SaaS user flows are visual representations of the steps users take within your website or app. When created well, they can help you better understand users, boost engagement, and increase long-term retention.
This article provides a curated list of 12 exemplary user flow diagrams and real-world examples to inspire your design and development process.
But first things first…
What’s your biggest challenge with your current user flows?
How do you currently analyze user behavior within your product flows?
Are you able to guide different user segments through unique, personalized paths?
Build exceptional user journeys without writing code.
Userpilot can help you analyze, create, and optimize your user flows to increase activation, feature adoption, and conversions. See how it works.
Try Userpilot Now
See Why 1,000+ Teams Choose Userpilot
Understanding user flows in SaaS (key elements + benefits)
Let’s quickly go over the key elements and core benefits of user flows:
7 Key elements of a simple user flow
A complete user flow has the following components:
- Entry points and end points: As the names suggest, these are the points where your flow starts and ends. For example, a SaaS signup flow typically begins with a CTA on a landing page and ends with the user successfully creating their account and being redirected to their dashboard.
- User interactions: These are the specific actions users must complete within the flow. Common examples early in the user journey include filling out a form, agreeing to the terms of service, and starting an onboarding flow.
- Decision points: These are customer journey touchpoints where users make choices that direct them down different paths within the flow. For example, if your signup flow requires email confirmation, a user who skips this step might be directed to a reminder screen or an alternative signup method.
- System responses: How does your system react to user actions? These responses can be anything from a simple button changing color to a complex animation or a new screen loading.
- Paths and branches: Paths are the specific sequences of steps a user takes within a flow, while branches are points in the user flow where the user encounters a decision. For example, a new user might take the “email signup path” or the “Google signup path.” The point where they choose which method to use is a branch in the flow.
- Feedback and notifications: These are messages that proactively inform users about system events or changes. For example, new users might receive a welcome email to confirm their registration.
- User goals and outcomes: In this context, a goal is the objective that drives a user to engage with a specific flow, while the outcome is what they hope to achieve.
The benefits of tracking user flows
There are several benefits to creating and tracking user flows. Here are the top three we’ve observed for SaaS:
- Identify bottlenecks and drop-off points: A complete user flow already gives you an idea of how users are supposed to go from point A to Z, making it easy to identify when they’re stuck at point “C.” You can then use an analytics tool like Userpilot to investigate the underlying issues and deliver a smoother user journey.
- Enhanced data-driven decision-making: User flow analytics provides concrete data for making informed decisions about product design, marketing strategies, and business goals. For example, if your business goal is to increase user engagement with a particular feature, you can analyze the flow leading to that feature and identify how to drive more clicks, increase time spent within the feature, or promote specific actions.
- Improved conversion rates: User flow analytics help you understand what drives users to complete desired actions and optimize for more of that. For example, if you notice users who regularly engage with a specific feature are more likely to upgrade their accounts, you can use that as a trigger for sending timely upsell prompts.
12 Real-life SaaS intuitive user flow journeys (+ user flow diagram examples)
This section showcases real-world examples from leading SaaS companies, complete with user flow diagrams that you can adapt and implement in your own product:
User flow example #1: Onboarding flow for new users
The entry point of this flow is a welcome message and a CTA to start a series of onboarding tutorials.
Users who proceed with the flow will receive step-by-step instructions and guidance on how the platform works.
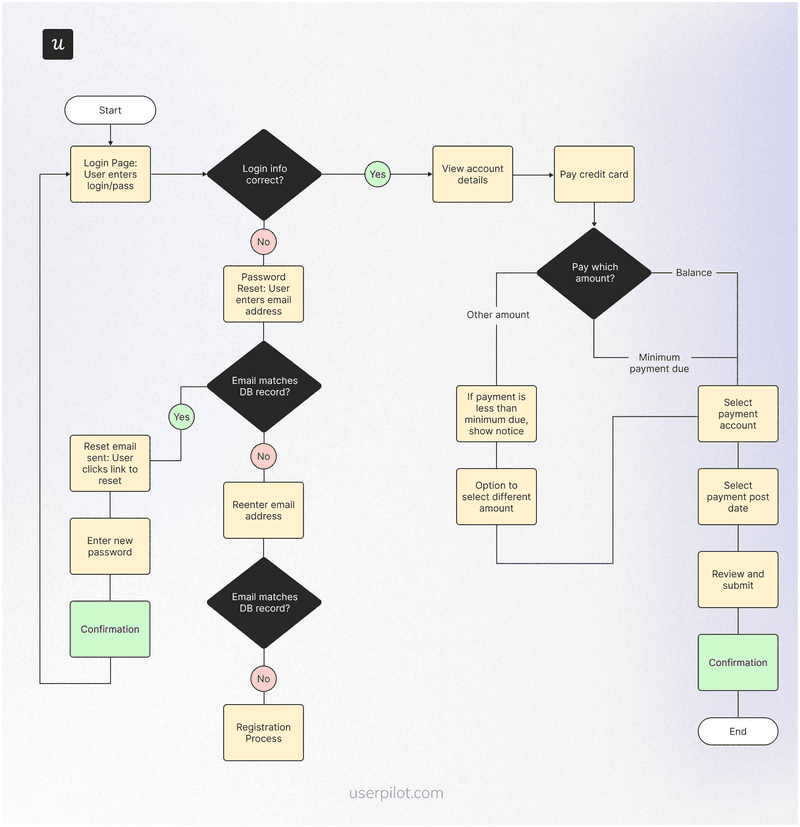
User flow example #2: From login to successful credit card payment
This flow begins when a user enters their login details. The system automatically redirects them to a password reset/registration process if the information they entered is incorrect.
Once the user logs in, they will be directed to the billing section, where they enter their credit card details and proceed with payment:
SaaS in action: Zoom
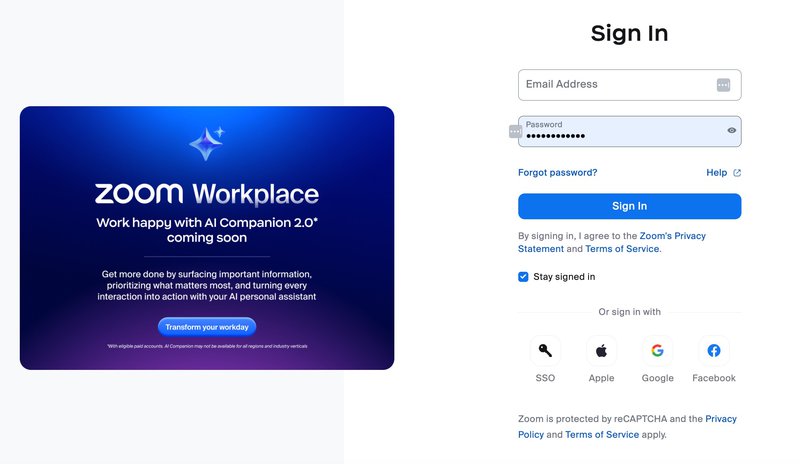
Zoom offers users the choice of signing up with their email and password or using a social login provider like Google, Facebook, or Apple for a faster login experience.
