Learning how to design a product is crucial for anyone aiming to bring an idea to life.
Whether you’re an aspiring entrepreneur, a seasoned product manager, a UX designer, or simply curious about the process, this guide will walk you through the essential steps, best practices, and tools you need to create successful products.
Summary of how to design a product
- Product design is the process of creating new products that solve problems or meet specific needs in a given market.
- The product design process extends beyond the product designer’s role, often requiring cross-functional collaboration among product designers, visual designers, UX designers, researchers, industrial design specialists, marketers, and engineers.
Design a product in 7 steps:
- Carry out market research and generate ideas to help you stand out.
- Conduct user research to understand your target audience.
- Define the product vision and strategy.
- Create your minimum viable product.
- Test your product prototype and note usability or UX design improvements.
- Finalize the product design and launch it on relevant channels.
- Continuously iterate your product based on data.
Best practices for the product design process:
- Prioritize product ideas that align with business goals.
- Foster cross-functional team collaboration and communication.
- Follow an agile mindset.
What is product design?
Product design is the process of creating new products that solve problems or meet specific needs in a given market.
It’s a multi-faceted discipline that involves understanding user needs, generating ideas, developing concepts, prototyping, testing, and iterating until a final product is ready for launch.
How to design a product in 7 steps
Product design cuts across almost every industry and applies to both physical and digital products.
However, the goal is always the same: create a functional and aesthetically pleasing product while meeting the target audience’s requirements.
Follow these steps to create designs that align with real user needs:
Carry out market research
Market research is a crucial first step in the product design process. It helps you better understand your industry, identify potential opportunities, and assess the viability of your product idea.
Begin by identifying your direct and indirect competitors. Analyze their strengths, weaknesses, pricing strategies, target markets, and unique selling propositions. If your product idea already exists in some form, determine how you can improve upon it or differentiate yourself.
Conduct user research to understand your target audience
User research helps you gain deep insights into your target audience’s needs, behaviors, and pain points. The data from this exercise will enable you to design a product that meets their needs and expectations.
Research can feel overwhelming, but a focused approach makes it manageable. Start by creating detailed user personas and mapping their pain points.
Then, build empathy maps to understand their emotions and motivations. Finally, craft user story maps to visualize their journeys and goals.
Don’t worry, we’ll discuss these steps in detail:
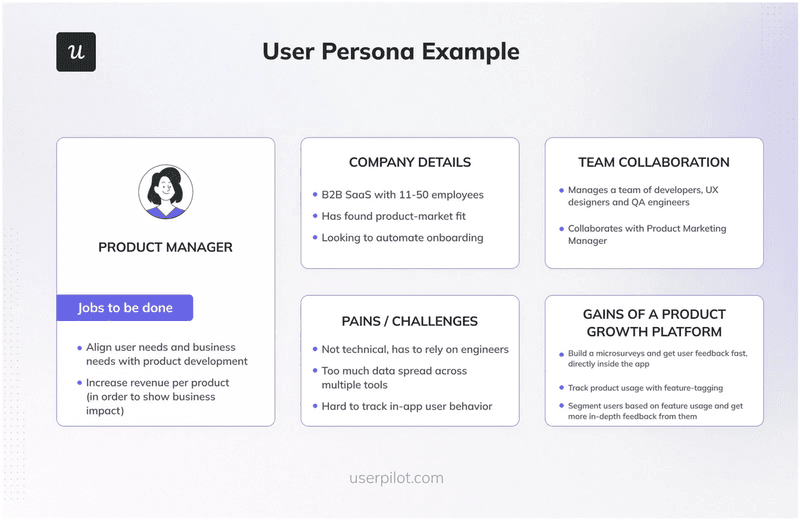
Map your user personas and their pain points
Create fictional characters (personas) that represent your target users and identify specific problems these users face when interacting with your product.
Clearly outline the outcomes of using your product to solve these challenges.
