Every seasoned product marketer knows that adding new features to your product is key to product management success. But not just any features will do. You need a robust ideation process to bring the right ideas to life and add more value for your users.
This guide explains what feature ideation is, what strategies to use to come up with new ideas, and how to focus on the right ones.
Summary feature ideation
- Feature ideation is a process through which product teams brainstorm ideas for new features to introduce to their product.
- It helps you meet user needs, enhance user experience, improve product value, and gain a competitive advantage.
- The first stage of an ideation technique involves gathering ideas from different sources such as feature usage trends, feature requests, customer reviews, user behavior, and competitor analysis.
- The second stage requires you to round out your ideas to make them more comprehensive. You can do this by asking key questions related to product gaps, competitor features, and more.
- The features then have to be prioritized based on your goals so that the resources are allocated to impactful endeavors.
- You then build prototypes of the features to gain an understanding of user experience and preferences.
- The last stage of the product ideation process involves testing the features with small focus groups and collecting feedback to fine-tune them.
- There are various techniques for ideating features—some involving user data and others relying on productive ideation sessions.
- Brainstorming sessions involve sitting down and coming up with unique ideas for your product features and prioritizing them.
- Mind mapping is a product design method that dives deep into various aspects of a central topic to get new feature ideas.
- User journey mapping helps you visually see gaps in the product experience that need plugging.
- The SCAMPER product ideation technique categorizes existing features into the following buckets: Substitute, Combine, Adapt, Modify (includes Magnify and Minify), Put to another use, Eliminate, and Reverse. Based on these, you can ideate feature enhancements.
- Role-play involves placing yourself in the user’s shoes to dive into user psychology and understand how they react to different situations.
- A SWOT analysis helps discover gaps and opportunities in your product for new feature development.
- Prototyping builds a minimum viable product with new feature ideas to test their impact on the user experience.
- The Analogy product ideation process helps you find innovative product feature ideas through analogies.
- Reverse engineering involves defining a goal and backtracking from it to find feature ideas to take you there.
- Userpilot is a product growth tool that lets you track feature usage with powerful data analytics, collect user feedback, and build in-app onboarding flows to introduce new features. Book your demo to learn more.
What is feature ideation?
Feature ideation is the process of brainstorming new feature ideas to add to your SaaS product. It informs the creative process for product roadmapping and helps focus on impactful feature enhancements.
Why do you need feature ideation in your product development process?
Here are some reasons why the idea-generation process is non-negotiable in product development.
- Effectively meet user needs: The ideation process helps propose new features that users might want. It involves understanding their needs and what they expect.
- Enhance user experience: A successful ideation session can help you develop features that can elevate the product experience.
- Gain competitive advantage: The ideation process brings fresh ideas to the forefront of product development to help you differentiate yourself and overcome product parity.
- Maximize product value: Creating features that users want helps increase product value, product stickiness, and in turn, retention.
Feature ideation phases
Follow the ideation process to discover new ideas for features and incorporate them into your business strategies.
Ideation phase 1: Generate ideas from different sources
Before you develop a new feature, it’s important to generate as many ideas as possible to get started. Here are various methods you can use to collect new product ideas.
Feature usage trends
Start by looking at your feature usage trend reports. Which features are popular among your users? How often are they used? Think about what can be done to improve the features as well.
Also, look at which features force users to try other platforms simply because you don’t have them. For instance, if your onboarding tool doesn’t offer a no-code builder, your users might use other platforms for creating email drafts.
With Userpilot, you can easily observe feature usage trends and use them to inform the ideation process.

Feature requests
Asking your users is one of the best methods for idea generation. Put up a modal asking users about the features they want in your product. Then, look at the feature requests feedback to identify the most common requests. This will help you build the most-requested features, giving users exactly what they want.
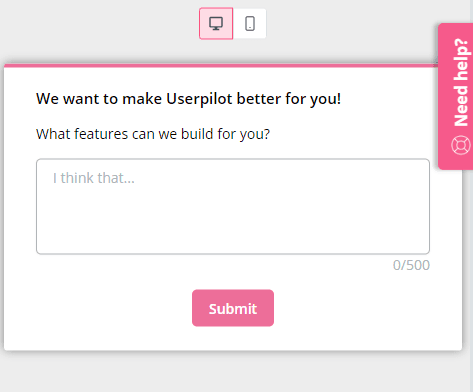
Customer interviews
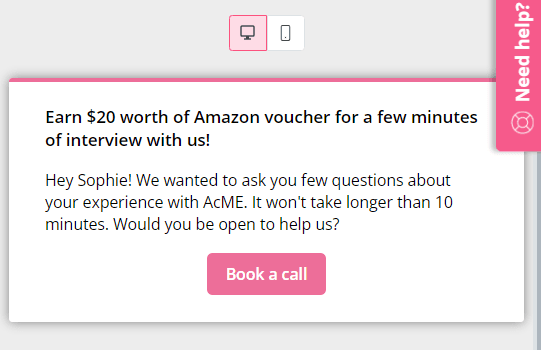
Another handy ideation technique is user interviews. Customer interviews can tell you a lot about what customers want from your product, allowing you to generate creative ideas for your features accordingly.
