
User Segment vs User Persona: What’s the Difference & How To Create Both in SaaS
User segment vs persona: what makes the two different from each other?
While segments and personas are not mutually exclusive, they have different purposes in the SaaS industry.
So let’s dive deeper and see how you can create both to improve your product marketing efforts.
Try Userpilot Now
See Why 1,000+ Teams Choose Userpilot
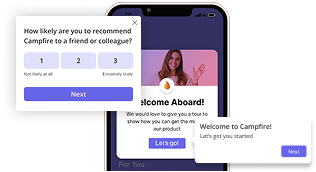
User segment vs user persona – quick summary
- A user segment is a distinct group of customers with specific shared needs, characteristics, or actions.
- A user persona is a fictional character whose characteristics and goals mimic those of your ideal customer.
- User segments are relatively high-level categorical classifications of groups of people. On the other hand, user personas highlight specific details that cater to a certain type of person and their goals, motivations, or experiences.
- The 6 main types of customer segmentation are behavioral segmentation, demographic, psychographic, geographic, firmographic, and need-based segmentation.
- The 3 primary types of user personas are proto personas, qualitative personas, and statistical personas.
- Here is how to create customer segments:
- Use welcome screens to segment new users based on their jobs to be done.
- Track in-app interactions to create behavioral segments.
- Track in-app engagement to create user segments, such as inactive users, power users, etc.
- To create user personas, use a combination of research techniques to get a detailed picture of different customers.
- Use various kinds of microsurveys to gather qualitative data before creating user personas.
- Use customer persona templates to build different personas.
What is a user segment?
A user segment is a distinct group of customers based on specific shared needs, characteristics, or actions. Some examples of user segments include power users, inactive users, new users, free trial users, etc.
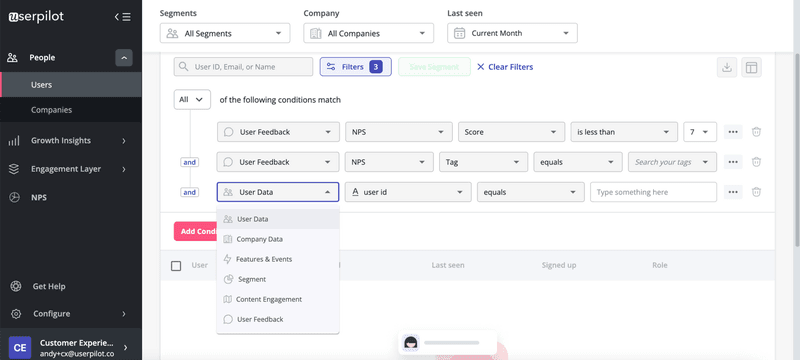
What is a user persona?
A user persona is a fictional character whose characteristics and goals mimic those of your ideal customer. Therefore, user personas can be used to represent the needs of a larger pool of customers.
User personas are built based on who you think will gain the most value from your product. The better you define the customer base who will get the most benefits, the fewer chances you have of investing in acquiring the wrong users. This also reduces the risk of churn in the future.
User segment vs user persona: Are they the same?
The segment vs persona debate still exists because it’s not uncommon for people to confuse the two. So if you are a newcomer in the industry or haven’t heard much about segments and personas, here’s how they differ.
Before we dive in, note that a combination of customer personas and segments can provide a detailed and comprehensive view of how a company should market to its target audience.
Although both personas and segments can group existing and potential customers, they offer different use cases for a SaaS business.
The main purpose of market segments is to understand whether your product or brand will resonate among the target market. Thus, they help you customize your brand’s messaging and content strategies to the needs of each segment.
Typically, large-scale research techniques are used to create customer segments. You can think of user segments as relatively high-level categorical classifications of groups of people. On the other hand, user personas highlight specific details that cater to a certain type of person and their goals, motivations, or experiences.
The main distinction between segments and personas lies in the details.
Personas work on an individual level. They are created using information from robust research on real people. Most importantly, personas allow you to get a deeper understanding of customers’ behavior and empathize with them.
Designing user personas gives you detailed fictional characters and their associated stories that your design teams can apply in real-life cases. It’s not possible for end users to always be available for these teams. But detailed character personas ensure that design teams can get a realistic picture of end users at any given moment.
While segments also help you personalize experiences for existing customers, personas take you at least one step further in improving your conversion and retention rates.
