![How to Become a Product Designer [+Tools and Resources]](https://blog-static.userpilot.com/blog/wp-content/uploads/2024/07/How-to-Become-a-Product-Designer-Tools-and-Resources.png)
How to Become a Product Designer [+Tools and Resources]13 min read
Get The Insights!
The fastest way to learn about Product Growth, Management & Trends.
Product designer’s main responsibilities
A product designer plays a vital role in the SaaS industry, focusing on creating user-friendly and visually appealing software products.
They collaborate with cross-functional teams to ensure the design meets user needs and business objectives.
Here are the main responsibilities and duties:
- Conduct User Research: Gather insights on user needs, behaviors, and pain points through surveys, interviews, and usability testing.
- Create Wireframes and Prototypes: Develop wireframes, mockups, and interactive prototypes to visualize design solutions and iterate based on feedback.
- Design User Interfaces: Craft intuitive and visually appealing user interfaces for web and mobile applications, ensuring a seamless user experience.
- Collaborate with Cross-Functional Teams: Work closely with product managers, developers, and other stakeholders to define and implement innovative design solutions that align with product goals.
- Maintain Design Systems: Create and manage design systems and component libraries to ensure consistency and efficiency across all products.
- Conduct Usability Testing: Test designs with users to gather feedback and make necessary adjustments to improve usability and user satisfaction.
- Stay Updated with Design Trends: Keep abreast of the latest design trends, tools, and technologies to ensure the products are modern and competitive.
- Advocate for User-Centric Design: Promote user-centered design principles and best practices within the organization to ensure all products meet high usability standards.
- Iterate on Designs: Continuously refine and improve designs based on user feedback, analytics, and changing business requirements.
- Document Design Processes: Maintain clear documentation of design processes, decisions, and guidelines to ensure transparency and consistency.
These responsibilities ensure that a product designer effectively contributes to creating exceptional SaaS products that meet both user needs and business goals.
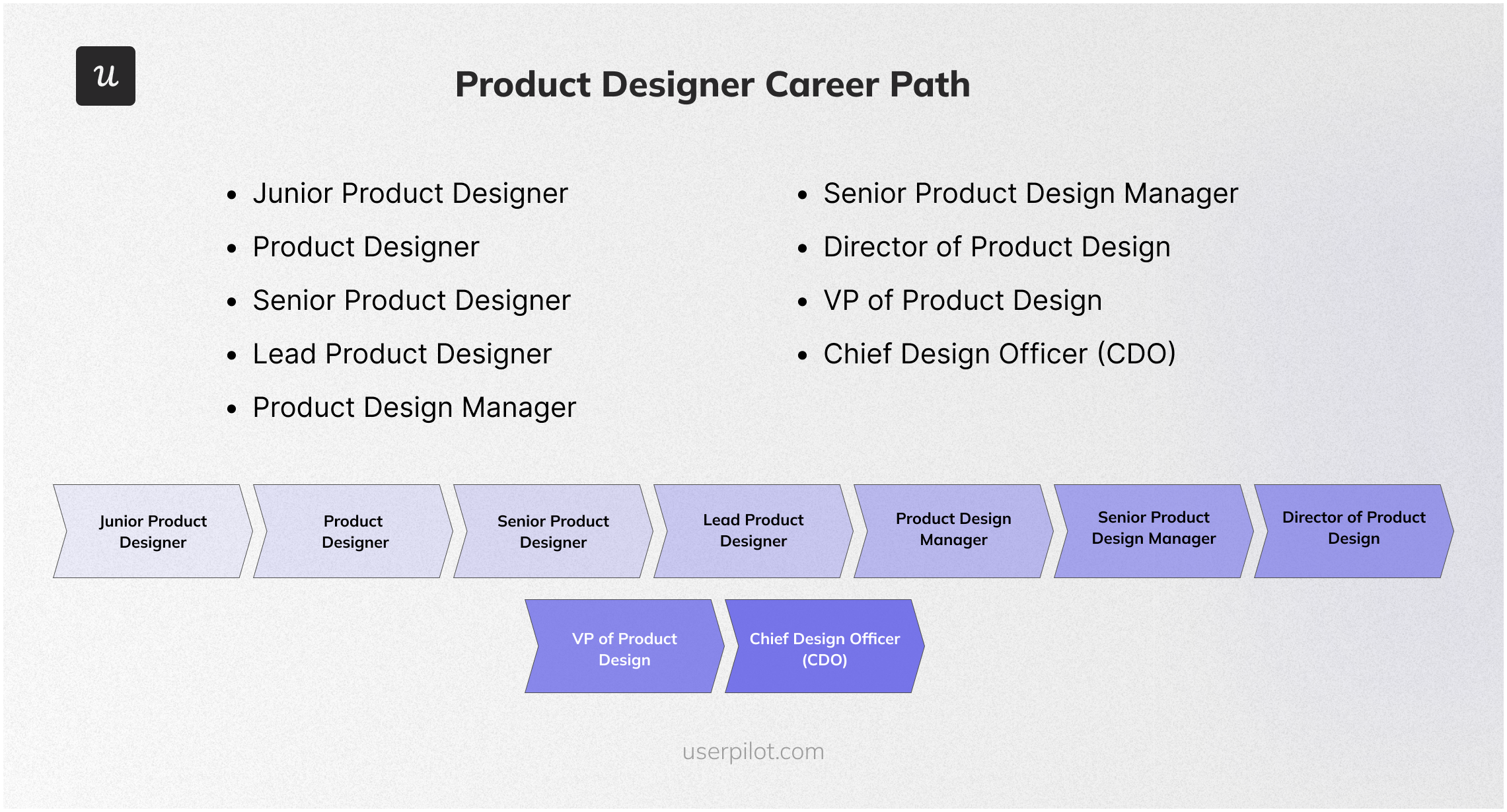
Product designer career path
A career in product design typically involves progressing through various roles that build on each other in terms of responsibility, expertise, and leadership.
Here’s a typical career progression for a product designer, from junior roles to senior leadership positions:
