![How to Become a Cx Designer [+Tools and Resources]](https://blog-static.userpilot.com/blog/wp-content/uploads/2024/07/How-to-Become-a-CX-Designer-tools-and-resources-450x295.png)
How to become a CX designer?
- A customer experience designer (CX Designer) focuses on creating and optimizing the interactions that customers have with a company’s products or services.
- This role is dedicated to enhancing every touchpoint in the customer journey to ensure a seamless, engaging, and satisfying experience. In the SaaS industry, a CX Designer uses user research, data analysis, and design thinking to improve user interfaces, streamline onboarding processes, and ensure ongoing customer satisfaction.
- Progressing in a career as a customer experience designer typically involves moving through various roles that build on increasing responsibility and expertise. Here’s a typical career progression:
- Junior Customer Experience Designer
- Customer Experience Designer
- Senior Customer Experience Designer
- Lead Customer Experience Designer
- Customer Experience Manager
- Senior Customer Experience Manager
- Director of Customer Experience
- To become a customer experience designer, start by obtaining a bachelor’s degree in a relevant field such as design, human-computer interaction, psychology, or a related discipline.
- Coursework should include user research, interaction design, and visual design principles. Gaining practical experience through internships is crucial; look for opportunities at tech companies, design firms, or startups where you can work on real projects.
- Customer experience designers utilize a variety of tools to enhance their work. Userpilot assists in user onboarding and engagement, while Monday and Jira Software aid in project and product management, etc.
- Looking into tools for CX designers? Userpilot is an all-in-one product platform with engagement features and powerful analytics capabilities. Book a demo to see it in action!
CX designer’s main responsibilities
A customer experience designer plays a crucial role in the SaaS industry, focusing on optimizing the entire customer journey to enhance satisfaction and loyalty. Here are the main responsibilities and duties of a customer experience designer:
- Conduct User Research: Gather insights into customer needs, behaviors, and pain points through surveys, interviews, and usability testing to inform design decisions.
- Develop Customer Journey Maps: Create detailed journey maps that visualize the end-to-end customer experience, identifying key touchpoints and opportunities for improvement.
- Design User Interfaces and Interactions: Craft intuitive and visually appealing user interfaces and interactions that enhance the overall user experience across all touchpoints.
- Collaborate with Cross-Functional Teams: Work closely with product managers, developers, marketers, and other stakeholders to ensure a cohesive and seamless customer experience.
- Analyze Customer Data: Utilize customer feedback and data analytics to identify trends, measure the effectiveness of design solutions, and make data-driven improvements.
- Create and Test Prototypes: Develop prototypes of new features or improvements and conduct usability testing to gather feedback and refine designs before implementation.
- Ensure Consistency in Design: Maintain design consistency across all customer-facing products and platforms, adhering to brand guidelines and design standards.
- Monitor and Evaluate Customer Experience: Continuously monitor and evaluate the customer experience, implementing iterative improvements based on user feedback and evolving customer needs.
- Advocate for Customer-Centric Design: Promote user-centered design principles within the organization, ensuring that customer needs are prioritized in all design and development efforts.
- Stay Updated with Industry Trends: Keep abreast of the latest trends, tools, and best practices in customer experience design to bring innovative ideas to the team.