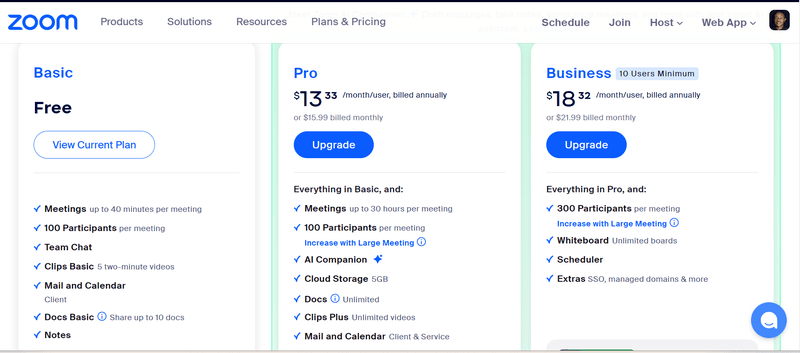
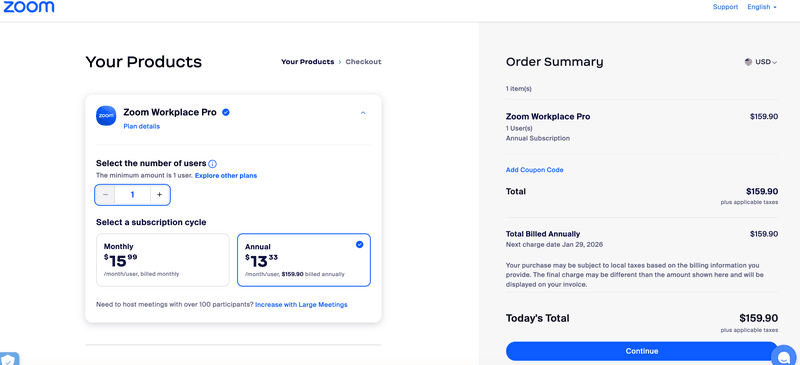
The intuitive interface makes it easy to navigate to the pricing page, where users can choose to renew or upgrade their plans. If the user doesn’t have a payment history, the system will prompt them to enter their card details and display a payment confirmation message upon successful payment.
User flow example #3: Basic user flow chart for logging in
The previous example was specifically about leading users to complete a payment, but that’s not something users do every day. Let’s consider a more generic flow that simply takes users to your app.
This flow follows the same principles:
- Offer multiple sign-in options to improve the user experience.
- Provide a clear account recovery process in case users forget their passwords or have other login issues.
- Keep the UI simple and easy to navigate.
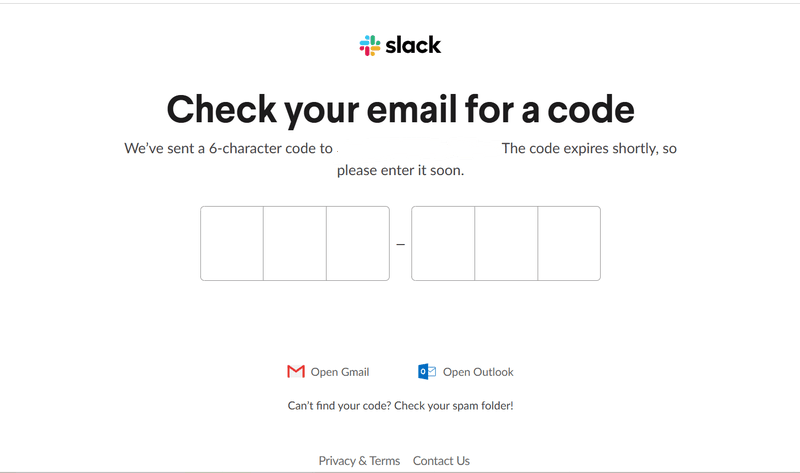
SaaS in action: Slack
Slack’s login flow stands out for a few reasons.
First, the login page is clutter-free, with a clean and visually appealing design.
Next, Slack understands its audience and proactively avoids frustration by asking users to sign in with the emails they use at work. This is because Slack workspaces are often tied to specific company domains (e.g., @company.com), and users may not have access to their organization’s workspace if they sign in with a personal email.
The platform offers quick sign-in options, but you can choose to be emailed a magic code for password-free sign-in.
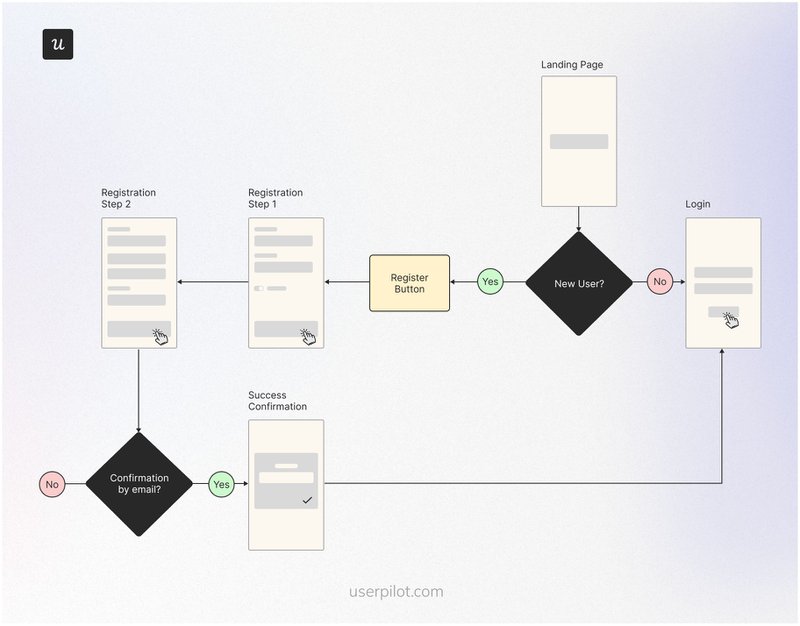
User flow example #4: Registration with authentication user flow
Authentication methods like email verification help you collect accurate customer data and prevent unauthorized access. However, poorly implemented authentication can create friction in your registration process and lead to drop-offs.
