![How to Read a Retention Table [+ Different Retention Analysis Alternatives] cover](https://blog-static.userpilot.com/blog/wp-content/uploads/2023/05/how-to-read-a-retention-table-different-retention-analysis-alternatives_0302a1f0bb25971a6e2572ad606dc3aa_2000-450x295.png)
How to Read a Retention Table [+ Different Retention Analysis Alternatives]
Have you ever come across a retention table and wondered what it all means?
Cracking the retention table will provide invaluable insights into user behavior and retention. So, if you want to boost your customer retention, you should know how to interpret and analyze the retention table.
Reading retention tables is just the tip of the iceberg when analyzing customer retention, and many other beneficial retention analysis alternatives are available.
In this article, we’ll go through how to read a retention table and explore different retention analysis alternatives.
Summary of how to read a retention table
- A retention table is a powerful report that tracks and analyzes user engagement over time.
- The retention tables help you measure retention rates, assess product health, and monitor product growth.
- Each data point in a retention table represents a specific measurement of user retention.
- User cohorts group users based on common characteristics or time periods.
- The number of users section indicates each cohort’s total number of users.
- Time frames in a retention table represent specific periods for measuring retention rates.
- Some best alternative ways to analyze retention impact include:
- Monitoring feature performance through feature audit, hover tracking, click tracking, etc., helps understand its impact on engagement, satisfaction, and retention.
- Tracking active users with user segmentation over time helps you determine the effectiveness of retention efforts.
- Trend analysis observes the retention curve for specific events or features over time.
- Funnel analysis tracks user churn and identifies drop-offs in the customer journey.
- Adding a starting event allows you to observe the path that power users often take and optimize the user retention path by following that happy path.
- Userpilot is the perfect tool to perform retention analysis with features such as user segmentation, event analytics, etc. Explore how you can improve the retention in your mobile app with Userpilot’s native mobile SDK.
What is a retention table?
A retention table (also called cohort table or retention chart) is a special and powerful report that lets you track and analyze how different user groups engage with your platform over time.
What is the importance of a retention chart?
A retention chart depicts customer retention trends and allows you to analyze the ins and outs of your retention efforts’ performance. In a broader sense, it helps you –
- Track and measure your retention efforts by serving as a visual representation of user retention KPIs (key performance indicators).
- Assess product health and performance by showcasing user engagement and highlighting significant drop-offs.
- Monitor product growth by providing insights into acquisition, retention, etc., over specific time frames.
Retention tables are a valuable component of retention analysis. However, a retention analysis encompasses many more metrics and insights beyond just the tables.
How to read each data point in a retention table?
Data points in a retention table refer to a specific measurement or observation of user retention. Reading and interpreting retention data points is essential for gaining valuable insights into each new user cohort’s retention rates and trends.
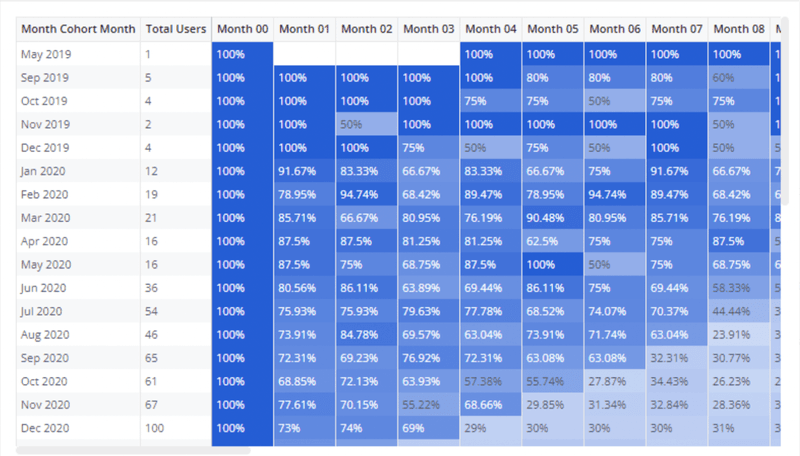
User cohort
A user cohort represents a group of users who share a common characteristic or belong to the same period. SaaS businesses often employ time-based cohorts to accurately analyze customer behavior and retention over specific periods.
Number of users
The number of users section is self-explanatory as it indicates each cohort’s total number of users. It provides critical information about the size and composition of user groups at any specific event or period.
Time frame
In a retention table, the columns usually represent the time frame, and you’ll find them organized in increments such as days, weeks, or months. They offer information about the specific periods over which you measure the retention rates.
Alternative ways to leverage data for retention analysis
Let’s look at some of the best ways to perform retention analysis.