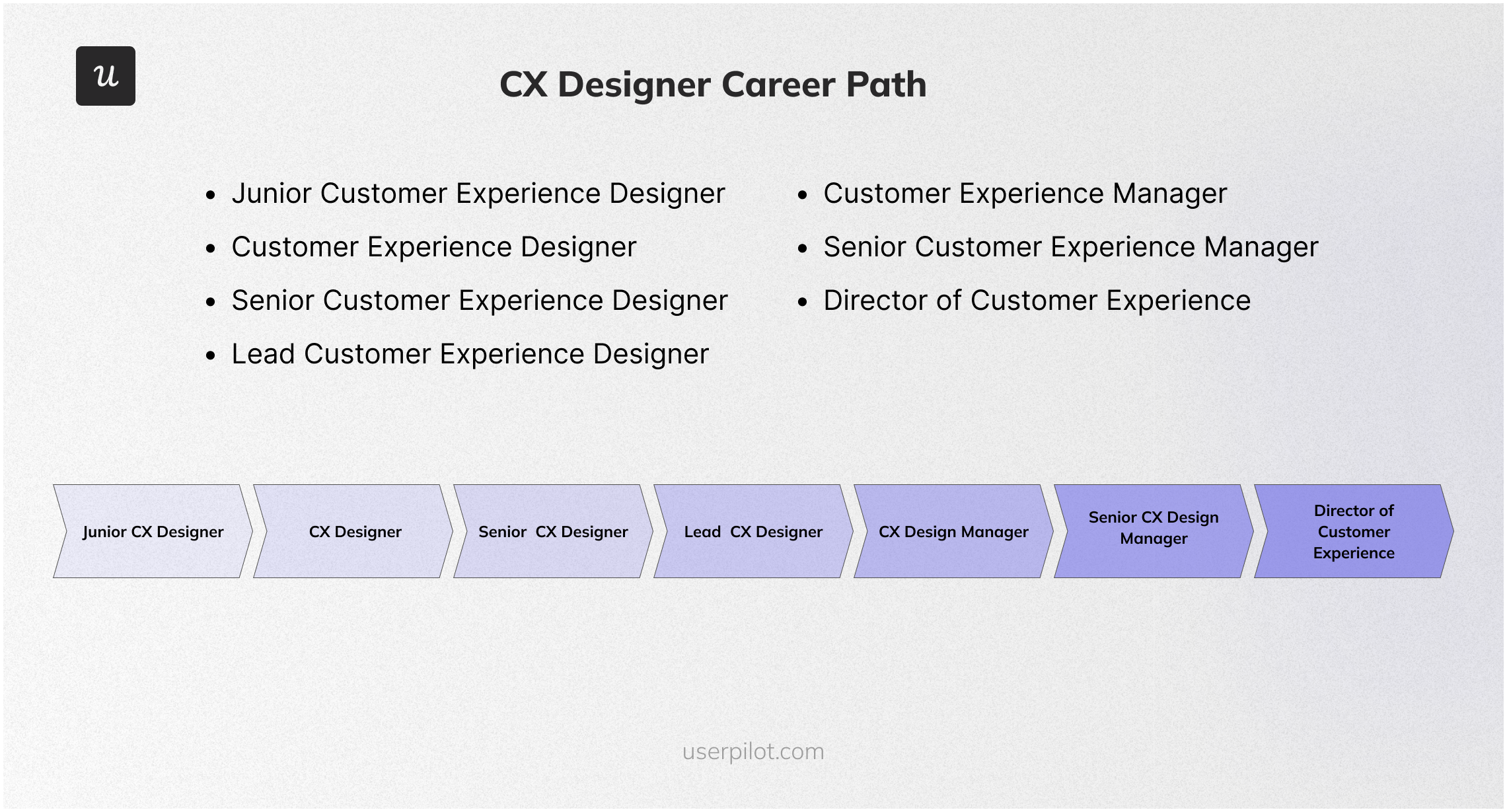
CX designer career path
Progressing in a career as a customer experience designer typically involves moving through various roles that build on increasing responsibility and expertise. Here’s a typical career progression:
- Junior Customer Experience Designer – Entry-level position focused on assisting senior designers, conducting user research, and creating basic design components. To progress, focus on learning design tools, building a portfolio, and gaining practical experience.
- Customer Experience Designer – Responsible for designing user interfaces and experiences, conducting usability tests, and collaborating with cross-functional teams. To advance, take on more complex projects and deepen your understanding of user-centered design principles.
- Senior Customer Experience Designer – Leads major design projects, mentors junior designers, and plays a key role in strategic design decisions. Enhance leadership skills, contribute to creating design systems, and build strong relationships with other departments.
- Lead Customer Experience Designer – Oversees the design team, ensures design consistency across projects, and aligns design goals with business objectives. Develop project management skills and engage in high-level strategic planning.
- Customer Experience Manager – Manages the customer experience design team, coordinates design projects, and ensures alignment with business goals and user needs. Enhance leadership and managerial skills, stay updated with industry trends, and focus on optimizing team performance and design processes.
- Senior Customer Experience Manager – Manages larger design teams, oversees multiple projects, and plays a critical role in company-wide design strategy. Develop a vision for the customer experience department and mentor upcoming leaders.
- Director of Customer Experience – Sets the overall customer experience strategy for the company, collaborates with top executives, and ensures the design vision aligns with the company’s mission. Focus on strategic leadership and drive the company’s customer experience innovation.
Each step in this career path builds on the previous one, emphasizing continuous learning, leadership, and strategic thinking to progress to higher levels of responsibility and influence in the field of customer experience design.
How to become a CX designer?
To become a customer experience designer, start by obtaining a bachelor’s degree in a relevant field such as design, human-computer interaction, psychology, or a related discipline.
