![How to Become a Data Scientist [+Tools and Resources]](https://blog-static.userpilot.com/blog/wp-content/uploads/2024/07/How-to-Become-a-Data-Scientist-Tools-and-Resources.png)
Try Userpilot Now
See Why 1,000+ Teams Choose Userpilot
Data scientist’s main responsibilities
The three responsibility pillars of a data scientist encompass Data Acquisition and Engineering, Data Analysis and Modeling, and Communication and Collaboration.
For a better understanding of this role, let’s break down the core responsibilities of a data scientist working in a SaaS company, for example:
1. Data acquisition and engineering:
- Data Extraction: SaaS products generate a ton of user data. Data scientists design and implement methods to extract this data from various sources within the SaaS application (e.g., user activity logs, product usage data). They may use APIs or write scripts to automate this process.
- Data Cleaning and Preprocessing: Raw data often contains errors and inconsistencies. Data scientists clean and prepare the data for analysis by identifying and handling missing values, outliers, and inconsistencies. This is crucial for building reliable models.
- Feature Engineering: Data scientists transform raw data into features that are informative for machine learning models. This may involve creating new variables, combining existing ones, and performing dimensionality reduction techniques.
2. Data analysis and modeling:
- Customer Segmentation: SaaS companies often have diverse customer bases. Data scientists use clustering algorithms to segment customers based on their behavior and characteristics. This helps personalize the user experience and target marketing efforts effectively.
- Churn Prediction: Customer churn is a major concern for SaaS companies. Data scientists build churn prediction models to identify customers at risk of leaving. This allows the company to take proactive steps to retain them (e.g., offering discounts, providing support).
- Recommendation Engines: Many SaaS products recommend content, features, or services to users. Data scientists develop recommendation engines using collaborative filtering or content-based filtering techniques to personalize recommendations and improve user engagement.
3. Communication and collaboration:
- Translating Insights to Action: Data scientists don’t work in isolation. They collaborate with product managers, marketing teams, and other stakeholders to translate their analytical findings into actionable business strategies. This might involve creating reports, dashboards, and presentations to communicate complex insights effectively.
- A/B Testing: Data scientists design and implement A/B tests to measure the impact of changes made to the SaaS product (e.g., new features, pricing models). This helps optimize the product for better user experience and conversion rates.
- Staying Updated: The field of data science is constantly evolving. Data scientists in SaaS need to stay updated on the latest tools, techniques, and industry trends to ensure their models remain relevant and effective.
Data scientist career path