- Junior Product Designer – Assists senior designers, creates basic design components, and supports user research. Focus on learning design tools, building a strong portfolio, and seeking feedback to improve your skills.
- Product Designer – Involved in designing product interfaces, conducting usability tests, and collaborating with cross-functional teams. Take on more complex projects, deepen your understanding of UX principles, and start leading smaller design initiatives.
- Senior Product Designer – Leads major design projects, mentors junior designers, and plays a key role in strategic design decisions. Enhance leadership skills, contribute to design systems, and build strong relationships with product managers and developers.
- Lead Product Designer – Oversees the design team, ensures design consistency across projects, and aligns design goals with business objectives. Develop project management skills, drive innovation within the team, and engage in high-level strategic planning.
- Product Design Manager – Manages the design team, coordinates design projects, and ensures alignment with business goals and user needs. Enhance leadership and managerial skills, stay updated with industry trends, and focus on optimizing team performance and design processes.
- Senior Product Design Manager – Manages larger design teams, oversees multiple projects, and plays a critical role in company-wide design strategy. Develop a vision for the design department, influence company design culture, and mentor upcoming leaders within the team.
- Director of Product Design – Sets the overall design direction for the company, collaborates with top executives, and ensures the design vision aligns with the company’s mission. Focus on strategic leadership, expand your influence across departments, and drive the company’s design innovation.
- VP of Product Design – Responsible for the entire design organization, driving design excellence and contributing to the overall business strategy. Strengthen executive leadership skills, maintain a forward-thinking design vision, and foster a culture of creativity and innovation.
- Chief Design Officer (CDO) – Top-level executive overseeing all design aspects of the company, ensuring cohesive design strategy across all products and services. Focus on visionary leadership, drive company-wide design integration, and champion design as a core business value.
Each step in this career path builds on the previous one, emphasizing continuous learning, leadership, and strategic thinking to progress to higher levels of responsibility and influence in the field of product design.
How to become a product designer?