Prevent this by implementing SSO and making sure the confirmation emails land in the user’s inbox in real time. Here’s the typical flow:
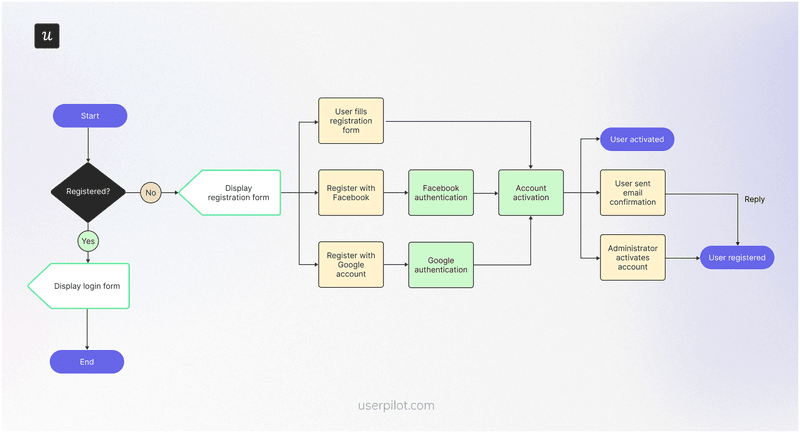
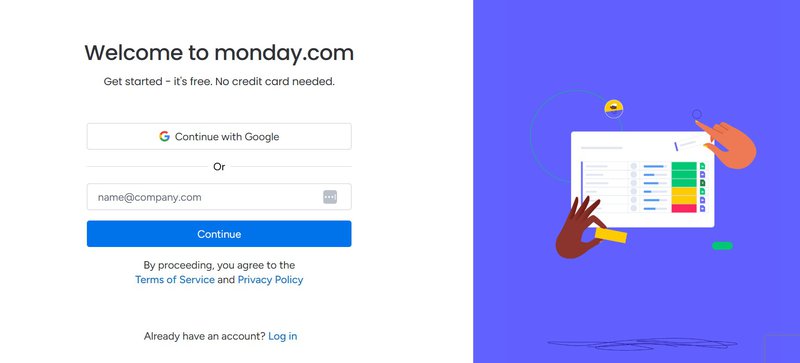
SaaS in action: Monday.com
Monday.com has an easy registration process that lets you securely create an account using Google’s SSO.
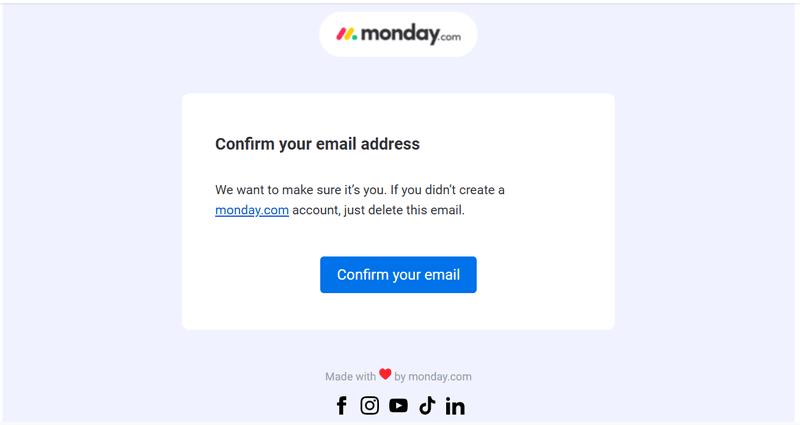
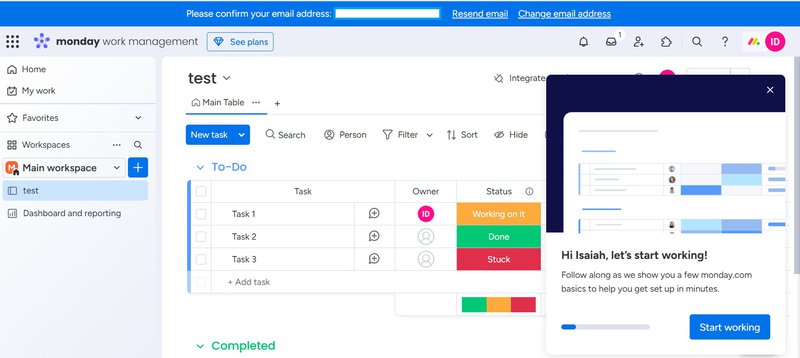
The platform requires email confirmation for account security, but it’s flexible enough to let new users explore the tool and confirm their emails later. As in the screenshots below, Monday.com uses a notification banner to remind users about email confirmation without disrupting the onboarding process.
User flow example #5: Forgot password user flow
Can’t remember your password? You’re not alone! Statista’s 2022 report shows that 34% of people reset their passwords roughly once monthly, while 15% do it multiple times a week.
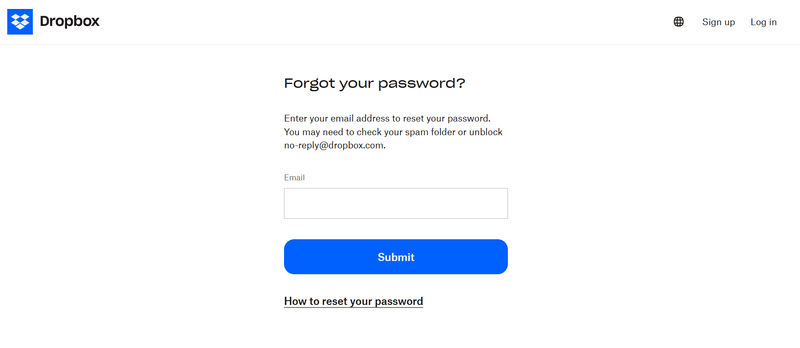
A smooth password reset flow helps to make this experience less annoying for your users. This flow typically starts with the user clicking a “forgot password” link and then being prompted to enter their email address.
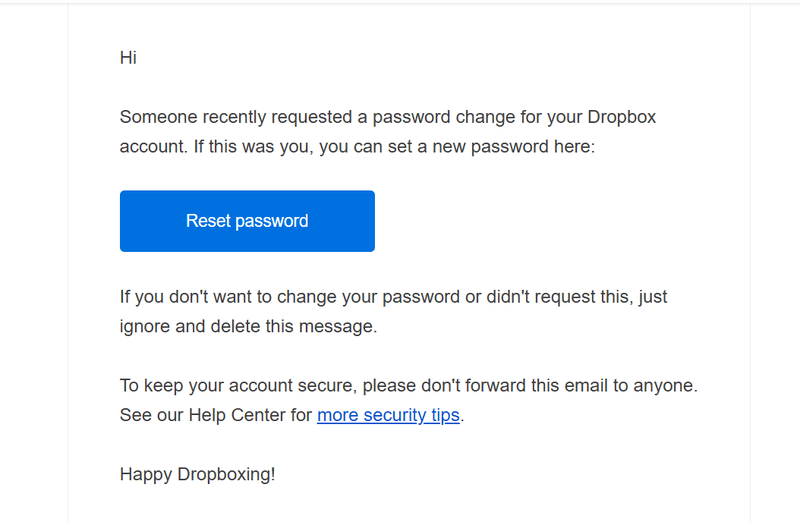
If the user’s email is in the database, they’ll receive a reset link. If the email doesn’t exist, they’re asked to try one more time and are redirected to the registration process if the second input is also invalid.