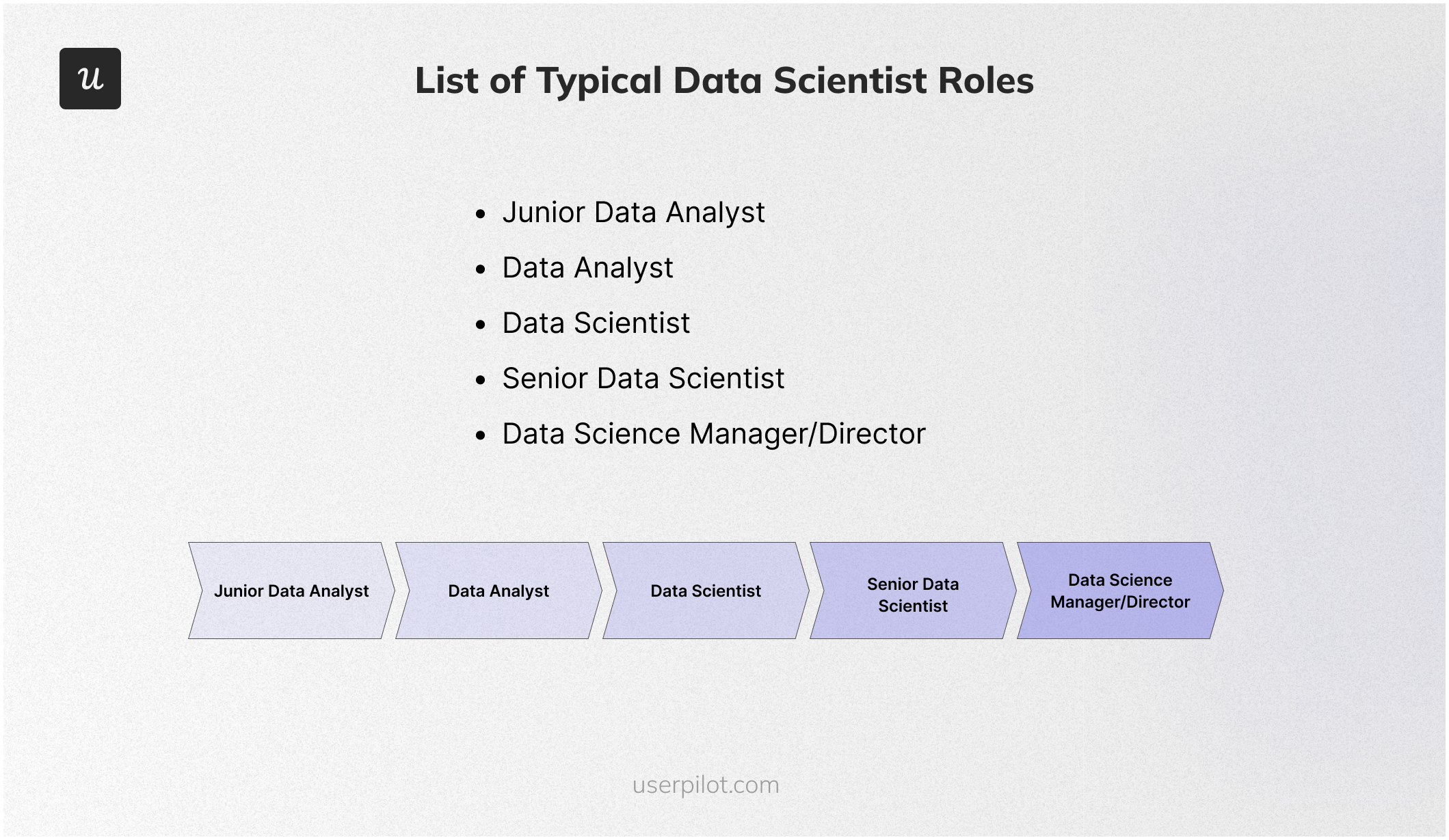
Here’s a breakdown of a typical data scientist career path, with information on how to progress and the estimated experience needed for each level:
1. Junior Data Analyst (0-2 years): You’ll need a bachelor’s degree in a relevant field (statistics, computer science, etc.), strong analytical skills, and basic programming experience (Python, R). You can look for internships or entry-level analyst roles.
2. Data Analyst (2-4 years): This position often requires a solid foundation in data analysis methodologies and data manipulation skills. You should deepen your technical skills in programming languages (Python, R) and data analysis tools (SQL, machine learning libraries) or contribute to data science projects alongside senior data scientists.
3. Data Scientist (4-7 years): This is a core data science role requiring strong programming, statistical modeling, and problem-solving skills. At this point, you must master advanced machine learning algorithms and techniques like deep learning. It also matters to specialize in a particular industry or domain (e.g., finance, healthcare) or lead and mentor junior data scientists.
4. Senior Data Scientist (7+ years): This senior-level role demands extensive expertise in data science techniques and the ability to manage complex projects and teams. You can continuously learn about new technologies and trends in data science.
5. Data Science Manager/Director (10+ years): This leadership role requires extensive data science experience combined with strong business management and communication skills. For example, you’ll be in charge of setting the strategic direction for the data science function within an organization. You also take responsibility for overseeing budgets and resources for data science projects.
How to become a data scientist?
The journey to becoming a data scientist can be tailored to your background and learning style. Here’s a roadmap gleaned from real-world discussions on platforms, along with insights from hiring managers:
Earn your foundational education
- A bachelor’s degree in data science, computer science, statistics, or a related field provides a strong foundation in math, statistics, and programming. However, some break into the field through alternative routes like boot camps or online courses.
- For boot camps, research reputable boot camps like Springboard, Flatiron School, or General Assembly to find programs that align with your learning style and budget. Look for boot camps with strong industry connections and career services to maximize your chances of landing a job.
- Platforms like Coursera, edX, and Udacity offer a vast array of data science courses and specializations from top universities and companies. These courses can be a great way to learn at your own pace and build specific skills. Popular options include the IBM Data Science Professional Certificate on Coursera or the Applied Data Science with Python Specialization on the University of Michigan platform. Look for courses that offer hands-on projects and industry-recognized certificates.
