Do you plan to design your product strategy around some examples of success metrics?
Implementing effective business strategies requires quantitative measures to understand their effectiveness. For example, what is your customer retention rate this year compared to last year?
As your strategies and objectives change, so should your success metrics. You can use different metrics to measure different aspects of your business, such as marketing, customer success, and product management.
What are some key success metrics you should track to gauge the health of your business?
Let’s dive deep!
Which examples of success metrics are you most focused on?
What’s your biggest challenge with tracking these success metrics?
Improving your success metrics would help you most with…
Ready to see how you can track and improve your success metrics?
Get a personalized demo of Userpilot and discover how to make data-driven decisions to grow your SaaS business. See success metrics examples in action!
Try Userpilot Now
See Why 1,000+ Teams Choose Userpilot
What is a success metric?
A success metric refers to a numerical measurement that managers use to determine the success of their business strategies. These are more commonly known as key performance indicators (KPIs) in SaaS.
Why are success metrics important to track in SaaS?
How do success metrics help your SaaS business? Let’s take a quick look.
Set specific goals
Success metrics help you establish a connection between your team’s objectives and company goals. This gives teams a clear picture, tells them what they are working to achieve, and allows them to prioritize their work.
For example, if you’re trying to measure customer loyalty, you can design an NPS survey and calculate the NPS score. After understanding the current level of customer loyalty, you can develop strategies to increase it.
Make data-driven decisions
Secondly, success metrics help you make more informed decisions. For example:
Do you have a higher customer acquisition rate this year? If so, what strategies did you implement to set you apart from previous attempts? If your rate is low, what possible reasons could there be?
By using quantitative measurements, you can identify changes easily and solve problems before they become too complicated.
Business success metrics to track in SaaS
Here are some metrics to measure your product’s success. You can leverage these business metrics to provide greater value to your customers and increase customer retention.
Business success metrics examples
Let’s look at the three most important metrics to measure your business success.
Customer Acquisition Cost
The Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC) is the sum of money you spend to get a new customer or convert a lead into a paying customer. It shows the effectiveness of your sales and marketing teams. Generally, you’d like to keep this number as low as possible.
To calculate this, simply divide your total sales and marketing expenses by the number of new customers acquired within a specified period.
For example, in the first quarter of 2022, you spent $4,600 on marketing and acquired 50 new customers. So, your CAC for the four-month period is (4600/ 50) = $92.

Monthly Recurring Revenue
The Monthly Recurring Revenue (MRR) is the revenue generated by your product in a month, typically through subscriptions.
This is calculated by determining the average revenue per active account and multiplying it with the total number of accounts in a given month.
For example, if you have 4,000 active accounts and the average revenue per active account is $30, then your MRR is (4,000 * 30) = $12,000.

MRR is an essential metric for any SaaS product. SaaS companies use this metric mostly for financial planning, forecasting, and measuring their product growth and momentum.
Total revenue
Total revenue, or gross revenue, is the total revenue your product generates from recurring (monthly subscriptions) and non-recurring revenue (one-time payments) streams.
To calculate this, simply sum the amount of money you’re getting from recurring and non-recurring streams.
This is an indicator of whether people are interested in purchasing your product/service or not, whether your marketing strategies are working, and how you are competing in the market.
Marketing success metrics examples
Let us take a look at three success metrics that determine the effectiveness of your marketing team and the strategies they implement.
Return On Investment
Return on Investment (ROI) is the ratio between net income and investment. When an investment has a high ROI, its returns outperform the expenses.
Frequently, it is used to determine whether a project is worth investing time and resources in.
Customer Lifetime Value
Customer lifetime value (CLV or CLTV, LTV) is the total revenue you expect a typical customer to bring your company throughout their entire relationship with you.
It demonstrates how much a customer is worth, their value, and how much you should invest in retaining the customer.
You can calculate the CLV by dividing the average revenue per account (ARPA) by the customer churn rate for a specified time period.

A high lifetime value indicates that your product offers long-term value to your customers, so they’re more likely to keep using it for a long period. For any SaaS business, customer retention is important as it can keep your cost down.
With this metric, you can identify your most profitable customers.
MQL to SQL rate
A marketing qualified lead (MQL) is a potential customer that has shown interest in your product or service but isn’t ready to be approached by the sales team yet. These leads are essentially free trials or signed-up users who have already tested the product.
A sales-qualified lead (SQL) is a prospective customer who has expressed a clear intent to purchase your product. They are in the final stages of the buying cycle.
That said, MQLs and SQLs are both potential customers. However, what sets them apart is the intent to buy.
To calculate the MQL to SQL rate, you need to first identify the number of MQLs and SQLs generated for a particular period. Then, divide the number of MQLs generated by the number of SQLs generated in that period and then multiply it by 100.
For example, if you generated 750 leads in a month-long sales campaign and then converted 300 of them into paying users, your MQL to SQL rate would be (300/750)*100% = 40%.

A product’s MQL to SQL conversion rate is related to its close rates. So, all companies should keep this ratio high. This can be done by sending personalized lead nurturing emails, training the sales team better by equipping them with success stories, and collecting qualitative customer feedback.
Customer success metrics examples
Here are some fundamental customer success metrics you can measure to gauge the health of your existing customers.
Customer Retention Rate
The customer retention rate is one of the most important metrics to measure customer success. It gives you insight into the number of customers that are likely to stay with your product over some time, not just those who make a one-time purchase.
To calculate this metric, you need to find out the total number of paying customers at the beginning of a period and the number of customers at the end of the period. Then, calculate their ratio as shown in the image below.
For example, at the beginning of January 2022, you had 5,000 paying customers. By the end of April, you have 3,450 customers left. So, your retention rate is (3450/5000) * 100 = 69.00%.