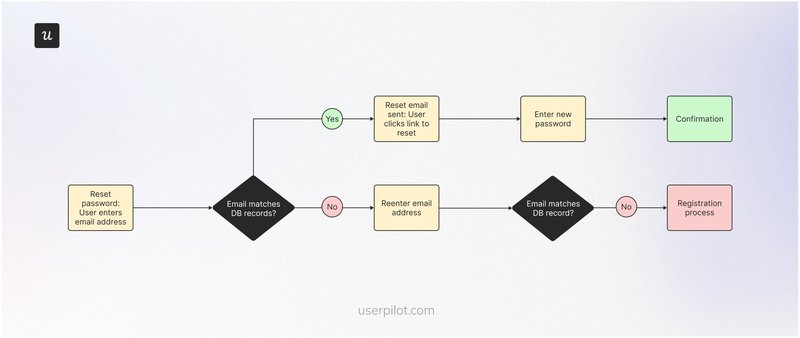
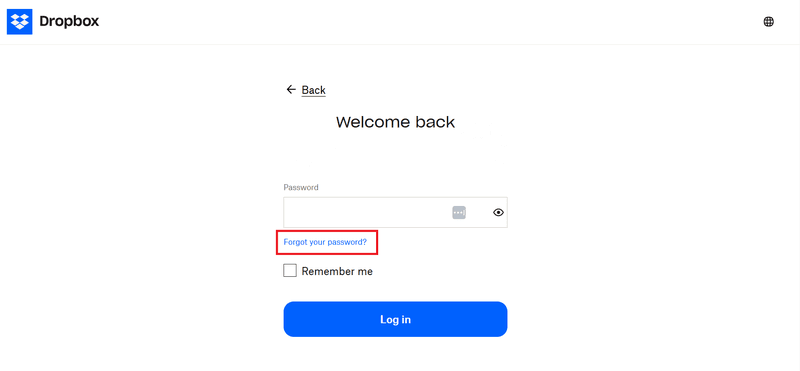
SaaS in action: Dropbox
What we love about Dropbox’s flow is the helpful tips it provides.
Besides the microcopy on the password reset page, Dropbox provides links to its help articles, which cover the step-by-step process for changing your password and additional tips for maintaining account security.
User flow example #6: Referral user flow
A referral program is a great way to attract new users while keeping acquisition costs low, but you have to make the flow stupidly simple if you want high engagement.
Your entry point should be a modal or landing page that advertises the referral program and ends with a CTA. Ask interested users to fill out a quick form containing details like their name and email. Then, send their unique referral code in-app or via email.
Don’t forget to make it easy for disinterested users to dismiss the flow and get back to their tasks:
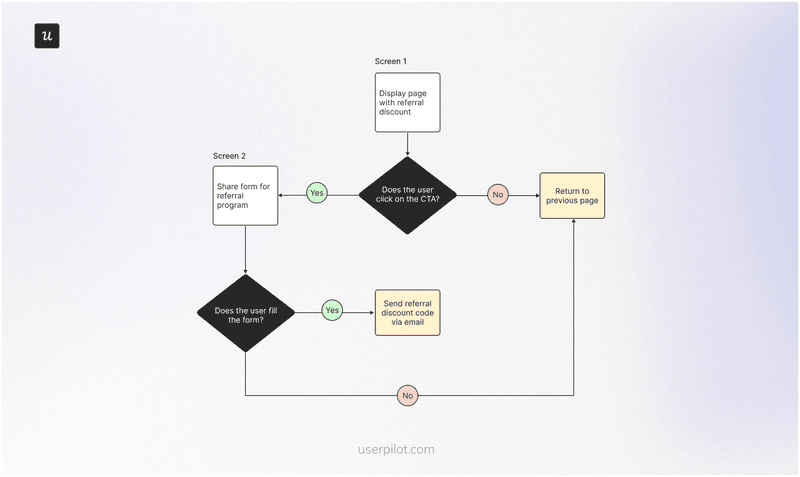
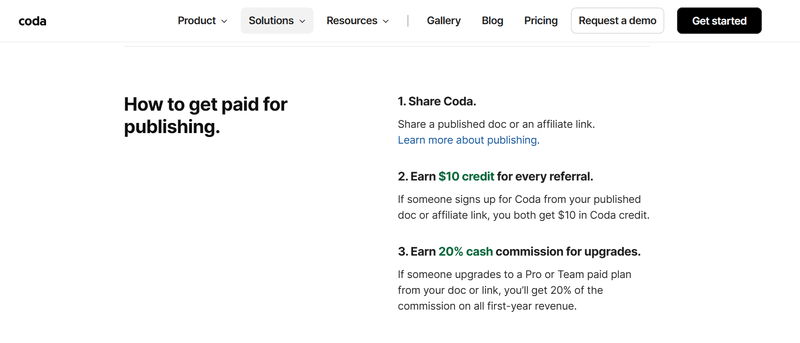
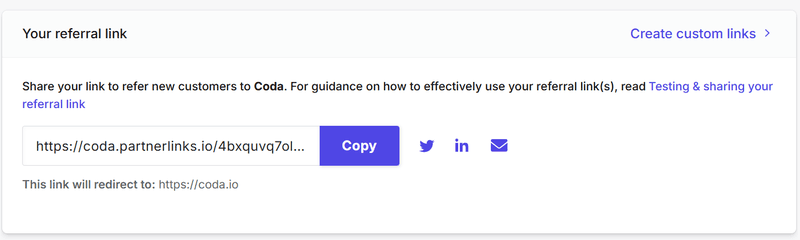
SaaS in action: Coda
Coda, a cloud-based document editor, lets users earn commissions for publishing their work or inviting new customers to the platform.
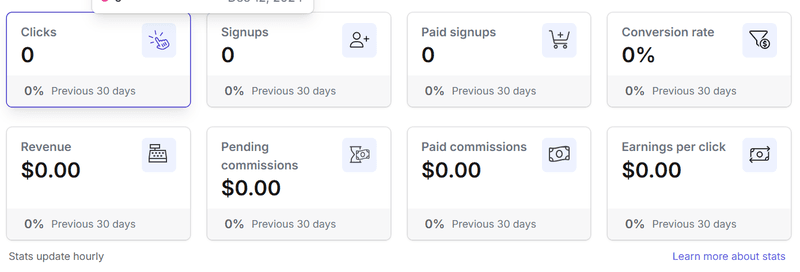
Coda has a landing page that explains all the details and shows interested users how to get started. The platform also provides rich referral analytics that lets users track clicks, signups, and conversion rates.
User flow example #7: Plan upgrade user flow
This flow begins by showing power users an upgrade prompt based on their usage patterns.
If the user dismisses the popup, the flow ends. However, interested users will be taken to the pricing page, where they can review higher-tier plans and make a decision.