Sharpen your skills
Regardless of your educational path, fortify your technical skills. Online courses, tutorials, and personal projects are fantastic ways to master in-demand programming languages like Python and SQL.
Look for internship opportunities
Internships provide invaluable hands-on experience and a chance to apply your skills in real-world scenarios. Look for opportunities at companies working in areas that interest you. Don’t be discouraged if your first attempt isn’t at a big tech firm – even smaller companies offer valuable learning experiences.
Here are a few job sources you can watch out for:
- Many companies, especially larger ones, post internship opportunities directly on their careers pages. Look for companies working in areas that pique your interest, such as healthcare, finance, or technology.
- In addition, popular job boards like Indeed, Glassdoor, and LinkedIn often have dedicated sections for internships. Utilize filters to search for “data science internship” or related terms, and refine your search by location, company size, or industry.
- You can also engage with online data science communities on Reddit, Quora, or data science forums. Many professionals actively share internship opportunities within their networks.
Build your portfolio
Showcase your abilities by contributing to open-source projects on platforms like GitHub. You can also work on personal projects that allow you to explore your interests and demonstrate your data science capabilities to potential employers.
Network and learn
Actively engage with online data science communities on Reddit, Quora, or data science forums. Attend meetups and conferences to connect with other aspiring and experienced data scientists. The data science community is welcoming and thrives on knowledge sharing.
What skills should a data scientist have?
We know that data scientists leverage data for actionable insights. But what exactly goes into their toolkit? Let’s dive into some of the most sought-after skills for data scientists:
- Data Visualization: The ability to translate data into clear and compelling visuals – using tools like Userpilot, Tableau, or Mixpanel – is crucial for communicating insights effectively to both technical and non-technical audiences.
- Statistical Savvy: Understanding of concepts like hypothesis testing, probability distributions, and regression analysis is crucial for extracting meaningful insights from data.
- Knowledge of Data-related Languages: For example, Python and SQL: Python offers a wealth of data science libraries like pandas, NumPy, and scikit-learn, making data manipulation, analysis, and machine learning a breeze. SQL is the language for interacting with databases, allowing data scientists to efficiently retrieve and manipulate data from various sources.
- Problem-Solving: Data science is all about tackling complex problems with innovative approaches. A curious mind and a knack for creative problem-solving are essential assets.
- Communication: Data science isn’t just about crunching numbers – effectively communicating findings to stakeholders and translating technical jargon into clear business language is a must-have skill.
Best certifications for data scientists
To pick out the most suitable certification to pursue, it’s essential that you consider factors like your background, desired specialization, and budget.
Here are a few suggestions to get you started:
- Senior Data Scientist (SDS) by Data Science Council of America (DASCA): They are well-respected in the industry and demonstrate expertise for senior-level roles. They cover advanced data science topics like machine learning, deep learning, big data technologies, and leadership skills.
- Data Scientist Certification (Associate Level) by DataCamp: This is a good starting point for beginners, with lessons focusing on foundational data science skills, including Python, data manipulation (pandas), statistics, machine learning basics, and data visualization.
- Microsoft Certified: Azure Data Scientist Associate by Microsoft: Ideal for those looking to specialize in Azure cloud data science.
- Open Certified Data Scientist (Open CDS) by The Open Group: A broad certification valued for its vendor neutrality and focus on core competencies. It includes core data science concepts such as data lifecycle, modeling, communication, and ethics.
Best resources for data scientists
Data science is a rapidly evolving field, and staying updated with the latest trends, tools, and techniques is crucial for success. In this section, we’ll explore some of the best resources for data scientists, including books, blogs, and online courses, that can help you enhance your skills and stay at the forefront of the industry.
Best books for data scientists
Data science is a vast field, so the best books for you will depend on your experience level and area of interest. Here are some highly-rated books across different categories to kickstart your data science journey:
- Python for Data Analysis by Wes McKinney: This book is a fantastic introduction to using Python for data analysis. It covers the basics of Python programming, data structures, and popular data science libraries like NumPy, Pandas, and Matplotlib.
- Hands-On Machine Learning with Scikit-Learn, Keras & TensorFlow by Aurélien Géron: This book dives deeper into machine learning algorithms and their practical implementation using popular Python libraries like scikit-learn, Keras, and TensorFlow.