Combined with your churn rate, this metric helps you get a better understanding of how many customers are leaving compared to how many are staying.
You may learn about issues you hadn’t noticed before, such as a lack of customer trust or poor service quality. You can also learn how good your product is to satisfy existing customers.
Customer Effort Score
The Customer Effort Score (CES) measures customer sentiment and how much effort a customer has to put in when it comes to interacting with your business.
To calculate this score, you can use a survey that asks customers any questions about their engagement with the business. The survey can use a numeric rating scale from 1 to 7.
For example, after you’ve introduced a new feature, your survey can ask “This feature has been able to solve my problems.” Customers can then choose how true the statement is.
The CES score is the ratio of the number of people who rated very positively (5 or greater) and the total number of survey responses multiplied by 100.

The customer effort score has a wide range of applications. You can use it to find out customer pain points and fix those before they churn.
Customer Satisfaction Score
A customer satisfaction score (CSAT) can be used to measure customers’ experience and satisfaction levels with a specific product, feature, or customer support team.
To calculate the CSAT score, you should start with a survey where you ask customers a question. This can include:
- How helpful was this support session?
- How user-friendly is this new feature?
Then, divide the number of respondents who are ‘happy’ with the product or feature by the total number of respondents.
You can measure the CSAT score at different touchpoints throughout the customer journey to identify the overall satisfaction level with your product. A high score shows that you have exceeded the expectations of your customers, which in turn leads to increased customer retention and loyalty, and lower churn rates.
Product management success metrics examples
With the following three metrics, you can measure the success of your product management strategies.
Free trial to paid conversion rate
Your trial to paid conversion rate refers to the percentage of trial users that purchased your product or became paid customers after their free trial was over.
To calculate this rate, divide the number of free trial users who converted by the total number of free trial users within a specified period.
For example, in December, your product had 600 trial users, and 200 of them converted into paying users. So, your free trial conversion rate is (200/600) * 100 = 33.3%.

Measuring the value of your product helps you determine whether or not users are willing to pay for it. A higher SaaS free trial-to-paid conversion rate shows faster product growth and lower customer acquisition cost.
Customer Engagement Score
The customer engagement score is a unique metric used to measure the engagement of a single customer. It measures various aspects of a customer’s interactions with your products.
To calculate the CES, you need to first define what events you’ll be measuring. For example, feature adoption rate, time spent within the app, and the number of resolved tickets are some events you can select to illustrate a customer’s engagement with the product.
Next, you find out the total event value by assigning the event importance (in numeric terms) and finding out the number of times the event occurs in a given time frame.
Finally, you sum all the total event values to calculate the CES.

This metric helps you identify your product’s power users and most satisfied customers. A high customer engagement score shows that the customer frequently interacts with your SaaS product and is getting value from it.
It also provides insights into various customer segments. This helps you identify customers that might churn, free trial users that might convert to paying users, and existing customers that will continue repeat purchases.
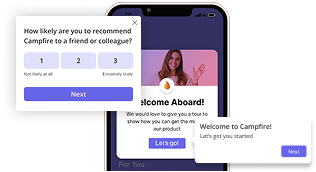
Net Promoter Score (NPS)
With the Net Promoter Score (NPS), you can measure the likelihood of your existing users promoting your products.
This is calculated by using an NPS survey, where you ask your customers one question: On a scale from 1 to 10, how likely are you to recommend our product to a friend or family member?
The respondents are divided into three categories. Your most loyal customers responding with a 9 or a 10 are called promoters, passives choose 7 or 8, and detractors choose 6 or below. They are quite dangerous as they can ruin your brand image with negative word-of-mouth.
To calculate the Net Promoter Score, you simply subtract the percentage of detractors from the percentage of promoters.

For example, when surveying 100 customers, 52 of them responded with a 9 or 10, 12 responded with a 7 or 8, and 36 responded with a 6 or below. So, your NPS is 52% – 36% = 0.16.
A high net promoter score indicates high satisfaction and loyalty, as your customers are willing to advocate for your product.
How to improve your business success metrics with Userpilot?
Now, let’s take a look at how Userpilot provides features that can improve your business metrics.
Userpilot is a product growth, adoption, and customer experience management tool that allows you to design personalized in-app experiences and increase growth metrics at every stage of the customer journey. But how does it help you achieve these?
For starters, it is super easy to use and requires no coding knowledge. You can create welcome screens to greet your customers and segment them to personalize customer interactions.
And now, with its new native mobile SDK, Userpilot also helps you onboard and engage mobile app users by creating personalized messaging, push notifications, and surveys.
Moreover, Userpilot allows you to design interactive walkthroughs and checklists that improve onboarding and teach customers everything your product has to offer. This can help increase the average customer lifespan.
You can create in-app help centers which can include FAQs or knowledge bases. This allows customers to solve their problems and minimize tickets, allowing customer support to focus on more important issues.
Moreover, you can create microsurveys that allow you to calculate CSAT and NPS scores. This helps you collect effective qualitative customer feedback, improve customer experience, and deliver a great product.
Conclusion
You can level up your product growth with the right business, marketing, product, and customer success metrics.
The success metrics can help you establish quantitative measures to align your company’s goals with your product teams and set the ideal benchmarks and KPIs.
Want to track and improve your success metrics? Get a Userpilot Demo and see how effectively you can do it.