Types of customer segmentation
There are 6 main types of customer segmentation:
- Behavioral segmentation
- Demographic segmentation
- Psychographic segmentation
- Geographic segmentation
- Firmographic segmentation
- Need-based segmentation.
We would recommend you use them in combination with each other to get a more comprehensive image of your target market.
Behavioral segmentation
This segmentation groups your users according to their behaviors, actions, and expressed patterns like their product usage rate and purchase history.
Behavioral segmentation can give valuable insights into users, such as product knowledge, feature adoption rate, usage rate, product awareness levels, and past purchase behavioral patterns.
The product usage data will help you identify and remove friction inside your product. You can also fine-tune the in-app marketing messages plus offer more timely and contextual customer service.
Demographic segmentation
Demographically segmenting your customers categorizes your leads based on their gender, age, income levels, etc. It gives you basic demographic information about your company’s target audience.
Using data from demographic segmentation, you can:
- Understand users from specific backgrounds better.
- Craft smarter digital marketing strategies.
- Launch personalized email campaigns.
Psychographic Segmentation
How do the beliefs and values of your customers vary? Psychographic segmentation answers these questions by grouping customers according to their personality traits, interests, attitudes, opinions, or values.
This form of customer segmentation allows marketers to understand the correlation between a customer’s socioeconomic status and their buying decisions.
Geographic Segmentation
Want to focus on customers from a particular region?
Geographic segmentation allows you to analyze which country, city, area, or location generates higher annual recurring revenue (ARR) and drives revenue growth. You can also run targeted ad campaigns based on the research reports.
Your marketing teams can assess and analyze the profitability of different groups of customers based on their geographical location. This will let them prioritize resources accordingly and serve these market segments better.
Furthermore, your customer support agents can help customers in varying time zones by working at different times of the day.
Plus, if you want to launch a new feature in select countries, geographic segmentation will help you to reach out to your target customers.
Firmographic Segmentation
Firmographic segmentation classifies B2B users according to their shared organization attributes. The major categories here are the users’ business model, job title, experience level, industry insights, and financial performance. There are also unique variables under each category.
This helps you to, for example, create different checklists for startups and large enterprises since they typically provide different solutions.
Needs-based segmentation
This segments customers by looking at their shared experience of a specific need or problem. It enables you to offer the right solutions to customers at the right time by:
- Providing clear information on various types of users.
- Using the company’s competitive advantage to market to opportunity segments.
- Customizing messages for each segment.
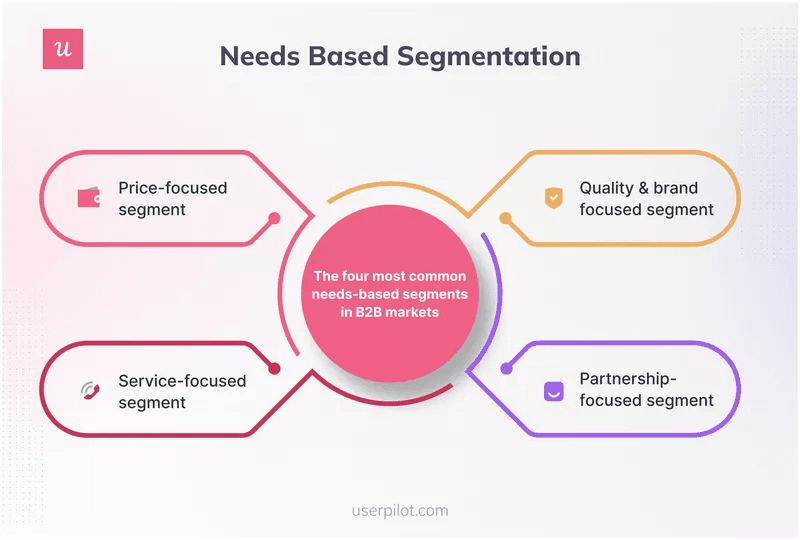
There are 4 types of needs-based segmentation:
- Price-focused segment: This charges different prices to different users for the same product.
- Quality & brand-focused segment: The users here are willing to pay for the best possible product.
- Partnership-focused segment: Customers see the SaaS company as a strategic partner and prioritize trust and reliability with it.
- Service-focused segment: Users emphasize customer service, product range, and quality.
Types of user personas
Now let’s look at the 3 different types of user personas.