- Naked Statistics: Stripping the Dread from the Data by Charles Wheelan: This book makes statistics approachable and engaging, even for those with math anxiety.
- Thinking with Data by Nathan Yau: This book goes beyond the technical aspects of data science and explores how to think critically about data, ask the right questions, and communicate findings effectively.
- Data Science for Business by Foster Provost and Tom Fawcett: This book bridges the gap between data science and business. It explains how data science can be used to solve real-world business problems and provides case studies of successful data science applications.
Best webinars for data scientists
Are you looking to level up your data science expertise but are short on time? Webinars offer a fantastic way to learn from industry leaders and gain valuable insights in a concise format. Here’s a list of highly-rated webinars:
- Data Science Salon: Offers both live and recorded webinars on a wide range of data science topics, from fundamentals to cutting-edge applications. They also have an active community forum for discussions.
- BrightTalk: Hosts webinars on various tech topics, including a dedicated section for data science with a good selection of free and paid options.
- Userpilot webinars: Covers topics relevant to SaaS user research for informed product development. It’s a great source for anyone working for a SaaS business.
- Meetup: Local groups focused on data science often host online webinars on various topics. Check for meetups in your area or browse online groups relevant to your interests.
- Major tech companies like Microsoft, Google, and Amazon frequently host webinars on data science tools and applications related to their platforms. Check their developer portals or social media for upcoming events.
Best blogs for data scientists
To empower your learning journey as a data scientist, here’s a curated list of top data science blogs:
- Data Science Central: This comprehensive resource hub covers everything in data science, from analytics and machine learning to code and career advice.
- KD Nuggets: Known for its in-depth dives into specific data science topics and algorithms, KD Nuggets is a favorite among data professionals for staying sharp on the latest trends.
- Towards Data Science (on Medium): This massive online community publishes articles from a wide range of data science professionals. You can follow it to stay updated on the latest advancements and to find diverse perspectives.
- The Mockup Blog: Authored by Thomas Mock, a data science leader at Netflix, this blog offers valuable insights into the real-world applications of data science within companies.
- DataCamp Blog: This blog caters to aspiring and beginner data scientists with clear tutorials, project ideas, and career tips.
- Userpilot Blog: While not strictly a data science blog, Userpilot offers valuable insights on user behavior analytics, a crucial skill for data scientists working on product development and customer insights.
Best podcasts for data scientists
Based on insights from online reviews and discussions, here’s our favorite list of podcasts for data scientists at different experience levels:
- Lex Fridman Podcast: This isn’t strictly data science, but Lex Fridman’s interview format delves deep into AI and its connection to data science.
- Data Skeptic: A long-running favorite, Data Skeptic tackles a wide range of data science topics with a critical eye.
- Not So Standard Deviations: Hosted by statisticians Roger Peng and Hillary Parker, this podcast offers a deep dive into statistical methods used in data science.
- Making Data Simple: Hosted by AI VP at IBM, Martin AI, this podcast focuses on making complex data science concepts understandable for a broader audience.
- SuperDataScience: With short and long episodes, Kirill Eremenko’s podcast, SuperDataScience, covers a wide range of data science tools and techniques in a lighthearted and informative way.