To become a product designer, you should start by obtaining a bachelor’s degree in a relevant field such as graphic design, industrial design, human-computer interaction, or a related discipline.
Coursework in these programs typically includes design principles, UX/UI design, prototyping, and user research. Additionally, learning design tools such as Sketch, Figma, and Adobe Creative Suite is essential.
Gaining practical experience through internships is crucial. Look for internships at tech companies, design firms, or startups where you can work on real projects and build a portfolio. A strong portfolio showcasing your best work and demonstrating your design process is vital when applying for jobs.
After your formal education, consider participating in online courses or boot camps to further refine your skills and stay updated with the latest design trends and tools. Networking through industry events, design communities, and online platforms like LinkedIn can also open doors to job opportunities and mentorship.
For more comprehensive guidance, you can refer to resources like CareerFoundry and Interaction Design Foundation.
What skills should a product designer have?
A successful product designer must possess a blend of technical and soft skills to create effective and engaging software products.
Soft skills are particularly crucial for collaboration, problem-solving, and effective communication.
Here are the essential soft skills for a product designer:
- Empathy: Understanding and sharing the feelings of users to design products that truly meet their needs and improve their experience.
- Collaboration: Working effectively with cross-functional teams, including product managers, developers, and other stakeholders, to ensure cohesive and aligned design solutions.
- Communication: Articulating design ideas and concepts clearly and persuasively to team members, stakeholders, and clients, ensuring everyone understands the design vision and objectives.
- Adaptability: Staying flexible and open to feedback, new ideas, and changes, which is essential in a fast-paced and ever-evolving design environment.
- Creative Thinking: Approaching problems with innovative solutions and thinking outside the box to design unique and effective user experiences.
- Time Management: Prioritizing tasks and managing time efficiently to meet deadlines and deliver high-quality designs on schedule.
- Problem-Solving: Analyzing and addressing design challenges effectively, finding solutions that balance user needs, business goals, and technical constraints.
- Attention to Detail: Ensuring precision and accuracy in design elements, which contributes to a polished and professional final product.
- Leadership: Guiding and mentoring junior designers, fostering a collaborative and innovative team environment.
- Critical Thinking: Evaluating design decisions critically to ensure they are based on solid research, data, and user feedback.
These soft skills enable a product designer to navigate complex projects, work well with diverse teams, and create user-centric products that meet both business and user needs.
Best certifications for product designers
While there aren’t many widely recognized certifications specifically for product designers, the following are often valued by employers:
- Google UX Design Professional Certificate (Coursera): This beginner-friendly program covers the fundamentals of UX design and provides a solid foundation for aspiring product designers. It’s well-regarded for its practical approach and job-ready curriculum.
- Interaction Design Foundation (IDF) Membership: While not a certification per se, an IDF membership offers access to a wide range of UX design courses and resources, including specialized courses on interaction design, user research, and information architecture. The IDF is highly respected in the UX design community and its courses are often cited as valuable learning resources.
- Nielsen Norman Group UX Certification: This certification program, offered by the renowned Nielsen Norman Group, covers a range of UX topics, including user research, information architecture, interaction design guidelines, and usability testing. It’s known for its rigor and focus on evidence-based design practices.
- Certified Usability Analyst (CUA): Offered by Human Factors International, this certification focuses on usability testing and evaluation, a critical skill for product designers. It demonstrates your ability to conduct effective usability tests and analyze user feedback to improve product design.
These certifications and memberships are not strictly “necessary” for product designers, but they can significantly enhance your credibility and demonstrate your commitment to professional development.
Best resources for product designers
To stay ahead in the dynamic field of product design, leveraging a variety of resources is crucial.
Here are some top recommendations for books, webinars, podcasts, and blogs that every product designer should explore.
Best books for product designers
Reading books by industry experts can provide deep insights and practical knowledge about product design and management.
- “The Design of Everyday Things” by Don Norman – This classic book offers deep insights into the principles of good design and human-centered design.
- “Hooked: How to Build Habit-Forming Products” by Nir Eyal – Explores the psychology behind user habits and how to create products that keep users engaged.