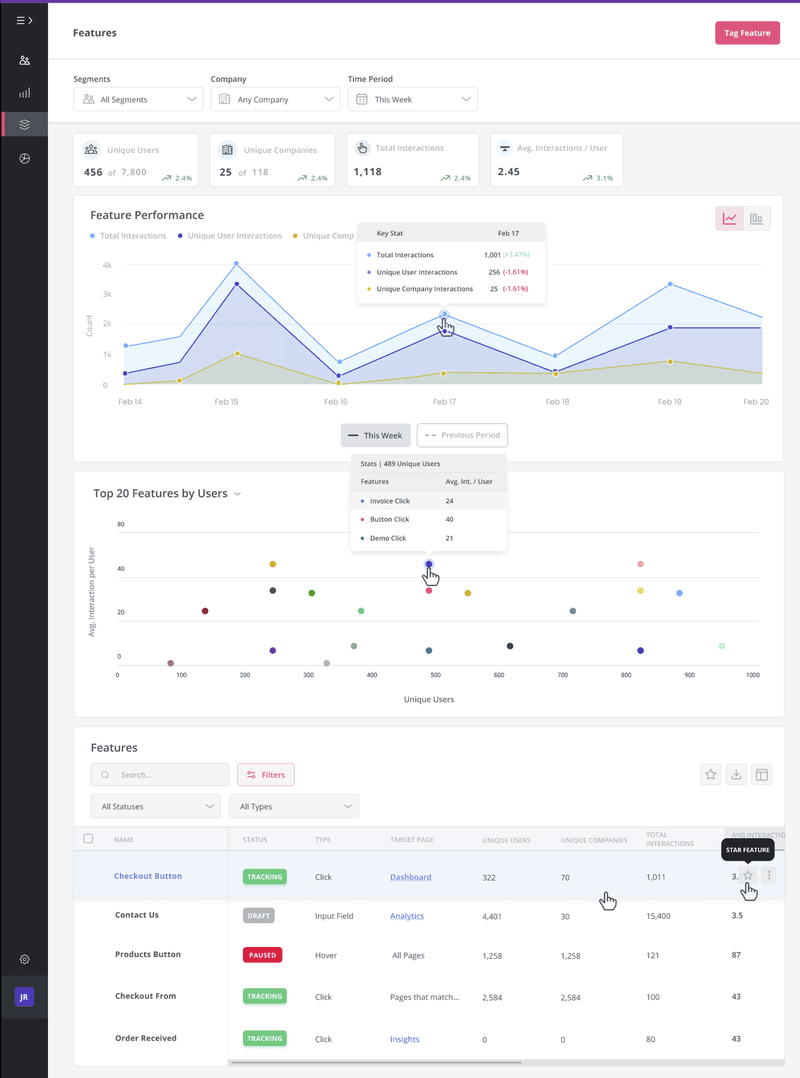
Monitor feature performance for retention impact analysis
One effective alternative to the retention table is to monitor feature performance and analyze how it impacts user retention. It helps you understand how specific product features contribute to better customer engagement, satisfaction, and retention.
You can tag features to monitor specific interactions, like click and hover, to assess your features’ performance. Along with hover and click tracking, you can also use feature audits to determine how much value your product features bring to customers and how they impact user retention.
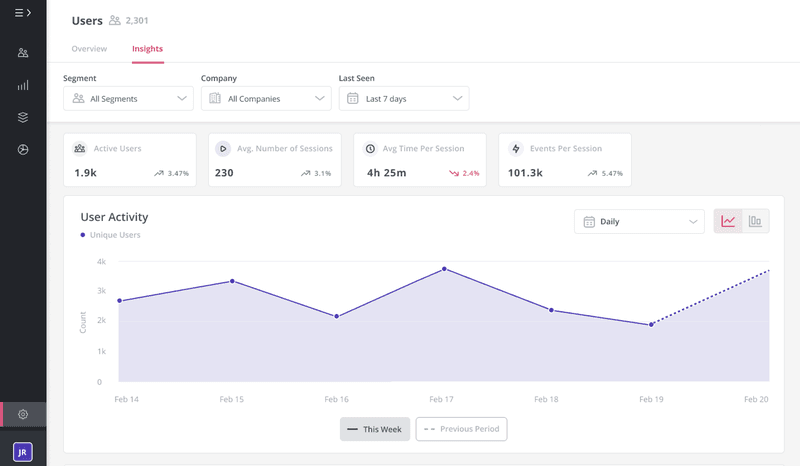
Track active users using event-based data to measure retention rate
The number of active users acts as a sign of how effective your retention efforts are.
You can segment your user base using filters and group users based on their characteristics, behavior, or interactions with your product. For example, you can create user segments based on feature interaction, in-app content engagement, or sign-up period.
After establishing user segments, you should monitor the number of active users within each segment over time. Visualizing this data using a bar and line graph will give you a comprehensive understanding of user retention trends. The bar graph represents the number of active users within each segment, while the line retention graph showcases the retention rate.
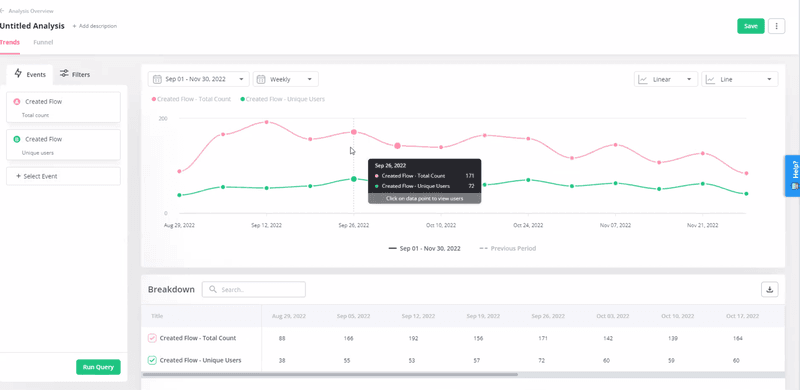
Use trend analysis to monitor the retention curve
Select specific events or features you want to track to begin the trend analysis. They can be actions within your product, feature usage, return event, etc.
