What is market validation?
Market validation is the process of confirming the demand for a product or service within the target market before committing resources to its development.
The process is very similar to product idea validation and helps you answer one key question: Are there enough potential customers who are willing to pay for the product?
What is the difference between market research and market validation?
Market research and market validation are two related concepts but they take place at different stages of the product development process and, more importantly, serve different purposes.
Research happens in the early stage of the product development cycle, often before the product concept is fully shaped. Validation, on the other hand, happens after the ideation stage, when you have a clear idea of what you’re trying to build.
Market research focuses on the wider market situation. Its aim is to collect data about the target market, competitors, customer pain points, needs and wants, and industry trends to guide future product development.
In contrast, market validation focuses on the market trends only in the context of the specific product and its goal is to verify if it’s viable.
How do you currently test demand for a new product or feature idea?
Why is it important to conduct market validation?
Market validation is essential for product success for a number of reasons.
To start with, it confirms that the product solves a genuine customer problem. This reduces the risk of developing a product that won’t be profitable, which is the main cause of product failure. This could boost the investor confidence in the product and the morale of the product team.
During the development stage, it helps teams allocate resources in the most optimal way to secure the best ROI.
What’s more, market validation gives you insights into customer perception of the product and allows you to capture the voice of prospective customers, which you can use to shape your marketing efforts and product messaging.
And it’s a great opportunity to start building relationships with early adopters and recruit beta testers.
Common market validation methods to use
Which market validation methods can you use to authenticate your business idea? Let’s look at a few popular choices.
Customer interviews
In-depth interviews of target customers or focus groups are a great source of qualitative data about customer needs and expectations.
Their main advantage is flexibility. During the interview, you can adjust your questioning and follow up on customer ideas in a way that’s not possible when conducting surveys.
The main downside of interviews is that they’re time-consuming and tricky to arrange, so they’re not very practical for large studies.
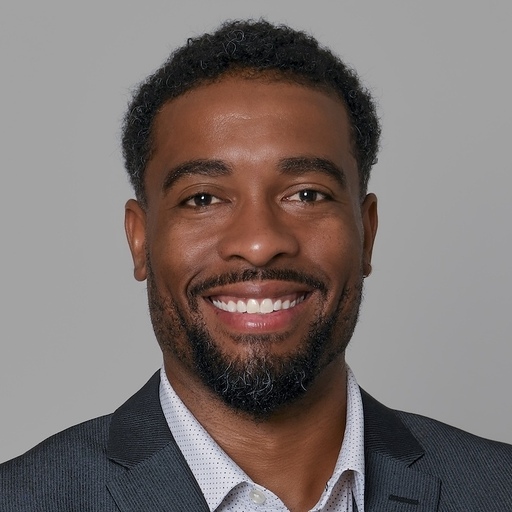
Surveys
In contrast to interviews, online surveys are great for collecting customer insights at scale.
Designing and triggering in-app surveys is dead easy. You can use them to target a specific user segment and use it to pick their brains on the new feature or product you’re planning to develop.
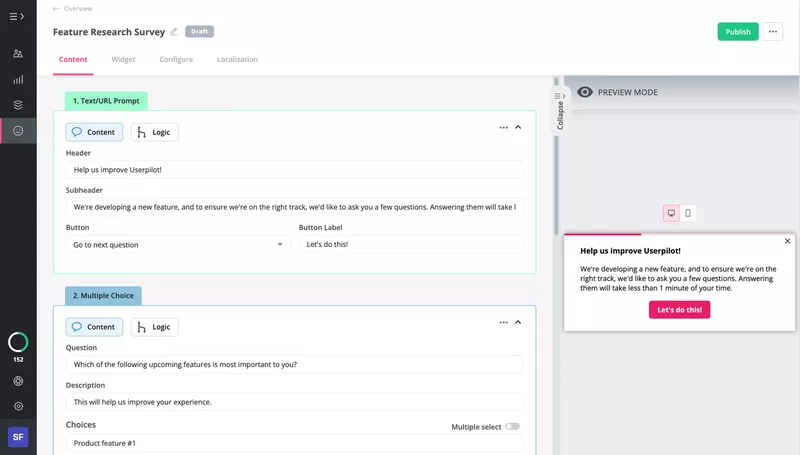
Market validation research
Some market research techniques can also be used for market validation. Here are a few examples:
- Competitive analysis – if your established competitors don’t offer a similar product or feature, it might be an indication that there’s no demand for it in the particular market.