Coursework should include user research, interaction design, and visual design principles. Gaining practical experience through internships is crucial; look for opportunities at tech companies, design firms, or startups where you can work on real projects.
Building a strong portfolio showcasing your work is essential. Additionally, consider taking online courses or attending workshops to stay updated with the latest design tools and trends. Networking through industry events and joining design communities can also help in securing job opportunities and mentorship.
What skills should a CX designer have?
A successful customer experience designer needs a blend of technical know-how and soft skills to create exceptional user experiences. Here are the essential soft skills for this role:
- Empathy: The ability to understand and share the feelings of customers is crucial. Empathy allows designers to put themselves in the users’ shoes, leading to more user-centric designs that address real needs and pain points.
- Collaboration: Working effectively with cross-functional teams, including product managers, developers, marketers, and other stakeholders, is vital. Collaboration ensures that design solutions are aligned with business goals and technical feasibility.
- Communication: Strong verbal and written communication skills are essential for articulating design ideas, presenting concepts to stakeholders, and explaining design decisions. Clear communication fosters better understanding and collaboration within the team.
- Adaptability: The design process often involves changes and iterations based on feedback. Being adaptable and open to feedback helps in refining designs and improving the overall customer experience.
- Creative Problem-Solving: The ability to think creatively and come up with innovative solutions to complex problems is crucial. Creative problem-solving enables designers to tackle challenges and design unique, effective user experiences.
- Attention to Detail: Ensuring precision and accuracy in design elements is important for creating professional and polished products. Attention to detail helps in maintaining consistency and quality across all design aspects.
- Time Management: Effectively managing time and prioritizing tasks ensures that projects are completed on schedule without compromising on quality. Good time management helps in balancing multiple projects and meeting deadlines.
- User-Centric Mindset: Always keeping the user at the forefront of the design process is key. A user-centric mindset ensures that all design decisions are made with the user’s needs and preferences in mind.
- Analytical Thinking: The ability to analyze user data, feedback, and trends helps in making informed design decisions. Analytical thinking aids in identifying areas for improvement and measuring the impact of design changes.
- Leadership: Guiding and mentoring junior designers, leading design projects, and advocating for customer-centric design principles within the organization are important leadership skills for a CX designer.
These soft skills enable a customer experience designer to effectively collaborate, communicate, and create designs that enhance the overall user experience.
Best certifications for CX designers
While there’s no single “must-have” certification for CX designers, the following are highly regarded and can significantly enhance your knowledge and skills:
- Certified Customer Experience Professional (CCXP): Offered by the CXPA (Customer Experience Professionals Association), this is the most widely recognized and respected certification in the CX field. It validates your knowledge across all CX disciplines and demonstrates your commitment to the profession.
- Customer Experience Design Certification (NPSx): Developed by Bain & Company, this certification focuses on applying design thinking principles to create customer-centric experiences. It’s especially valuable for those interested in using design thinking to drive CX improvements.
- Forrester CX Certification: Forrester, a leading research and advisory firm, offers various CX certifications for different roles and levels of expertise. These certifications are highly regarded for their industry relevance and focus on practical skills.
- Agile Customer Experience (CX) Design Expert Certification: This certification, offered by the Institute of Digital Marketing New Zealand, focuses on applying agile methodologies to CX design. It’s a good choice for those working in fast-paced environments where rapid iteration and adaptation are key.
- Nielsen Norman Group UX Certification: While not specifically for CX, this certification covers many relevant UX principles and research methods that are essential for CX design.
Best resources for CX designers
To stay ahead in the dynamic field of customer experience design, leveraging a variety of resources is essential.
Here are some top recommendations for books, webinars, podcasts, and blogs that every customer experience designer should explore.
Best books for CX designers
Reading books by industry experts can provide deep insights and practical knowledge about customer experience design.
- “The Elements of User Experience” by Jesse James Garrett – Covers the fundamentals of user experience design.
- “Service Design: From Insight to Implementation” by Andy Polaine, Lavrans Løvlie, and Ben Reason – A comprehensive guide to service design principles.
- “Smashing UX Design” by Jesmond Allen and James Chudley – Provides practical advice and real-world examples for UX design.
- “Designing for Interaction” by Dan Saffer – Focuses on creating engaging and effective interaction designs.
- “Change by Design” by Tim Brown – Explores how design thinking transforms organizations and inspires innovation.
Best webinars for CX designers
Participating in webinars can offer real-time learning and insights from industry experts.
- Userpilot Webinars – Focused on user onboarding, engagement, and product growth.