Proto personas
These personas are a kind of ad-hoc personas that help to align the stakeholders’ view of customers.
Without any new research, teams can create proto-personas based on their best assumptions or knowledge of who their customers are and what they need. They may even use existing customer data if there are any.
Proto personas thus carry the risk of incorrect representation of customers, and teams may find little value in them.
Qualitative personas
Such personas are best created using in-depth small-sample qualitative research through usability tests, field studies, or user interviews.
Since qualitative personas are built using customer data, they offer actionable insights into users’ expectations, needs, and motivations that you will probably not get from quantitative analysis alone.
However, small samples make it difficult to know the proportion of the target market that’s represented by each user persona.
Statistical personas
You need to use a mix of quantitative and qualitative research to create statistical personas.
First, you have to carry out qualitative research to determine the questions to use in the survey. You should also have a solid knowledge of customer expectations to create a viable survey.
Then you need to survey a large sample of the target customer base and perform statistical analysis to identify groups with similar answers. The large sample ensures that the persona is representative of the bigger customer population.
How to build customer segments to create a personalized marketing strategy?
Here’s how you can create user segments and personalize your marketing strategy.
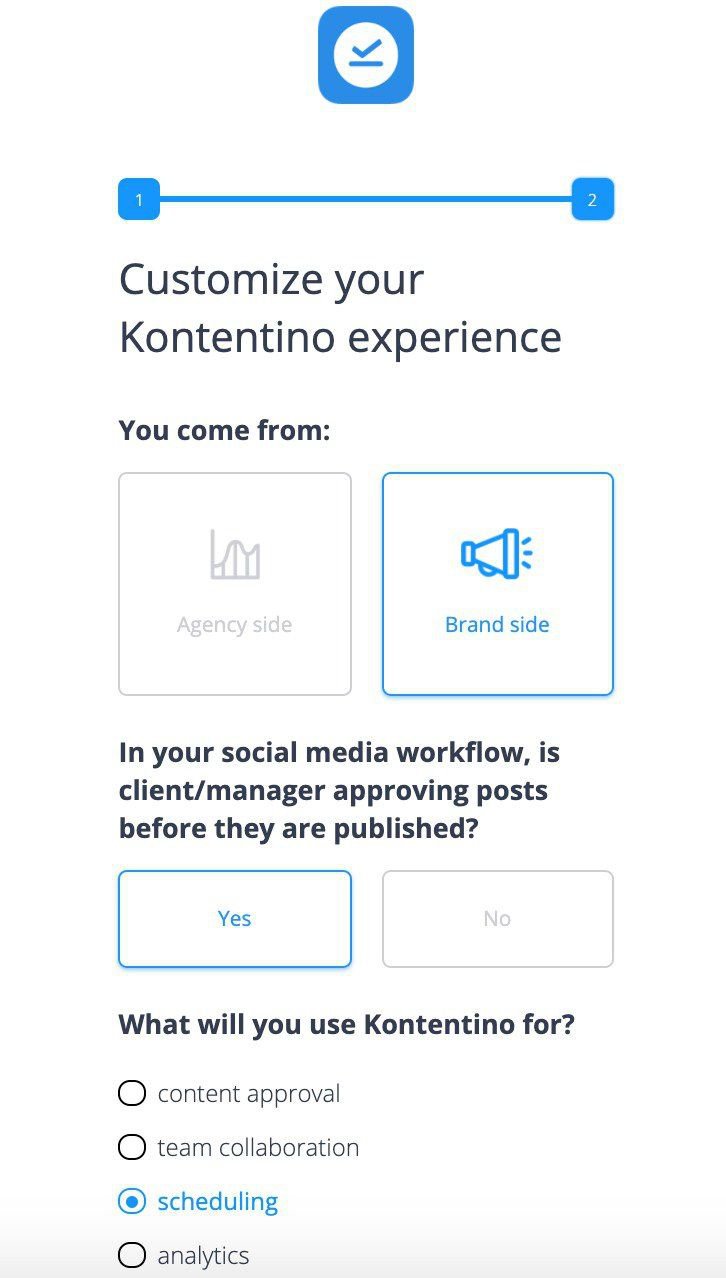
Use welcome screens to capture customer data and segment them based on jobs to be done
Welcome screens are not only useful for greeting users but also for collecting data.