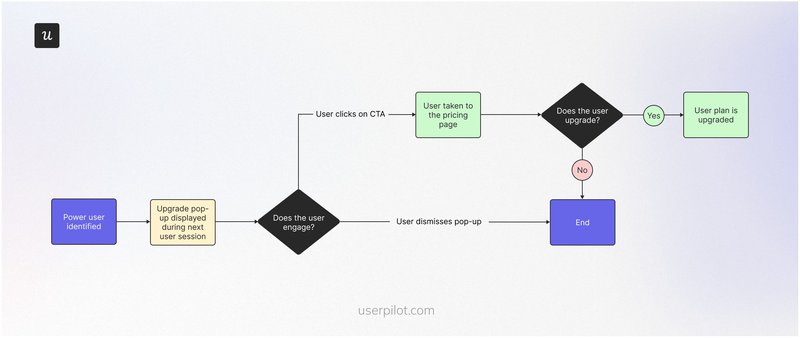
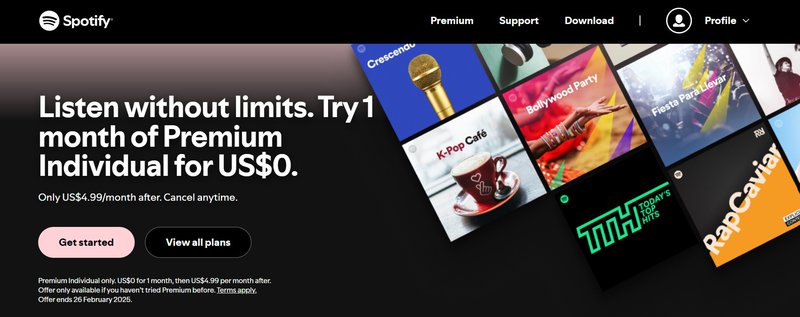
SaaS in action: Spotify
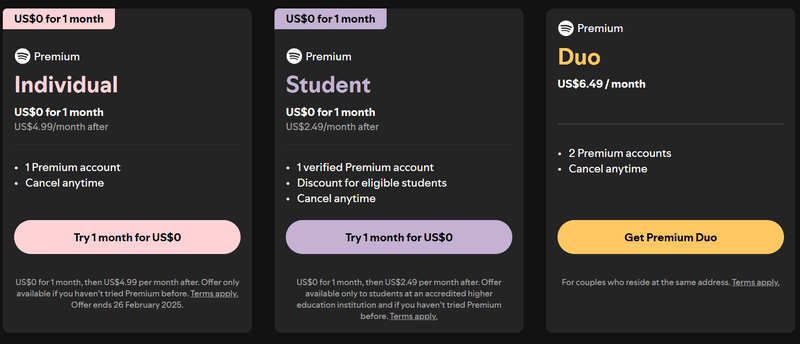
Spotify triggers occasional upgrade pop-ups as free users interact with the platform. The company offers an irresistible sweet deal to try the premium plan free for one month, after which users will be downgraded to the free plan if they don’t upgrade. Users can also choose to skip the trial and become paid subscribers right away.
This strategy seems to be working for Spotify, as its 2025 report shows over 60% of its paid users were once on the free plan.
User flow example #8: Review generation user flow
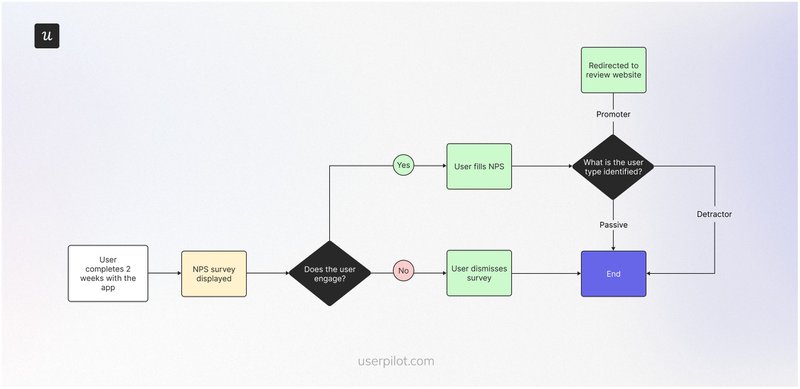
This simple flow helps you automate reviews from your most loyal customers. It starts by displaying an NPS survey to users who have used your app for two weeks.
The flow ends if a user dismisses the survey. If they don’t, they’re prompted to fill out an NPS survey, and the system automatically divides them into promoters, passives, and detractors based on their responses.
Promoters are redirected to a review site like G2, while the flow stops for passives and detractors.
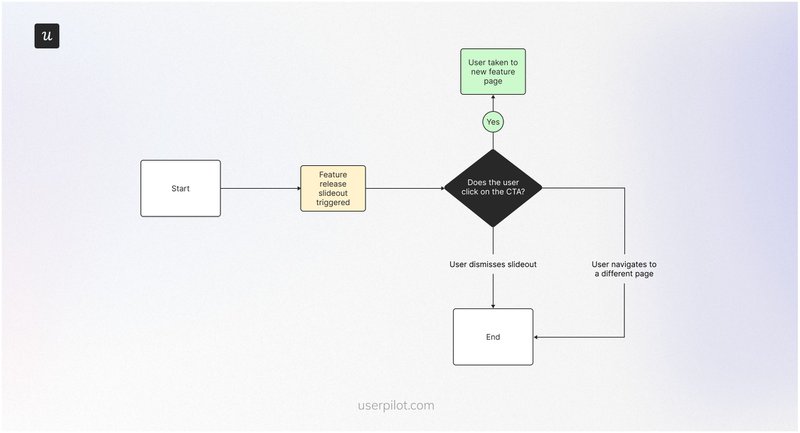
User flow example #9: New feature release user flow
This flow starts with an in-app message that notifies users about the new feature and invites them to try it.
Users who dismiss the message or navigate to a different page will automatically end the flow. Those who demonstrate interest by clicking the CTA will learn more about the feature and receive a guided tutorial on how to maximize it.
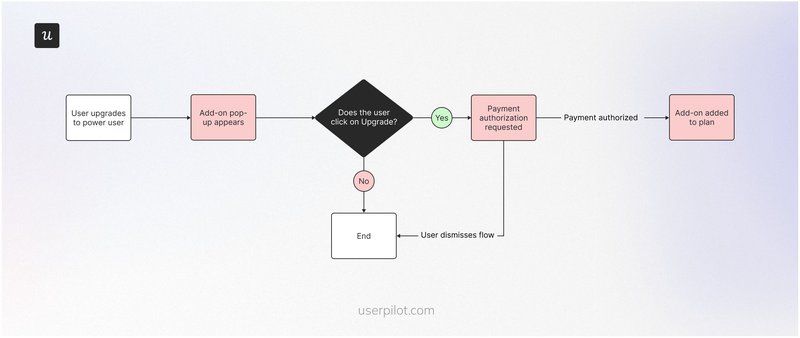
User flow example #10: Cross-sell user flow
A cross-sell flow provides timely and personalized add-on recommendations based on user behavior.
Depending on the company’s pricing model, the flow could lead users to start a free trial and upgrade later or simply ask them to upgrade immediately.
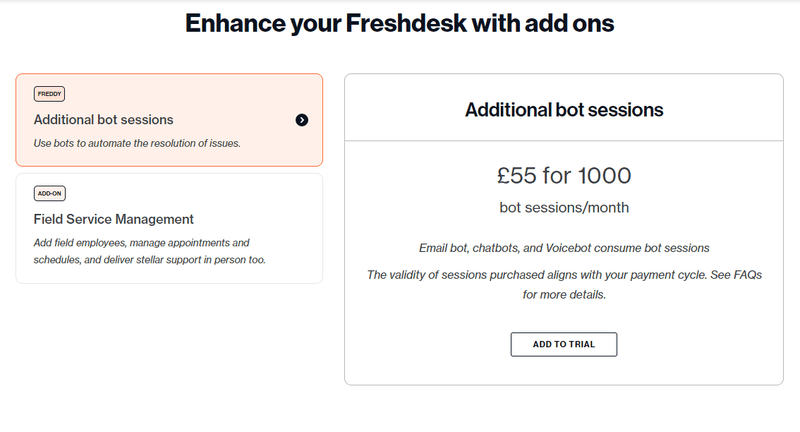
SaaS in action: Freshdesk
Freshdesk offers additional bot sessions and field service management as add-ons. What makes this conversion flow stand out is its clear messaging that lets users know exactly what to expect from each product.