Here’s a persona template you can copy:
Create empathy maps to better connect with potential users
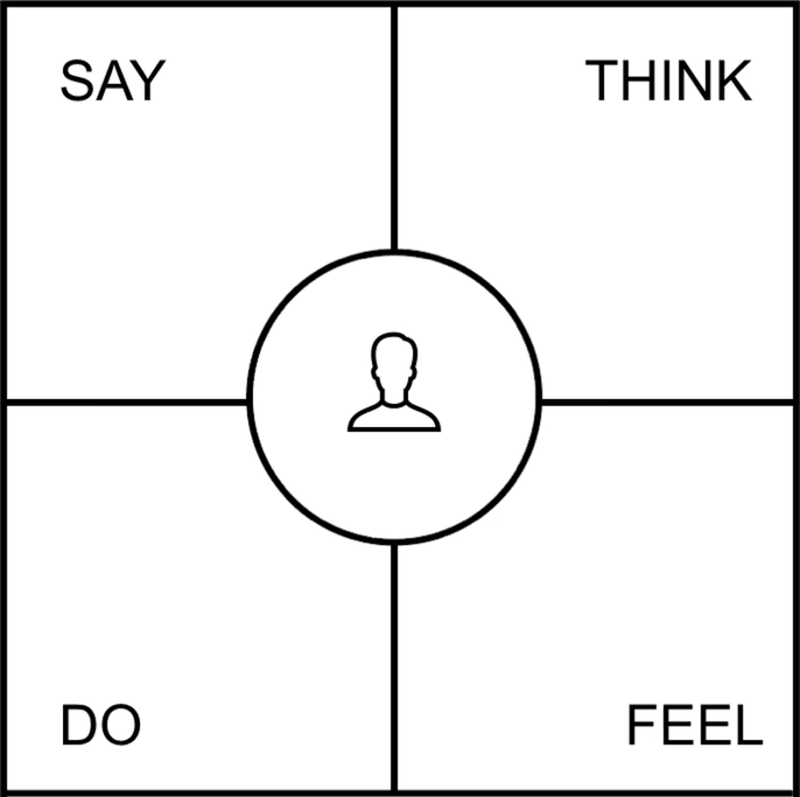
An empathy map is a step up from basic user personas This tool allows you to gain deeper insights into potential customer thoughts, feelings, and experiences.
Create your empathy map by collecting data through targeted user surveys. If you’re building on an existing product, it also helps to involve customer-facing teams. For example, the support team regularly interacts with users, so they can tell you more about the attitudes of each customer group.
Split the map into four quadrants: Says, Thinks, Does, and Feels.
- Say: Direct quotes from the user.
- Think: User thoughts, beliefs, and opinions that may not be expressed verbally.
- Do: How you anticipate users will interact with your product.
- Feel: The user’s customer’s emotional state and reactions at key phases in the product journey.
Map user stories
User stories are short, simple descriptions of a feature from the perspective of the end user. They are used in agile development to capture product functionality and serve as a basis for prioritization.
How to begin?
Use your personas and empathy maps to understand what users need, then craft stories that follow this format:
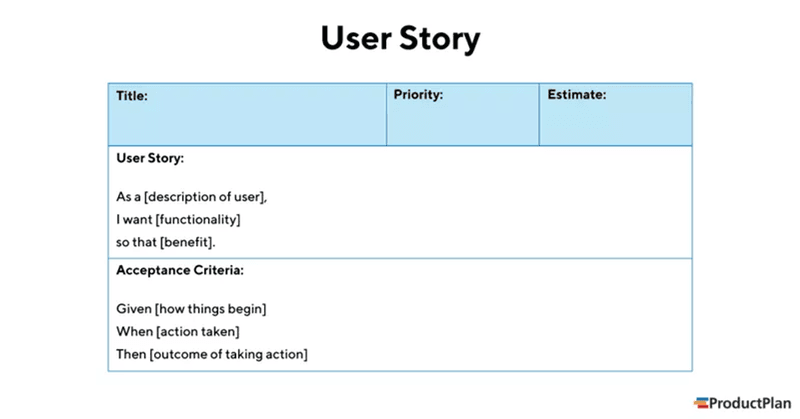
Example: “As a sales manager, I want to track the progress of each lead in the pipeline so that I can prioritize follow-ups and allocate resources effectively.”
Rank the stories based on importance and impact on the user, then use the information to decide which features to prioritize.
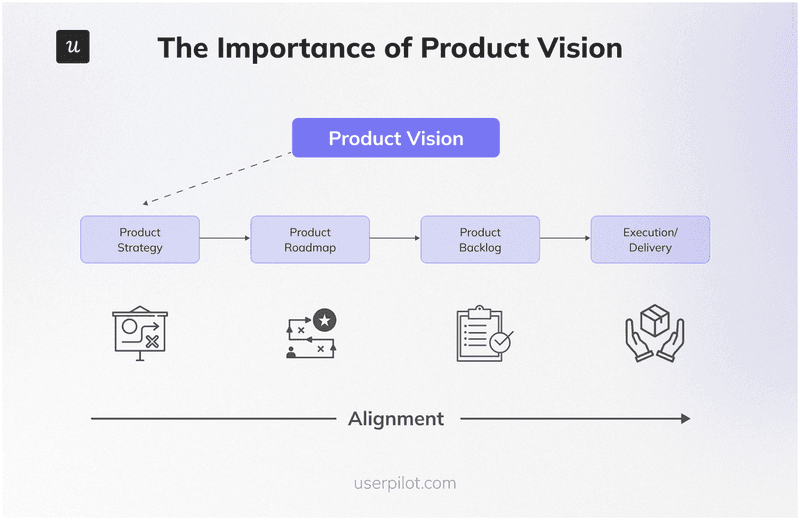
Define the product vision and strategy
After researching the market and figuring out user needs, it’s time to outline your product vision and strategy.