This will allow you to use the data to build segments and personalize their user journey. Userpilot lets you create welcome screens and segment customers without any coding required.
Take a look at Kontentino’s example of how they collect data to later use it for onboarding personalization.
Track in-app interactions and have a rich understanding of customer behavior
To have a good understanding of your customers, you need to know what they do and how they interact with your product. To do so, you can track in-app user interactions and see what features they engage with the most.
Userpilot’s feature tagging allows you to track feature engagement, completely code-free. You can even track interactions such as hovers, clicks, and text inputs to collect more user data.
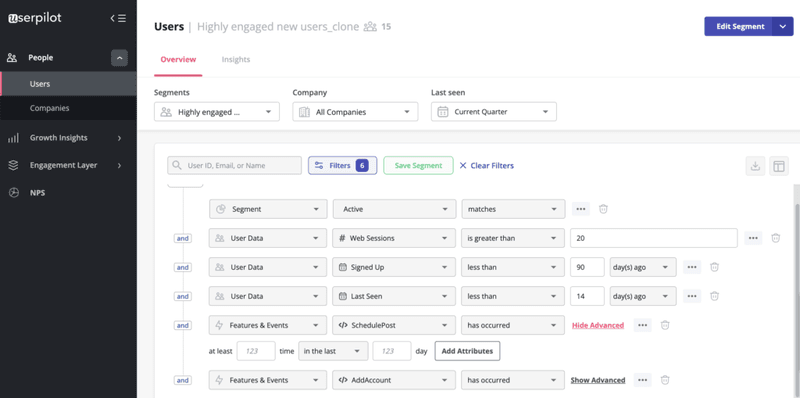
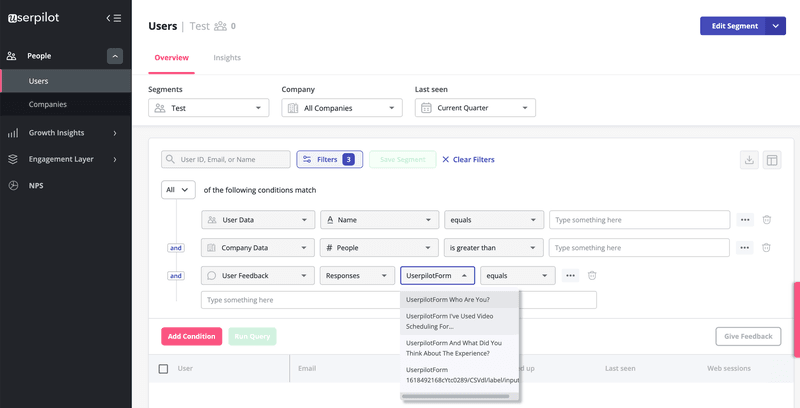
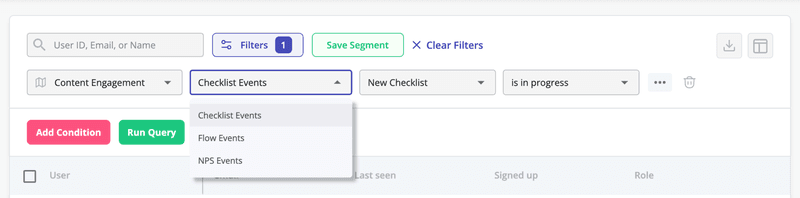
Build segments based on in-app engagement and behavior
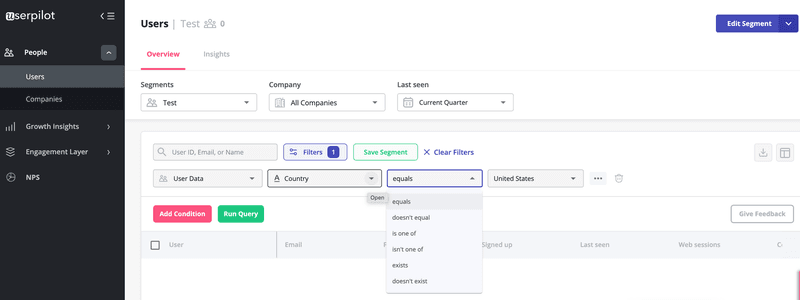
By tracking interactions in the app, you can now segment your customers. Userpilot’s advanced segmentation functionality comes with several filtering attributes like the user, company data, user feedback, feature and events, content engagement, etc.