And the best part? Users can try the add-ons free for a limited time to see if the extra cost is worth it.
User flow example #11: Customer support user flow
This flow lets users access support through multiple channels like live chat, email, phone, or a knowledge base.
The system automatically routes inquiries appropriately to help users get the help they need as soon as possible.
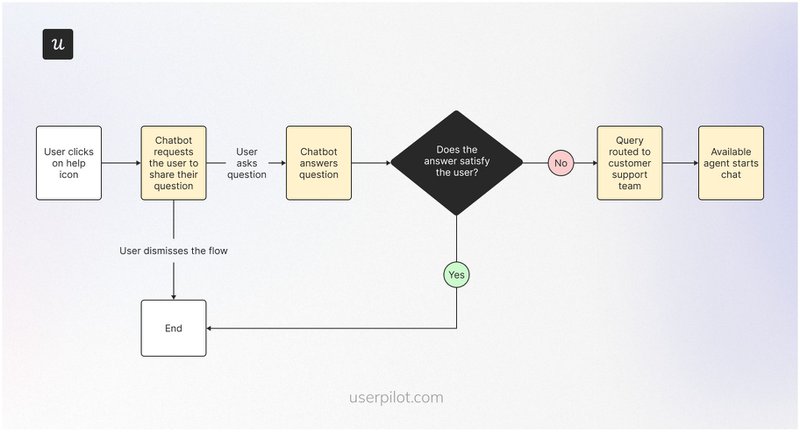
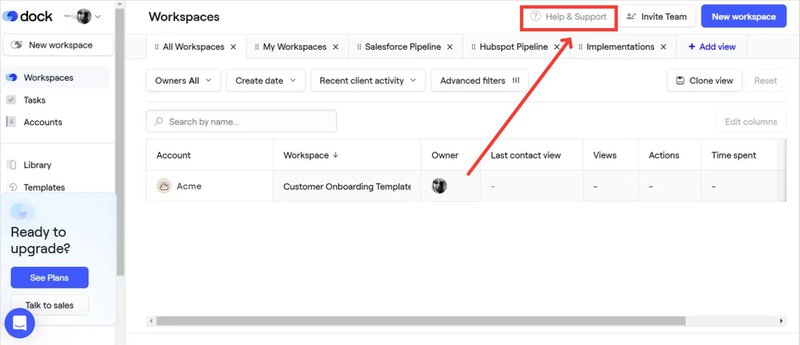
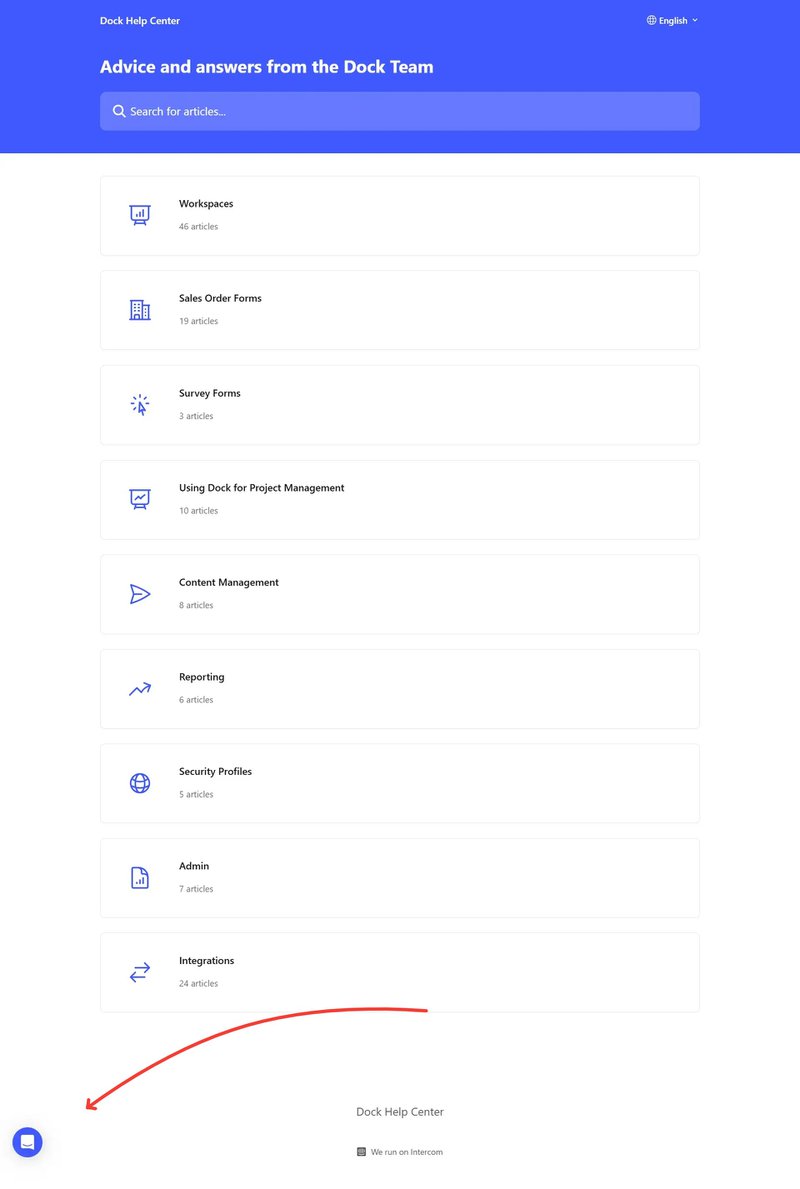
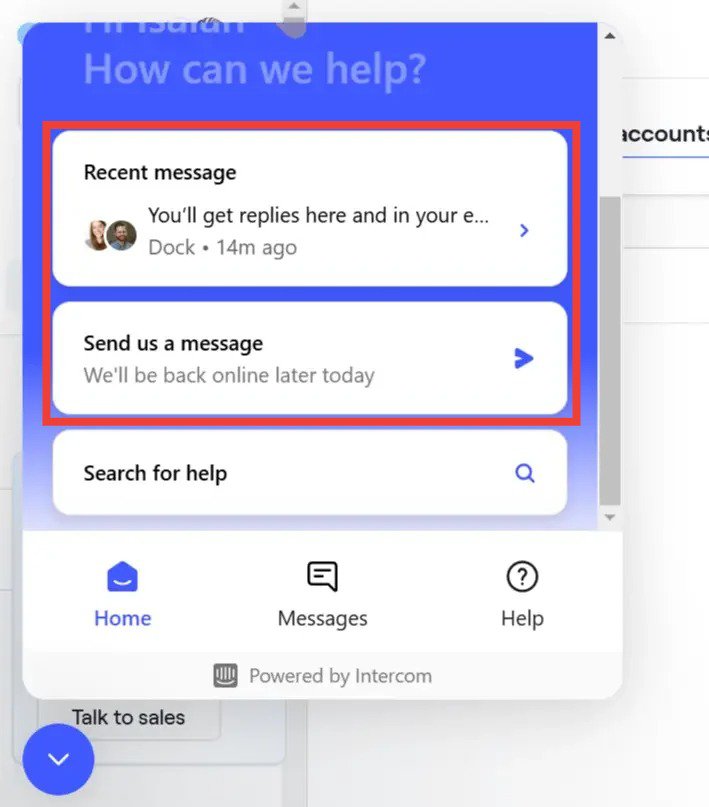
SaaS in action: Dock
Dock provides multichannel customer support options that users can easily access from the app.