Trend analysis allows you to observe the retention curve over time for users interacting with the selected events or features. You can then use it to monitor the retention curve of users who use those specific features or do those certain events. It visualizes the percentage of users who continue to remain engaged or active over time.
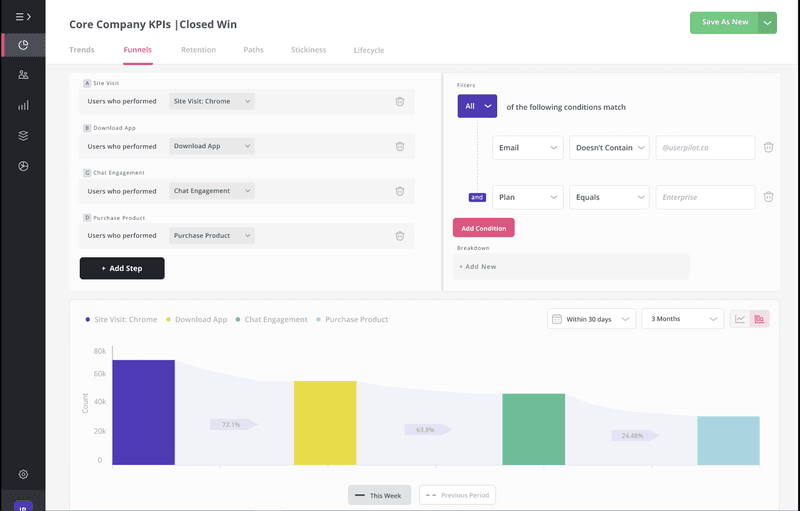
Track how many users churn across the customer journey using funnels
Tracking the number of churned users throughout the customer journey gives you a comprehensive picture of user retention. You can map touchpoints and utilize funnel analysis to identify drop-offs and friction points that may lead to churn.
The first step is to map out the touchpoints to create a customer journey. Then you should use funnel analysis to monitor the number of users at each stage and observe how they move from one stage to the next. Analyzing funnel conversion rates helps you identify drop-offs and friction points that potentially contribute to churn.
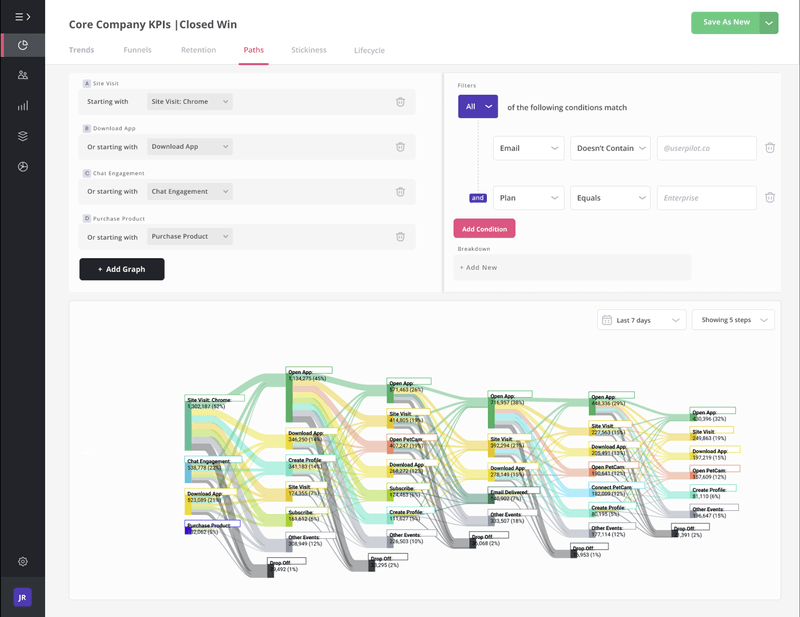
Add a starting event to observe and optimize user retention path from that event
Another effective alternative to the retention table is to start events and optimize these retention paths. When you use this data-driven approach, it gets easier to replicate the successful user paths and create a compelling user experience.
At first, you need to add starting events, like activity events, pages, etc., to observe meticulously. Then you should observe what path users often take to adopt your products and become power users. It offers unique insights into the adoption process and the path that leads to higher user retention.
After uncovering the key steps behind user satisfaction, you should replicate this “happy path” and optimize the experience for new users. As a result, you’ll be more effective in creating more power users and significantly driving more retention.
Conclusion
Understanding your retention table is highly critical if you want to achieve a great customer retention rate. But as we’ve discussed, there are also many other alternatives to analyze retention analysis, which you should utilize to the fullest.
Want to get started with a retention table and other alternatives? Get a Userpilot Demo and see how you can effectively perform retention analysis.






