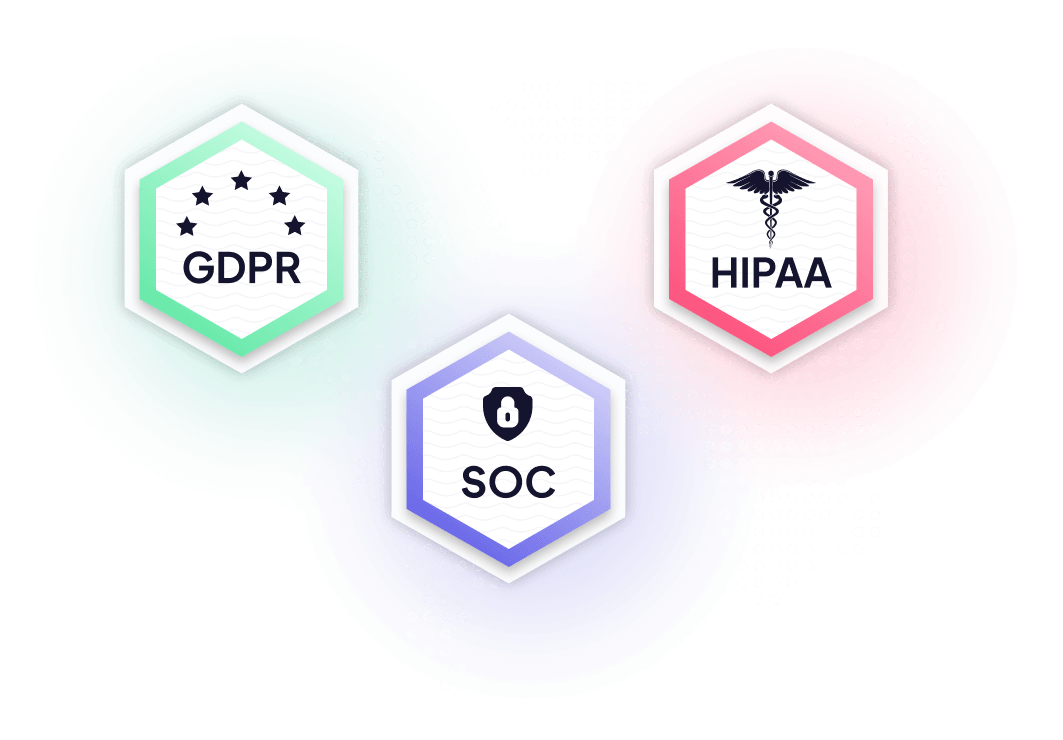
Security standards at Userpilot
As a vendor that processes millions of data points on a daily basis, we take our customers and their users’ data very seriously.
Our data is fully encrypted, managed, and stored by SOC-compliant vendors such as Amazon AWS and Google Cloud.
- SOC 2 Type II
- GDPR
- HIPAA
FAQ
3 major ways:
- All-in-one platform: Unlike other Product Analytics platforms, Userpilot is an all-in-one platform that combines product analytics with user onboarding and in-app surveys. This helps you reduce your tech stack, maintenance headaches, and costs.
- Event auto-capture: Your events are captured automatically, without any coding. You don’t need to chase your developers to track events!
- Priced by MAUs, not events: Your invoices are predictable and consistent as it’s easier to predict the number of Monthly Active Users (MAUs) than events. Not just that, our pricing is more affordable than most Product Analytics, especially when you consider the cost of purchasing onboarding and survey tools.
Because it’s far easier to predict the number of monthly active users (MAUs) than events per month. Your invoices remain fairly consistent and you pay less than other tools that charge by events.
Userpilot combines 3 tools: Product Analytics, User Onboarding, and In-app Surveys.
This means you not only track product analytics but also take action with that data, such as by running a survey for dropped-off users in the funnel or creating a better onboarding experience to improve retention.
Trends: Visualize the usage of your features over time
Funnels: Identify and reduce drop-offs within your product
Paths: Track user routes before or after any event
Retention: Track and improve the stickiness of your product
Dashboards: Create dashboards to keep track of key metrics at a glance
Session Replay: Replay a user’s journey within your app
Besides these reports, you also get auto-capture events, which lets you track your events without any code.
All 3 modules are inter-connected:
For example, you can track data with Product Analytics, and then create a survey or in-app experience to improve the metrics.
Or the other way: Create a survey or in-app experience and track its performance with Product Analytics.
Some of the KPIs you can improve are:
- New user Activation
- Feature Adoption
- Retention
- Customer lifetime value
- Trial-to-paid conversion rate
- Net Promoter Score (NPS)