- Industry reports – just like competitive analysis, they can tell you what’s selling and what’s not.
- Keyword research and Google Trends analysis – high search volume for terms related to the product could be an indication of high demand.
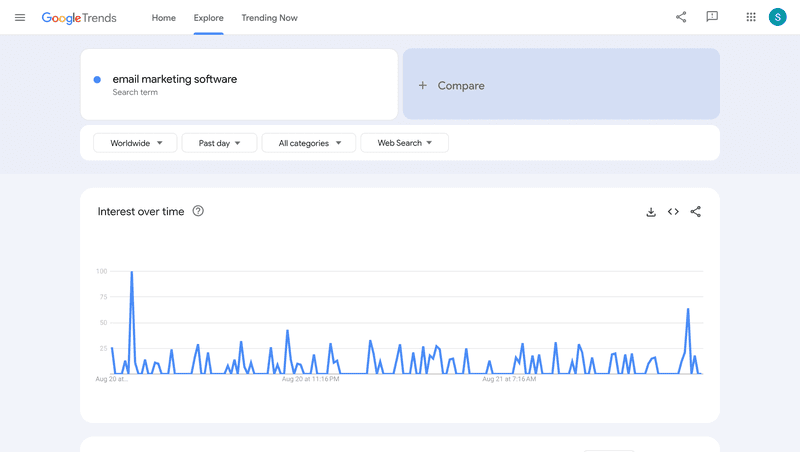
Fake door testing
Fake door testing is a popular lean market validation method.
First, you make your users believe that the feature already exists, for example, by adding it to the UI and driving engagement with in-app messages, like in this hypothetical Asana example.
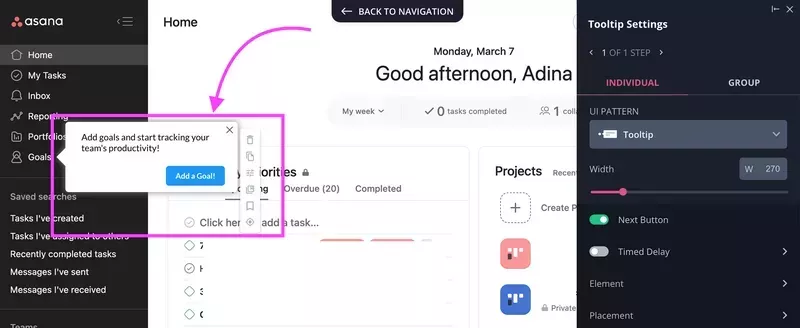
By tracking user engagement, you can tell how much interest they have in the new functionality.