Cross-referencing usage data from customer segments with product analytics will help you discover the features that customers engage with the most. This way, you can try to increase feature adoption among customers with low engagement levels.
Similarly, with Userpilot’s mobile SDK, you can create targeted onboarding flows using slideouts, carousels, and push notifications without writing extra code.
How to create user personas?
Now let’s see how you can develop personas.
Combine different research techniques to get an accurate picture of your customers
Use a combination of user research techniques to understand your customers more accurately.
UX researchers use various research methods to understand users and their different needs and behaviors. Collect as much data as possible through research methods like surveys, interviews, usability testing, tree testing, field studies, card sorting, etc.
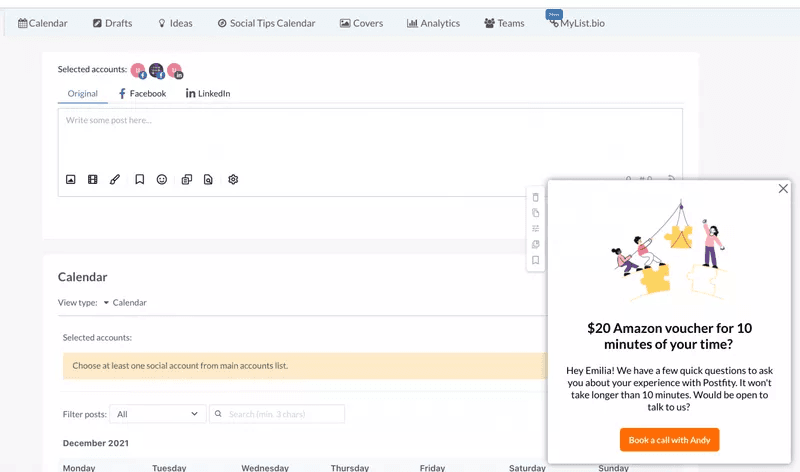
Launch a voice of the customer (VoC) program to collect and analyze individual user feedback. For example, Postfity offers incentives to customers to participate in user interviews. Such one-on-one interactions help you empathize with users and serve them better.
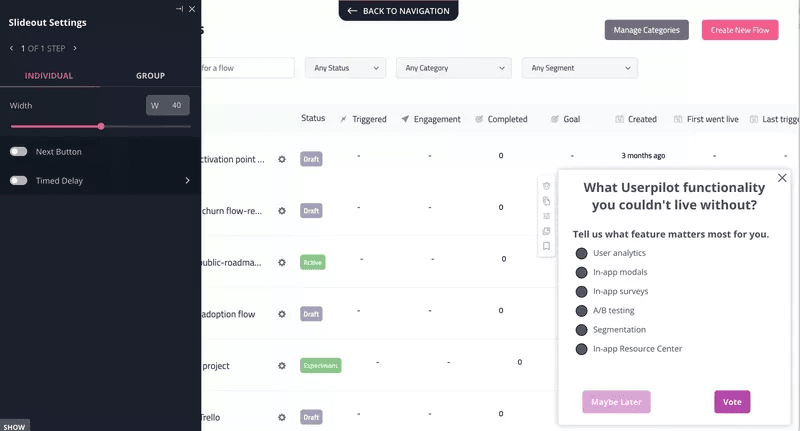
Send different types of microsurveys to collect qualitative data
Use various microsurveys at different stages of the user journey. Such surveys include net promoter score (NPS) surveys, customer satisfaction (CSAT) surveys, customer effort score (CES) surveys, and product-market fit surveys.
Although these surveys usually collect quantitative data, you can add follow-up qualitative questions to understand the reasons behind each customer’s score and gain more in-depth insights.
Userpilot enables you to build microsurveys code-free and analyze qualitative data.
Use customer persona templates to develop personas
You can use a user persona survey template that consists of a pre-built questionnaire.
There is a wide range of such survey templates, including the welcome screen mentioned earlier in the article, signup flow, churn surveys, and long-form surveys. They help you understand customers’ pain points, goals, and motivations before categorizing buyer personas.

Wrapping it up
Now that you know how user segments and personas differ from each other, you can use them properly.
A combination of segments and personas will offer actionable insights to help you select the right advertising channels and personalize user experiences.
Want to track in-app interactions, segment customers, or build microsurveys to collect feedback code-free? Get a Userpilot demo and boost your product growth.