User behavior research
You can also generate new ideas by performing user behavior analysis. This helps identify how users leverage your features, what UI elements they’re attracted to, and where they face friction.
For example, a trend analysis report can help identify popular features. You can use the insights to ideate related features knowing they would likely please your user base.

Competitive research
While other ideation techniques involve user and product analysis, this one deals with your competitors. Comparing your product with existing solutions allows you to identify feature gaps and understand what your target audience is expecting from other companies.
For inspiration, head over to competitor websites to explore their offerings. Learn more about their feature sets, explore new releases, and analyze their roadmap if it’s public.
Ideation phase 2: Round out product ideas
Now that you’ve used ideation techniques to get a bunch of new ideas for product feature design, let’s get them sorted. They’re still quite raw, and you need to make them more comprehensive.
Here are some questions that can help round out and refine the ideas you’ve collected through the design thinking process.
- Are there any overlooked or emerging needs that need to be addressed?
- What features do your competitors offer, and how do yours compare?
- Are there any gaps in the market that our product can fill?
- How do the proposed features enhance the overall user experience?
- Do we have the technical capabilities to implement the proposed features?
- Do the proposed features align with the product’s value proposition?
- What resources (e.g., budget, employees) are required to implement and support the new features?
- Do the proposed features align with the product’s long-term roadmap and vision?
- How will the features evolve to keep up with changing user needs and market trends?
Ideation phase 3: Prioritize feature ideas based on your objectives
Now that you’ve rounded out your ideas, it’s time to prioritize them based on their importance. This is where feature prioritization comes in.
Decide the objective of your feature development and use it to guide your prioritization framework.