- “Lean UX: Designing Great Products with Agile Teams” by Jeff Gothelf and Josh Seiden – Provides practical advice on integrating UX design with Agile methodologies.
- “Inspired: How To Create Products Customers Love” by Marty Cagan – A comprehensive guide on product management and creating products that delight customers.
- “Sprint: How to Solve Big Problems and Test New Ideas in Just Five Days” by Jake Knapp – A step-by-step guide to solving problems and testing ideas quickly.
Best webinars for product designers
Participating in webinars can offer real-time learning and insights from industry experts.
- Userpilot Webinars – Focused on user onboarding, engagement, and product growth.
- Nielsen Norman Group Webinars – Expert insights on various UX topics, including usability, user research, and interaction design.
- UX Design Institute Webinars – Covers UX design principles, methodologies, and career advice.
- Adobe XD Webinars – Tutorials and deep dives into design tools and best practices using Adobe XD.
- InVision Webinars – Discussions with industry experts on design, collaboration, and product management.
Best blogs for product designers
Following blogs can help you stay updated on the latest trends, tips, and best practices in product design and management.
- Userpilot Blog – Insights on user onboarding, product growth, and UX design.
- Nielsen Norman Group Blog – In-depth articles on usability, user experience, and design research.
- Smashing Magazine – Covers a wide range of topics, including UX design, web development, and product management.
- UX Collective – Community-driven platform with articles on UX design, product design, and industry trends.
- IDEO Blog – Shares stories and insights from one of the leading design firms.
These resources provide valuable knowledge and practical advice, helping you stay current and excel in your role as a Product Designer.
Best podcasts for product designers
Listening to podcasts is a convenient way to stay informed and inspired by industry leaders while on the go.
- “The Design Better Podcast” by InVision – Interviews with design leaders discussing the craft and business of design.
- “High Resolution” – In-depth conversations with design leaders from top companies.
- “The UX Podcast” – Discusses UX design, strategy, and how to integrate UX into business practices.
- “Product to Product” – A podcast for product people, by product people, covering various aspects of product management and design.
- “Product Love” – Focuses on product management and features interviews with product leaders.
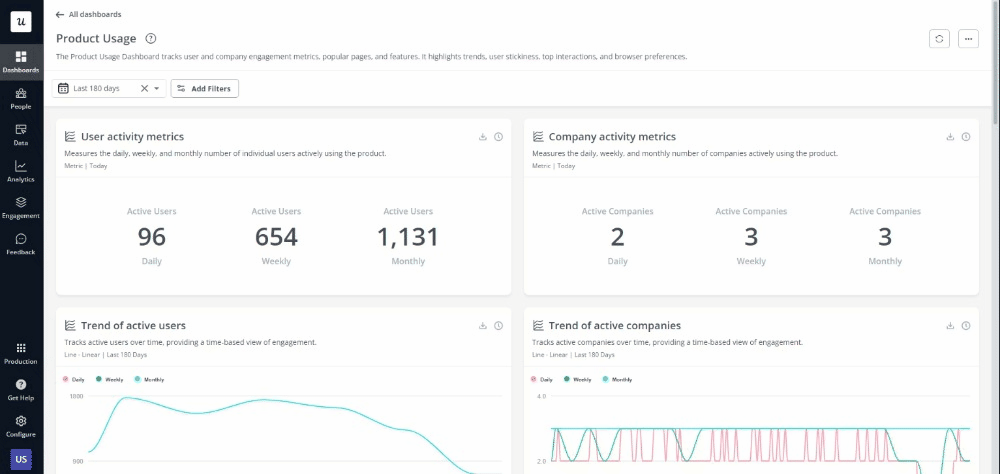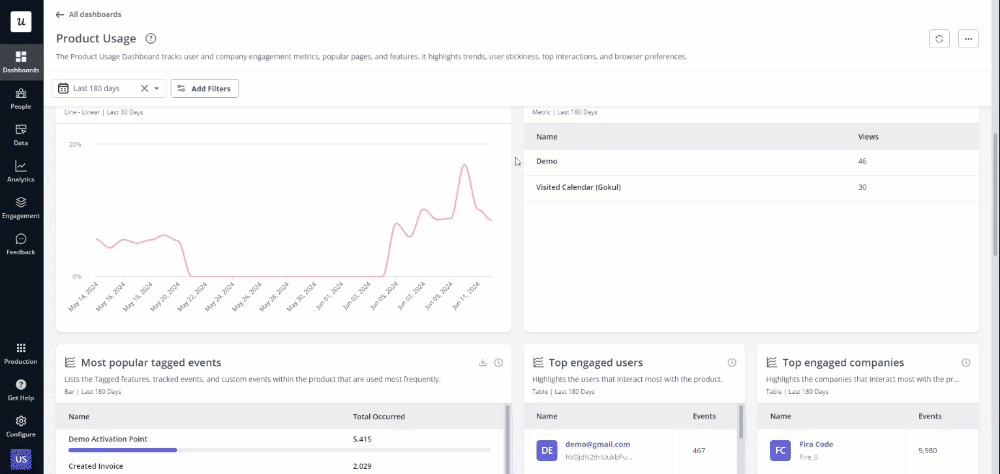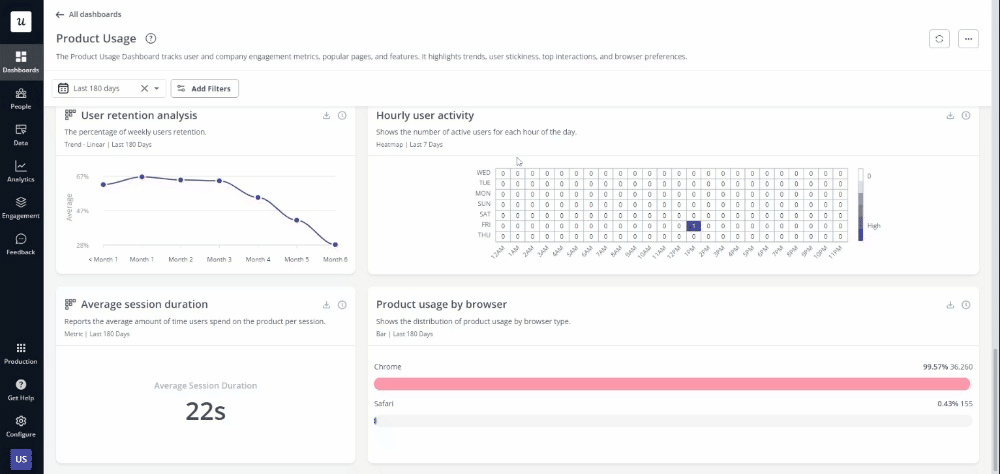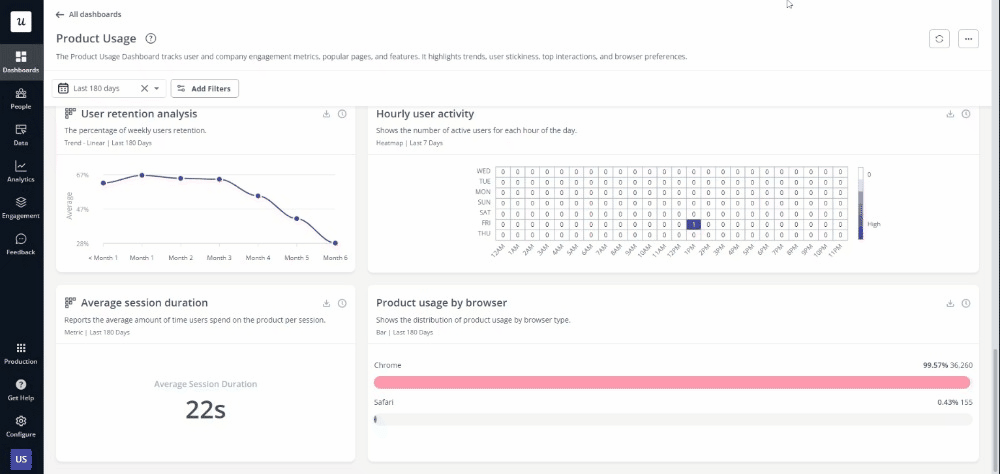
Best tools for product designers
Leveraging the right tools can greatly enhance productivity, creativity, and collaboration.