Create a compelling and concise statement that describes your product’s future state. This vision should inspire and guide the design team.
For example, “Our product will democratize data, empowering businesses of all sizes to make informed decisions based on actionable insights and real-time analytics.”
The next step is to develop a product roadmap—a high-level timeline that outlines the major milestones and phases of your product development. This roadmap should be flexible enough to accommodate changes based on resources, feedback, and market conditions.
Create your minimum viable product
An MVP is a stripped-down version of your product with just enough features to be usable and gather feedback from early adopters. It allows you to test your assumptions, validate your product concept, and iterate quickly.
There are different types. Here are a few:
- Landing page MVP: A simple, informative landing page that highlights your product’s key features and benefits and includes a CTA inviting users to try it.
- Email MVP: A detailed email (or email series) describing the product and its features. Like landing page MVPs, this also includes CTAs asking readers to sign up for a waitlist or test the product and provide feedback.
- Demo video MVP: This is a product tour that visually demonstrates the product’s value proposition and features, and then invites users to try it.
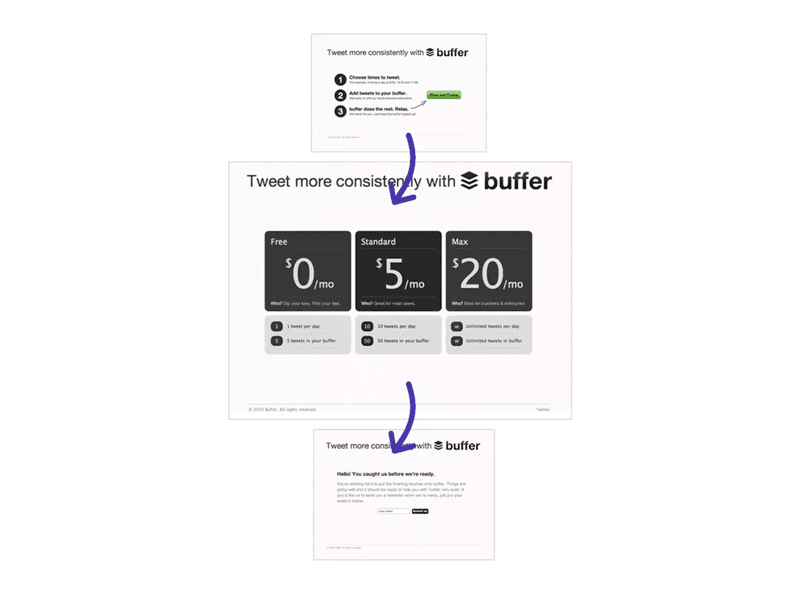
Test your product prototype with real users
Testing is a critical phase in the design process where you validate your product’s usability, functionality, and overall appeal before investing significant resources into further development.
The key is to gather feedback from beta users who represent your target audience.
Here’s how to approach it:
- Usability testing: Observe users interacting with your prototype, identifying any pain points, confusion, or areas where they get stuck. Gather feedback on the overall user experience.
- A/B testing: If you have multiple design variations, test them with key user groups to see which performs better in terms of engagement, conversion rates, or other key metrics.
- Feedback collection: Actively seek feedback from users through surveys, interviews, or feedback forms. Analyze the data to identify patterns and areas for improvement.
Finalize the product design and launch it on relevant channels
Based on the feedback from testing, iterate on your design and refine it until it meets your quality standards and addresses user concerns. Once you’re confident in your product, it’s time to launch it.
Create a launch strategy to build awareness and excitement for your product. Most early adopters hang around on Product Hunt, so you want to ensure you launch your new product there and drive traffic to the page through social media posts, emails, and paid advertising.
Continuously iterate your product based on data
Product design is an ongoing process. Once your product is launched, continue gathering data on user behavior, feedback, and performance metrics.
Use this data to identify areas for improvement and iterate on your design to enhance user satisfaction and drive business growth.