- UXPin Webinars – Offers webinars on design systems, UX strategy, and prototyping.
- Interaction Design Foundation Webinars – Covers various aspects of UX design and usability.
- Baymard Institute Webinars – Provides insights into UX research and e-commerce usability.
- UX Design Institute Webinars – In-depth discussions on UX design principles and career development.
Best blogs for CX designers
Following blogs can help you stay updated on the latest trends, tips, and best practices in customer experience design.
- Userpilot Blog – Insights on user onboarding, product growth, and UX design.
- UX Booth – Articles on user experience, usability, and interaction design.
- Usability Geek – Focuses on usability, UX, and HCI (Human-Computer Interaction).
- NNG Blog (Nielsen Norman Group) – Research-based articles on UX design and usability.
- Smashing Magazine – Covers a wide range of topics, including UX design, web development, and product management.
Best podcasts for CX designers
Listening to podcasts is a convenient way to stay informed and inspired by industry leaders while on the go.
- “User Defenders” – Interviews with UX design heroes who share their stories and insights.
- “The Crazy One” – Hosted by Stephen Gates, covering creativity, leadership, and innovation in design.
- “UI Breakfast” – Conversations about UI/UX design, product strategy, and business.
- “What is Wrong with UX” – Two experienced UX designers discuss and critique current trends and practices.
- “Awkward Silences” – Focuses on user research and customer experience insights.
Best tools for CX designers
To enhance productivity and collaboration, customer experience designers utilize a variety of tools tailored to different aspects of their work.
Here are ten essential tools for various use cases:
- Best tool for User Onboarding and Engagement – Userpilot: Userpilot helps design personalized in-app experiences and onboarding processes to enhance user engagement and retention.
- Best tool for Project Management – Monday: Monday.com offers a visual platform for managing projects and tasks, facilitating efficient collaboration and progress tracking.
- Best tool for Product Management – Jira Software: Jira Software is ideal for tracking and managing development tasks, sprints, and releases, ensuring seamless communication between teams.
- Best tool for Customer Experience – Zendesk: Zendesk provides comprehensive customer support solutions, enabling efficient handling of customer inquiries, feedback, and support tickets.
- Best tool for Customer Success – ClientSuccess: ClientSuccess assists in managing and measuring customer relationships, ensuring customers achieve their desired outcomes with the product.
- Best tool for UX/UI Design – Figma: Figma supports real-time collaboration, making it perfect for teams working together on UX/UI design projects and creating interactive prototypes.
- Best tool for UX/UI Design – Sketch: Sketch is a vector graphics editor tailored for digital design, offering numerous plugins and integrations to streamline the design process.
- Best tool for Documentation and Collaboration – Confluence: Confluence is a collaboration tool that allows teams to create, share, and manage project documentation effectively.
- Best tool for Customer Feedback – Freshdesk: Freshdesk helps in collecting and analyzing customer feedback, improving the overall customer experience.
- Best tool for Data Analytics – Tableau: Tableau offers powerful data visualization capabilities, allowing teams to analyze and present data in an intuitive and visually appealing manner.
These tools collectively empower customer experience designers to create user-centric designs, manage projects effectively, and collaborate efficiently with their teams.
Conclusion
Becoming a successful CX designer requires dedication, continuous learning, and a proactive approach to developing relevant skills.
By following the outlined steps and leveraging the resources available, you can effectively navigate your career path and achieve your professional goals.
We hope this guide has provided you with valuable insights and practical advice to help you on your journey to becoming a proficient and impactful CX designer!
Looking into tools for CX designers? Userpilot is an all-in-one product platform with engagement features and powerful analytics capabilities. Book a demo to see it in action!
FAQ
What is designing customer experience?
Designing customer experience involves creating and optimizing all interactions customers have with a brand, ensuring a seamless and satisfying journey from start to finish.
What is the difference between CX and UX?
CX covers the entire customer journey across all touchpoints with a brand, while UX focuses specifically on the interaction between users and a product or service.
What is the meaning of experience designer?
A customer experience designer creates and optimizes user interactions with products, services, or brands to ensure engaging, efficient, and enjoyable experiences.
How do I become a user experience designer?
Obtain a degree in design, human-computer interaction, or a related field, gain practical experience through internships, build a strong portfolio, and consider specialized courses or certifications in UX design.
Is CX a good career?
Yes, CX is a growing field with high demand, offering opportunities to improve customer interactions and brand loyalty, with competitive salaries and career advancement potential.