Best tools for data scientists
Data scientists rely on a suite of powerful tools designed to collect, process, analyze, and visualize data. So here’s a list of the top tools that every data scientist should consider:
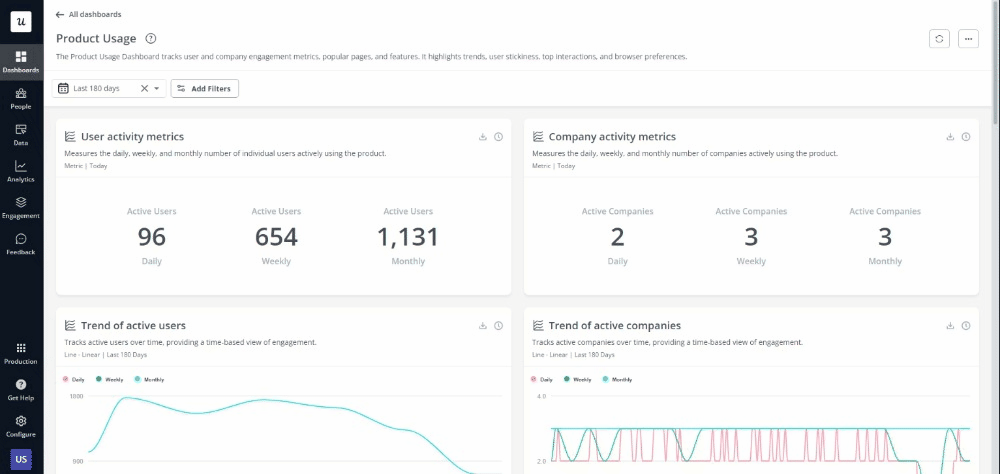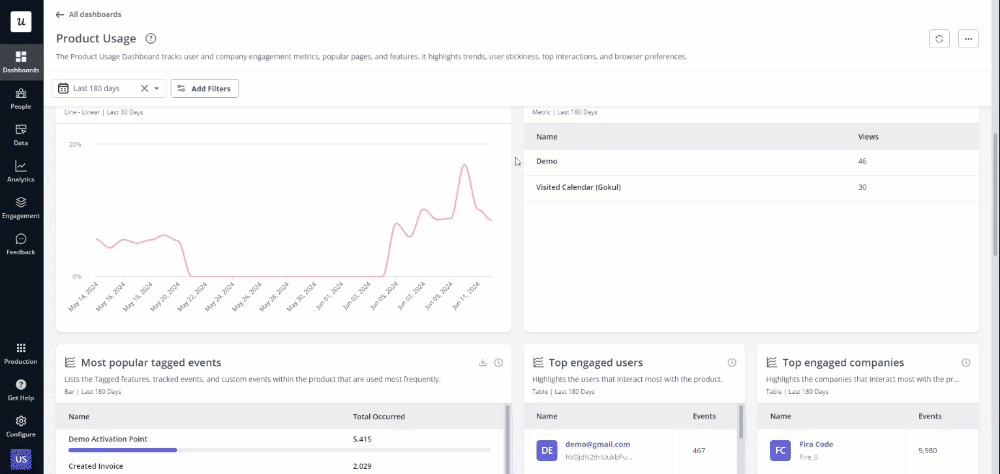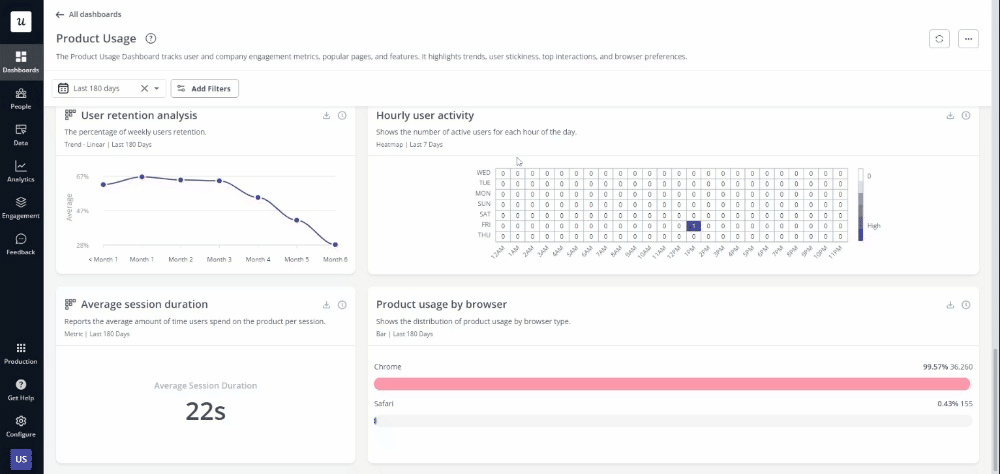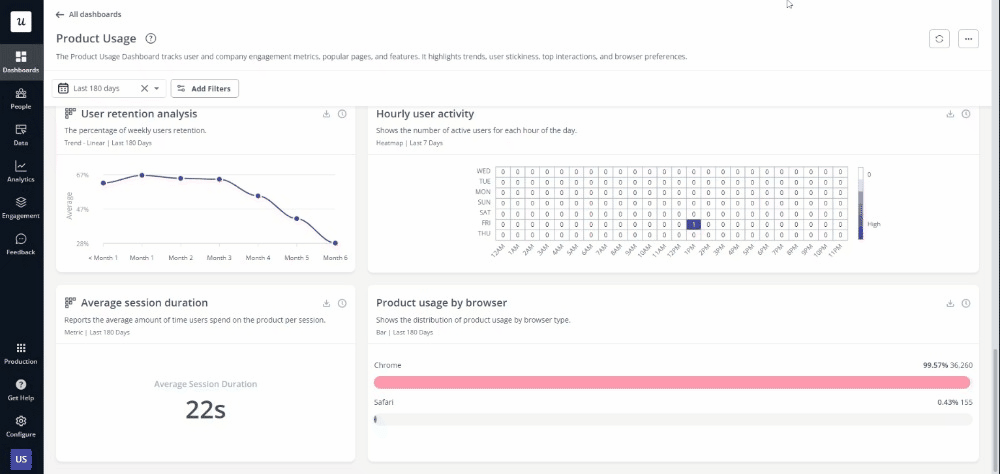
- Userpilot (Best for no-code product analytics): Userpilot is a no-code product analytics tool that helps product managers and data analysts understand user behavior and track product adoption. It provides features like metrics dashboards, reports (funnel, path, trend, cohort), user feedback, etc. This tool can help foster cross-team communication, bridging the gap between technical and non-technical teams.