For example, if you encounter issues while using a feature, you can visit the help center by clicking the “Help & Support” button (shown in the screenshot below). If you don’t find something satisfactory, you can click the support button right on the left to chat with human support agents.
User flow example #12: Account cancellation user flow
Sadly, not all users will stick with you for long. But on the bright side, you can turn their departure into a growth opportunity.
After asking users to confirm their decision to cancel their accounts, this flow triggers a quick churn survey to learn why users are canceling. The system then offers contextual recommendations based on the user’s response.
Users who decline the survey or reject the alternative option will successfully cancel their accounts, while those who liked the recommendation will retain their accounts.
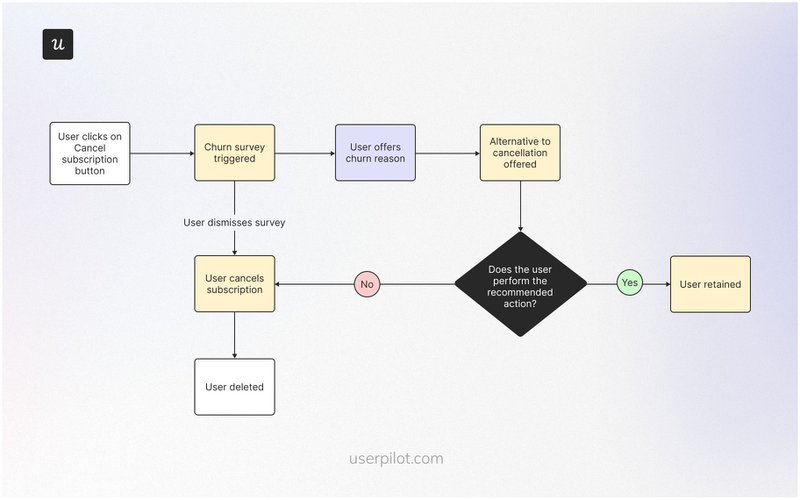
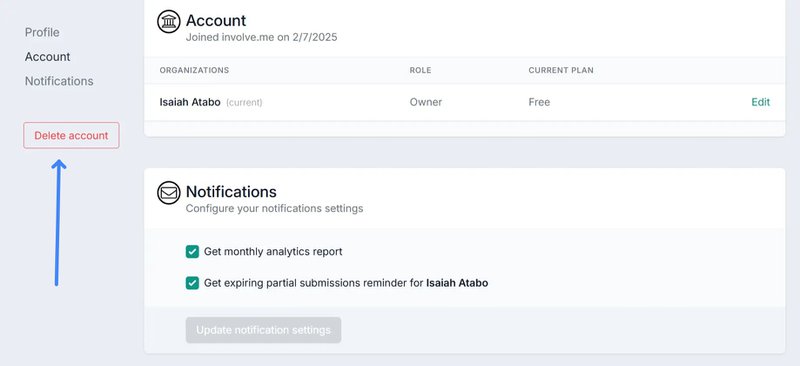
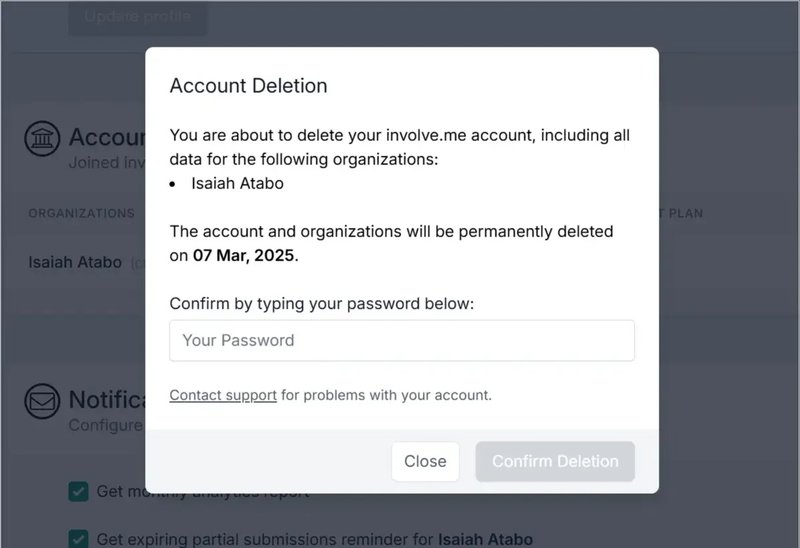
SaaS in action: Involve.me
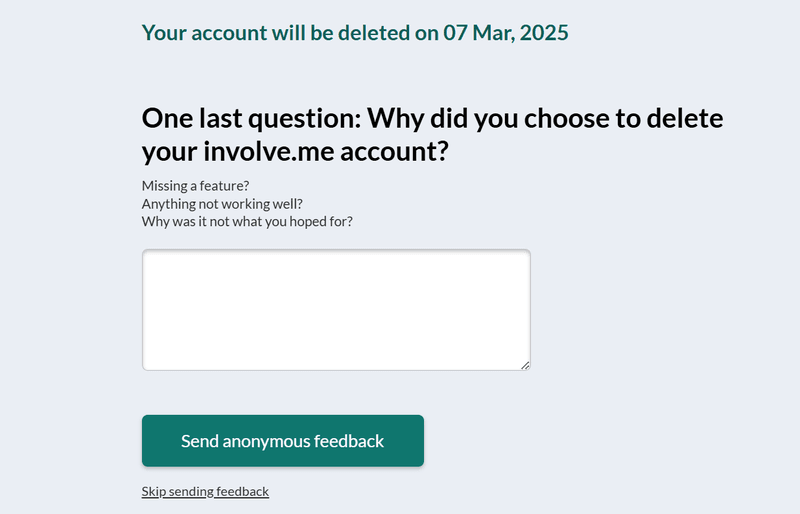
Involve.me notifies users that their data will be permanently deleted after 30 days of initiating the cancellation. This is a subtle way to tell users, “Hey, we’re giving you extra time to reconsider your decision.”
Next, the system asks users to confirm their decision to cancel by entering their passwords. The flow ends with an open-ended churn survey asking users to optionally explain the reason they’re leaving.
Best practices for creating user flows for your SaaS
Ready to start designing user flows? Let’s discuss a few best practices to help you maximize engagement.