For instance, if you’re an email marketing tool and your current goal is to automate email creation with ease, you would prioritize features like drag-and-drop builders, HTML editors, image library, and so on.
Ideation phase 4: Build the prototype
Now, it’s time to put your feature ideas to the test. Start developing the feature set you’ve prioritized from the idea development process and build the prototype.
Prototyping will help you create the feature set at a smaller scale and collect user feedback for it. The main advantage is that you’re able to validate your feature ideas and make modifications before investing extensive time and money into developing full-scale features.
Ideation phase 5: Test with small focus groups
Prototyping gives you an idea of how the feature should be developed and what it should accomplish. But the testing shouldn’t stop there. You also need to collect feedback on the completed feature design.
Focus groups help in this case. You can build beta tester groups from your current customer base and invite them to beta test the feature by offering free access to it.
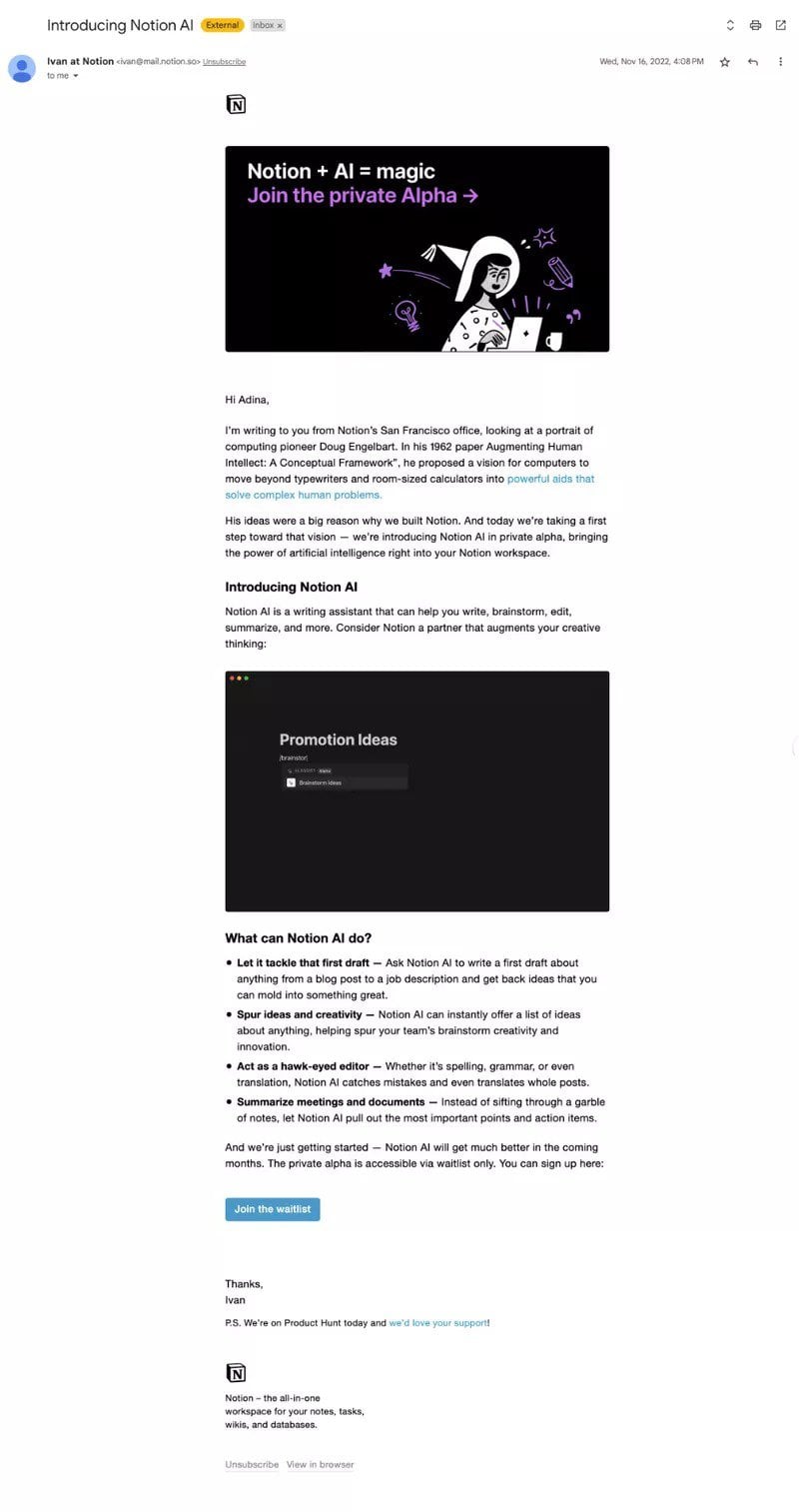
For instance, here are the email invites Notion sent to selected users to try out their latest AI feature.
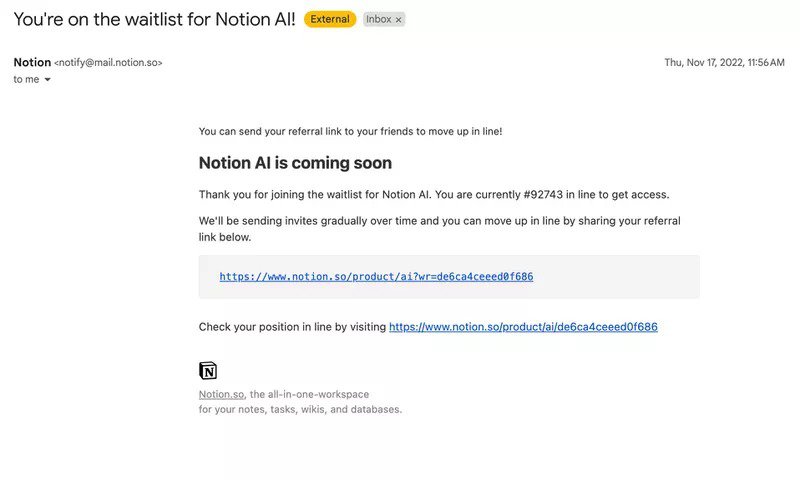
Once the user opts in to start testing the feature, Notion also lets them know that they’re on the waitlist. It helps build anticipation and hype for the new feature.
Once they’ve played around with the feature, ask them for their feedback. Analyze the responses to identify the most common ones. Use these to guide feature modifications and improvements.
After you’ve incorporated the changes, roll out the feature for your entire user base.
Most popular ideation techniques
Now that you know the steps involved in the ideation process, let’s look at a few ideation methods you can use to discover new feature ideas.
Brainstorming session
The simplest ideation technique to start with is brainstorming. All you have to do is get your product, sales, and marketing teams together for brainstorming sessions. Each team will be able to give their input for feature ideas.
Pros:
- Teams contribute based on their customer interactions.
- Brings diverse opinions from various teams.
- Includes qualitative interactions.