How to go about it:
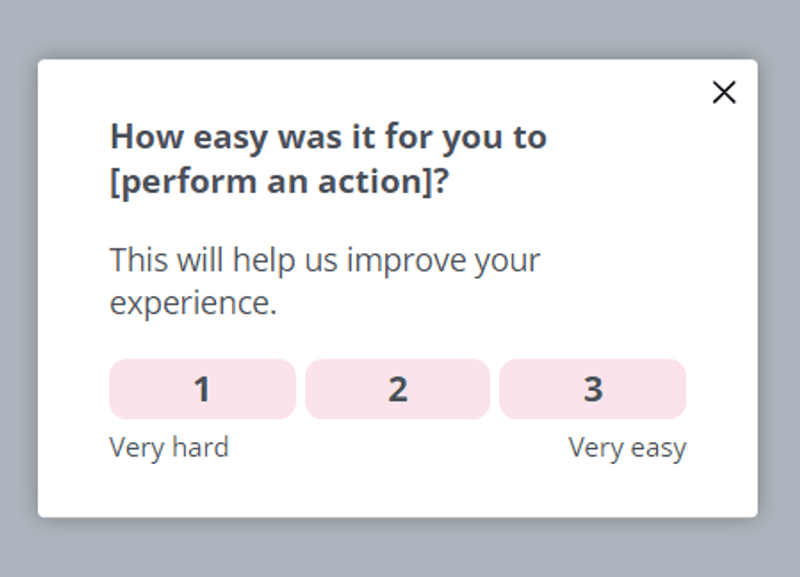
Collect user feedback and act on it to improve your product
Trigger in-app CSAT and CES surveys when users interact with specific features for the first time.
Collect data about their satisfaction with the solution your tool provides and the ease of using it.
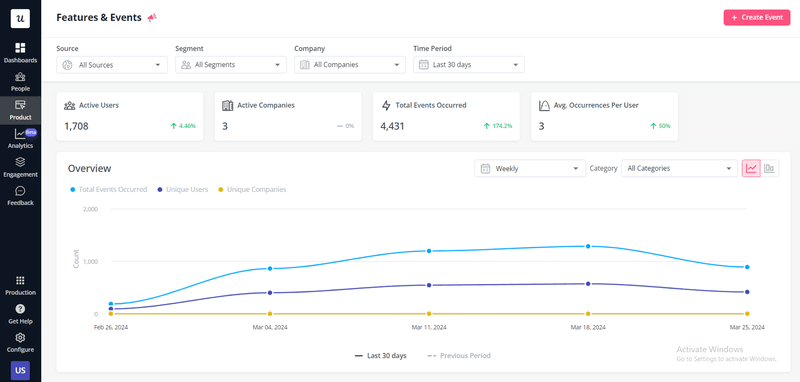
Analyze how users interact with the product with product analytics
Sometimes, user feedback isn’t enough to get the full picture. Use product analytics tools like Userpilot to track in-app user behavior and identify usage patterns, spot friction points, and measure the success of your product features.
With Userpilot, you can divide users into segments based on different characteristics and track how each user group interacts with key features and events. This allows you to gain granular insights and make more targeted improvements.
Best practices for the product design process
As you’ve seen so far, designing a successful product requires more than just innovative ideas; it demands a structured approach that integrates market demand and business objectives to create something users will love interacting with.
Here are some best practices to maximize your efforts throughout the design process:
Prioritize product ideas that align with business goals
Not all product ideas are created equal.
By focusing on ideas that directly contribute to the company’s strategic goals, you ensure that your efforts are aligned with the overall business vision. This maximizes the potential impact of your product and helps justify resource allocation.
Foster cross-functional team collaboration and communication
Product design isn’t just about the design team. It requires input and expertise from various departments like marketing, engineering, sales, and customer support.
Effective collaboration ensures that everyone’s perspectives are considered, leading to a more well-rounded and successful product.
Utilize tools like Slack, email, or project management software to facilitate easy information sharing. Depending on your company structure, you might need to have occasional meetups with key members from each of the cross-functional departments to discuss progress, challenges, and ideas.
Follow an agile mindset
An agile mindset emphasizes flexibility, adaptability, and iterative development. This allows you to respond quickly to changes, incorporate user feedback, and continuously improve your product over time.
How to do it:
- Work in sprints: Break down the project into smaller, manageable chunks with specific goals and deadlines.
- Frequent testing and feedback: Gather user feedback early and often to identify issues and make necessary adjustments.
- Embrace change: Be open to revising plans and pivoting strategies as new information emerges.
Conclusion
Understanding how to design a product is only the first step towards creating a successful product.
With Userpilot, you can take the next leap by understanding your users’ behavior and using that data to drive product adoption and engagement. Let us show you how—book a demo now.