Here are ten essential tools for various aspects of product design:
- Best tool for User Onboarding and Engagement – Userpilot: Userpilot helps product designers create personalized in-app experiences and effective onboarding processes, improving user engagement and retention.
- Best tool for Project Management – Monday: Monday.com offers a visual and flexible platform for managing projects and tasks, aiding teams in efficient collaboration and keeping projects on schedule.
- Best tool for Product Management – Jira Software: Jira Software is a robust tool for tracking and managing development tasks, sprints, and releases, ensuring seamless collaboration between designers and developers.
- Best tool for Customer Experience – Zendesk: Zendesk provides comprehensive customer support solutions, enabling teams to manage customer inquiries, feedback, and support tickets effectively.
- Best tool for Customer Success – ClientSuccess: ClientSuccess helps manage and measure customer relationships, ensuring customers achieve their desired outcomes with the product.
- Best tool for UX/UI Design – Figma: Figma is a cloud-based design tool that allows for real-time collaboration, making it ideal for teams working together on UX/UI design projects.
- Best tool for UX/UI Design – Sketch: Sketch is a vector graphics editor focused on digital design, offering a wide range of plugins and integrations to streamline the design process.
- Best tool for UX/UI Design – InVision Studio: InVision Studio provides advanced prototyping and animation capabilities, enabling designers to create interactive and high-fidelity prototypes.
- Best tool for UX/UI Design – Adobe XD: Adobe XD is a powerful design and prototyping tool that offers seamless integration with other Adobe Creative Cloud apps, enhancing the overall design workflow.
- Best tool for Data Analytics – Tableau: Tableau provides powerful data visualization capabilities, allowing teams to analyze and present data in an intuitive and visually appealing way.
These tools collectively enable product designers to create user-centric designs, manage projects efficiently, and collaborate effectively with their teams.
Product designer FAQs
- Is product design the same as UX design? Product design encompasses UX design but also includes other aspects such as UI design, interaction design, and even some elements of product strategy and development. While UX design focuses specifically on the user’s experience and interaction with the product, product design takes a more holistic approach, covering the overall look, feel, and functionality of the product.
- Is product designer a good career? Yes, product design is a rewarding career that offers opportunities for creativity, innovation, and impact. Product designers are in high demand, especially in tech industries, and they play a crucial role in creating user-friendly and aesthetically pleasing products that meet business goals. The field offers competitive salaries and opportunities for growth and advancement.
- Does product design require coding? While coding is not a primary requirement for product designers, having a basic understanding of coding can be beneficial. Knowledge of HTML, CSS, and JavaScript can help designers better communicate with developers, understand technical constraints, and create more feasible and efficient designs.
- Who earns more, UX or product designer? Salaries for UX designers and product designers can vary depending on the company, location, and level of experience. Generally, product designers tend to earn slightly more than UX designers because their role often encompasses a broader range of responsibilities, including both UX and UI design, as well as some aspects of product strategy.
- Can I be a product designer without a degree? Yes, it is possible to become a product designer without a degree. Many successful product designers have built their careers through self-study, online courses, boot camps, and practical experience. A strong portfolio showcasing your design skills and creativity is often more important than formal education in this field.
Conclusion
Becoming a successful product designer requires dedication, continuous learning, and a proactive approach to developing relevant skills.
By following the outlined steps and leveraging the resources available, you can effectively navigate your career path and achieve your professional goals.
We hope this guide has provided you with valuable insights and practical advice to help you on your journey to becoming a proficient and impactful product designer!
Looking into tools for product designers? Userpilot is an all-in-one product platform with engagement features and powerful analytics capabilities. Book a demo to see it in action!