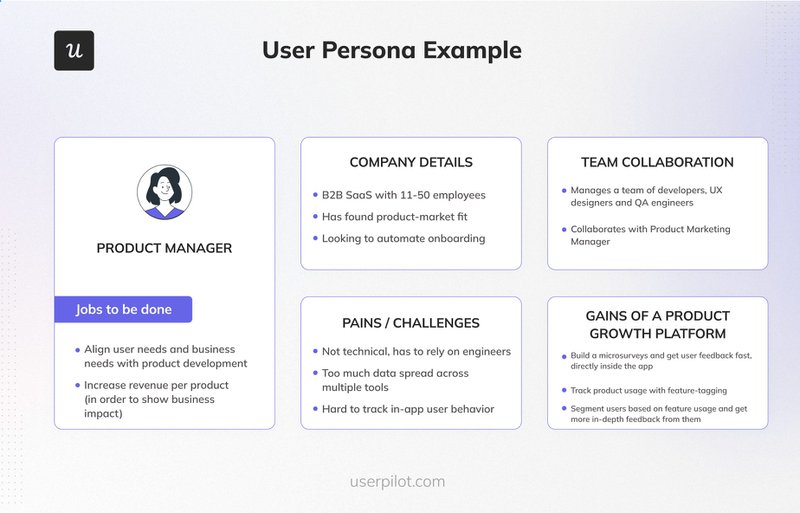
1. Segment and understand your users
Create detailed user personas that represent all the audience groups your company is targeting. For example, if you’re a product design tool, your customers might include freelancers, design agencies, SMBs, and large enterprises.
Map out the specific needs of each user group and tailor your flows accordingly. It also helps to personalize your flow to the user’s journey stage. For instance, guide new users towards essential features and prompt power users to explore advanced capabilities and upgrade options.
Here’s a user persona template you can use:
2. Start with high-level flows
Avoid overwhelming yourself with too many details at once. Instead, begin by identifying the key processes in the flow and creating simplified diagrams.
Once you have this high-level structure in place, you can then break down each stage into more detailed steps.
3. Design with accessibility principles in mind
Help users navigate better by incorporating accessibility features like keyboard support, screen reader compatibility, and adequate color contrast.
4. Use conditional logic wisely
Clearly indicate branching points in your user flow to account for different user paths and decisions. For example, you can use if-then scenarios to show the paths for free vs. premium users:
If: User has a free account
- Then: Show limited features and display upgrade prompts
If: User has a premium account
- Then: Grant access to all features
However, be mindful of creating user flow diagrams with excessive branching, as this can make the diagram difficult to read and understand.
5. Collect user feedback to improve your user flows
Incorporate feedback mechanisms within the user flow and use product analytics to identify areas for improvement.
For example, you could use our platform to trigger NPS surveys at the end of critical user flows like the login-to-successful-card-payment process:
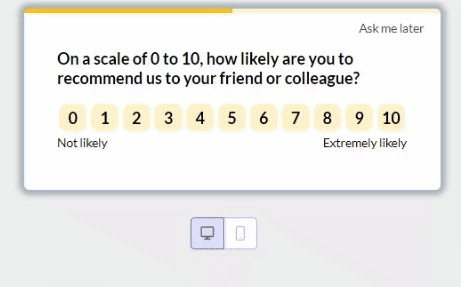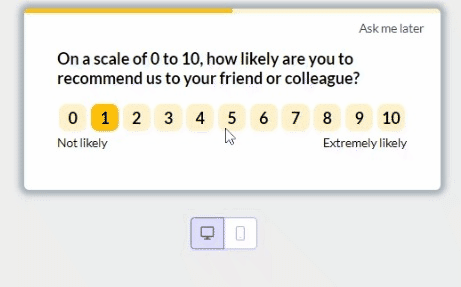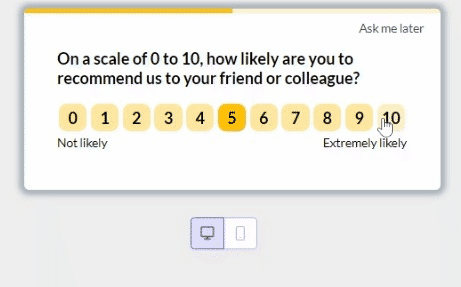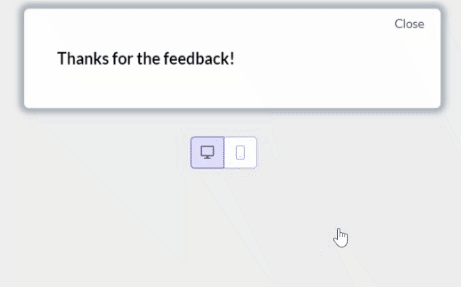
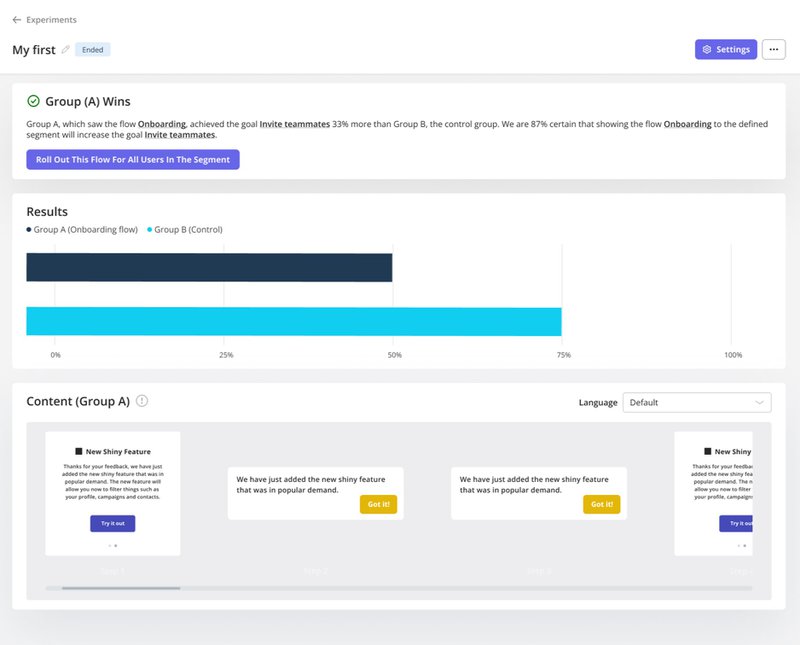
6. A/B test different user flows to improve user experience
Utilize A/B testing to compare different design variations and identify which performs best. For example, you could experiment with element placing, messaging, or even flow variation to see what converts more.
Our platform lets you create and track A/B test campaigns with ease:
Optimize your SaaS user flows for success
The best user flows come from a deep understanding of your users and their needs. So, be bold about experimenting and iterating based on observed user behavior (or even your own hypothesis).
Ready to recreate some of the user flow examples we discussed in this article? Book a demo to see how our platform can empower you to understand user behavior, segment users, and trigger personalized experiences.








![What are Release Notes? Definition, Best Practices & Examples [+ Release Note Template] cover](https://blog-static.userpilot.com/blog/wp-content/uploads/2026/02/what-are-release-notes-definition-best-practices-examples-release-note-template_1b727da8d60969c39acdb09f617eb616_2000-1024x670.png)