- Tableau (Best for data visualization): Tableau is a data visualization tool that allows users to create interactive dashboards and reports. This can help data scientists identify trends and patterns in their data that would be difficult to see in a spreadsheet.
- Power BI (Best for business intelligence): Power BI is a business intelligence tool from Microsoft. It allows users to connect to a variety of data sources, create reports and dashboards, and share insights with others.
- Google Charts (Best for simple data visualization): Google Charts is a free data visualization tool from Google. It allows users to create a variety of charts and graphs, such as bar charts, line charts, and pie charts.
- Amplitude (Best for product analytics): Amplitude is a product analytics tool that helps businesses track user behavior and understand how users interact with their products. It provides features like funnels, user paths, and cohort analysis.
- Heap (Best for digital analytics): Heap is a digital analytics tool that automatically captures all user interactions on a website or app. This makes it a good option for businesses that want to track every user interaction, even if they don’t know what specific data points they are interested in yet.
- Mixpanel (Best for user behavior and predictive analytics): Mixpanel can help data scientists by providing them with a wealth of data on user behavior. This data can be used to improve product design, marketing campaigns, and overall user experience.
- Qualtrics (Best for survey research): Qualtrics can help data scientists by providing them with a way to collect data from a large number of people. This data can be used to identify trends and patterns in customer or employee sentiment.
- Optimal Workshop (Best for user research): Optimal Workshop is a user research tool that helps businesses conduct user testing and gather feedback from users. It provides features like card sorting, tree testing, and surveys.
- UserTesting (Best for user testing): UserTesting is a platform specifically designed for conducting remote user testing. Users can be recruited through the platform itself, allowing data scientists to gather feedback from a diverse range of people.
Data scientist FAQs
What does a data scientist do?
Data scientists identify the key questions that need answers and determine where to source the relevant data. They possess a blend of business acumen and analytical expertise, coupled with the skills to extract, clean, and present data effectively.
What is required to be a data scientist?
A bachelor’s degree in a relevant field, such as computer science, statistics, mathematics, or engineering, is typically required for entry-level data scientist positions. When discussing the qualifications for data scientists, it’s worth noting that some companies may prefer candidates with a Master’s or PhD in a related discipline.
Is data scientist a tough job?
The role likely requires a strong foundation in various technical areas and the ability to keep up with evolving technologies based on the skills mentioned. However, the specific difficulty might depend on the industry, company size, and the problems being tackled.
Is it hard to become a data scientist?
There can be a steep learning curve for those entirely new to the field due to the required technical and analytical skills. However, there are certifications, online courses, and data science degrees available to help bridge the knowledge gap.
Overall, data science seems like a demanding but rewarding field that uses data to solve problems and make informed decisions. The difficulty of entering the field depends on your background and how much you’re willing to learn.
Conclusion
Becoming a successful data scientist requires dedication, continuous learning, and a proactive approach to developing relevant skills.
By following the outlined steps and leveraging the resources available, you can effectively navigate your career path and achieve your professional goals.
We hope this guide has provided you with valuable insights and practical advice to help you on your journey to becoming a proficient and impactful data scientist!
Looking into tools for data scientists? Userpilot is an all-in-one product platform with engagement features and powerful analytics capabilities. Book a demo to see it in action!