Cons:
- Not based on user data.
- This could lead to missed opportunities.
Mind mapping
Mind mapping is a popular product design ideation technique that helps cover most major ideas related to a central topic. With mind maps, you write a central idea and then create various branches for feature ideas related to it.
Pros:
- Helps collect similar ideas in a single spot.
- Gives a visual representation of your ideas.
- Shows how each idea is connected to another.
Cons:
- Time-consuming to come up with linked ideas.
- Ideas may not be as detailed.
- Can get complicated if you try to add many branches.
User story mapping
This method leverages user behavior to inform ideation. It involves visually mapping the user journey to understand what they need at every stage and how they interact with your product. This helps determine which existing features have the greatest impact on users and how can they be improved further with new enhancements.
Pros:
- Analyzes user data for feature ideas.
- Helps spot gaps in the user experience.
- Makes it easy to customize the experience with feature reshuffling.
Cons:
- No clear idea of the problems users face.
- Doesn’t account for user feedback.
SCAMPER technique
SCAMPER is a design thinking process and stands for Substitute, Combine, Adapt, Modify (includes Magnify and Minify), Put to another use, Eliminate, and Reverse. These are the parameters that you need to compare your existing features with. The SCAMPER technique can help determine what needs to be changed in the product, giving rise to new feature ideas.
Pros:
- Gives a comprehensive analysis of the existing product.
- Extensive brainstorming while categorization leads to innovative ideas.
Cons:
- Effectiveness depends on how well you ask questions for each category.
- May spring up some ideas that may not be feasible.
Role-playing
Instead of relying on user feedback, you can role-play to ideate. Here, you can put yourself in the users’ shoes and build custom scenarios. Determine what the user would need in those situations.
Pros:
- Gives diverse perspectives as you can create unlimited scenarios.
- Doesn’t require the collection of user feedback.
Cons:
- Doesn’t take user opinions into consideration.
- Role-playing may not give you a full picture of user needs and pain points.
SWOT analysis
SWOT stands for Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats. This sort of analysis should be done for your product as a whole. It can help you find where opportunities lie to improve your product. You can also spot weaknesses that can be rectified with new feature ideas to improve product experience.
Pros:
- Gives a holistic view of your product instead of a pinhole perspective.
- Discovers opportunities for product and feature development.
- Helps identify areas you can double down on to boost your strengths.
Cons:
- Doesn’t involve in-depth analysis into the causes of SWOT.
- Decisions aren’t based on user data.
Prototyping
Unlike other ideation methods, prototyping involves ideating first and then creating prototypes of the features you wish to introduce. You can create prototypes with limited resources, see them in action, and understand how they impact user experience.
Pros:
- Tests user responses regarding new features and extracts unparalleled insights.
- Allows experimenting with variations of your feature to find the best-performing one.
- Makes it easy to implement the full-scale feature as the base would be ready.
Cons:
- Takes up a lot of time as it involves prototype creation from scratch.
- Features introduced in a prototype might keep changing before they’re finalized, leading to confusion among users.
- Relatively expensive as you’d have to invest time and resources into prototype creation.
Analogy technique
The Analogy technique encourages product teams to use feature analogies for ideation. This is a creative way to brainstorm new ideas.
Imagine your app is a toolbox. Just like a toolbox helps you fix things with all sorts of tools, your app solves problems by offering a variety of features. So, if a toolbox has a hammer for nails, a helpdesk tool could add a chatbot to solve user problems. This way, by comparing your app to something familiar, you can come up with creative features that make your app useful.
Pros:
- Challenges your team to think out of the box.
- Helps simplify a complicated concept.
- Enables you to come up with unique solutions to user problems.
Cons:
- If not done right, you end up creating ineffective solutions.
- Doesn’t offer enough insight into the users’ minds, so solutions might not be highly targeted.
Reverse Engineering
Instead of making challenging assumptions and developing ideas based on problem statements, reverse engineering works by setting a goal and backtracking from there. It helps you understand what steps can help achieve product growth, leading to new feature ideas.
Pros:
- Helps chart a clear path to your product goals.
- Gives you a series of features that can be introduced to accomplish goals.
Cons:
- Long process as you have to backtrack from your goal to find feature ideas.
- Can be complicated if you don’t get the steps right.
Conclusion
Introducing the right features can help you win over your users’ trust and play an important role in retaining them. But it only works if you do feature ideation right.
This is a problem that user behavior analytics can solve, and that’s where Userpilot helps. It equips you with powerful user data that offers direction for feature development and helps boost user satisfaction. Book a free demo now to build innovative solutions for your users.