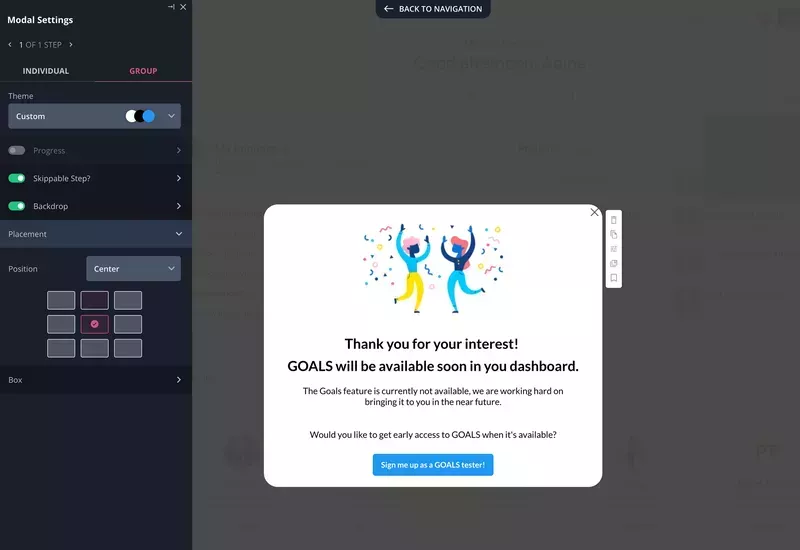
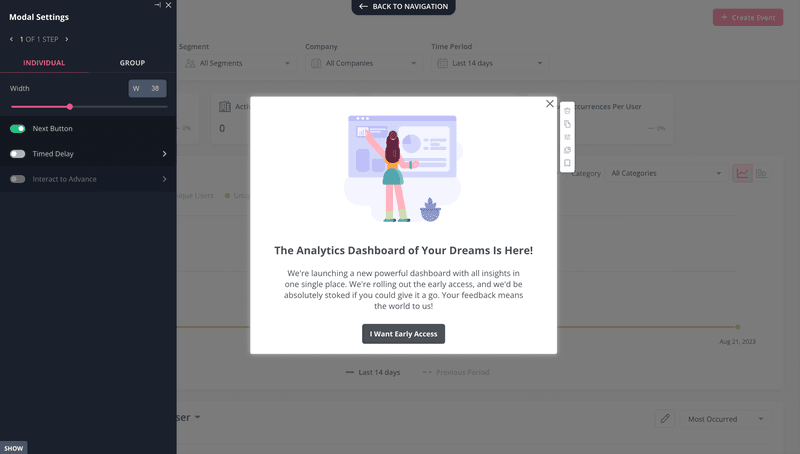
Of course, once they click on the feature, they’ll know they’ve been tricked, so you’ll have to explain that it was a test. For instance, you could trigger a modal like the one below.
Prototype testing
Fake door tests are a kind of prototype test. In this case, it’s a very low-fidelity prototype.
If the response to the test is positive, you create more realistic prototypes and carry on testing them iteratively.
These could be wireframes, videos, or animations. You could also do a Wizard of Oz experiment and make it look like a fully functional product while doing all the work manually behind the scenes. Or hack existing products to develop the functionality of the final product and make users believe the product is ready.
Each iteration not only validates your idea and the design but is also a learning opportunity that increases the chance of launching a strong MVP.
Beta testing
Beta testing is often the ultimate stage before the MVP launch. It’s the final opportunity to test the product with real users and in real-life conditions but with limited exposure to risk.
How can you recruit beta testers?
Start with your power users. They are the most successful and loyal customers so they make good testers, and they will be delighted to get early access to the new feature or product. You can identify them by using product analytics and survey data.
Then, simply trigger a modal to invite them to take part in the test.
What are the steps in the market validation process?
The market validation process consists of 6 key steps. Let’s have a quick look at each of them.
1. Determine market validation goals and hypothesis
The process starts by defining your research goals and developing hypotheses. Basically, you try to list all the questions you need to answer.
Here are some examples of research questions:
- What is the feature, product, or service?
- Which customer problems does it solve?
- Are there other similar products?
- How successful are they?
- What is the target market?
- Who are the prospective customers?
- Are there enough potential users?
- Are they ready to pay for the product? How much?
- Is it financially viable?
2. Research the market to gauge market demand
Once you have the research questions lined up, it’s time for market research.
There are lots of different techniques that you can use here, like competitive analysis or studying market trends.
The process is not easy though. For starters, it requires expertise that only large enterprise-level organizations can have at their disposal. That’s why hiring a market research company might be a good shot to ensure unbiased and valid research results.
3. Identify the target market of your business idea
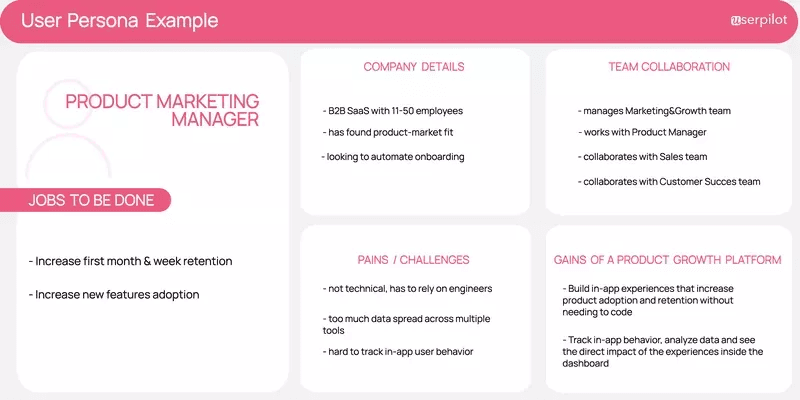
Market research should give you the insights necessary to identify your target market and the target audience.
Use them to develop target user personas of your product, focusing on their JTBDs, pain points, and desires. Applying a template like the one below will give structure to persona mapping.
4. Validate product ideas through multiple methods
Once you identify the target market, it’s time to validate the product idea.
Using a range of techniques and methods will help you ensure that the results are reliable and valid. For example, you could run fake door tests and prototype tests and use surveys and interviews to collect user feedback.
5. Develop the minimum viable product
As you’re running subsequent tests, your prototypes will be getting more and more complex. At some point, you will reach a stage where you have a functional product. That’s your minimum viable product, or the MVP for short.
The idea behind the MVP isn’t to launch a ready product. It only needs basic functionality – enough to satisfy the key user needs and communicate the value proposition of the product.
Your MVP won’t be enough to cross the chasm and captivate the imagination of the majority of your target user base. However, it should be good enough for innovators and early adopters. That’s all you need at this stage.
6. Iterate the MVP by collecting customer feedback
When you launch your MVP, collect customer feedback and track user in-app behavior.
Use the insights to iterate on the previous version to iron out the kinks and keep adding value, just like you did with prototype testing.
As you keep testing and improving the product, it’s going to be more and more appealing to wider audiences beyond early customers.
What is an example of market validation?
Let’s imagine that you’re a product manager developing an analytics platform. You come up with an idea of a feature that leverages AI to enhance the analysis process.
While AI solutions are taking other sectors by storm, your market research reveals no competing analytics tools offer such functionality.
You start the validation by running a fake door test. In this way, you can test the demand without investing any resources.
The results are optimistic, so you iterate on the idea and develop more and more advanced prototypes. Once the MVP is ready, you first dark launch it and carry out beta tests to further refine it.
Finally, you launch it on Product Hunt to attract the attention of early adopters.
Best practices when conducting market validation tests
- Make your users commit – in your validation interviews, tell users the product is ready and ask them to commit to the purchase. This is the ultimate test of their interest. In this way, you could also get your first paying customers.
- Validate with the right audience – innovators and early adopters are only a small part of your target user population. Most money comes from the early and late majority categories of adopters, so make sure to test the product with a representative sample.
- Recruit beta testers early on – as you’re testing different prototype versions, keep recruiting beta testers for when the product is ready. For example, ask users to sign up at the end of the fake door test.
- Stay open to critical feedback – to avoid bias seek diverse perspectives and test to encourage research participants to provide honest opinions, even if they don’t align with your initial assumptions.
- Keep your surveys brief – to get higher response rates, limit your surveys to no more than 2 questions. Include both quantitative and qualitative questions, but don’t make them compulsory to answer.
Conclusion
Proper market validation helps organizations ensure that they’re developing the right solutions for the right audience in the right markets.
This reduces the risk of wasting resources on developing products or features that the market doesn’t need. Ultimately, it increases the chances of building a successful product.
If you want to see how you can use Userpilot for market validation, book the demo!





